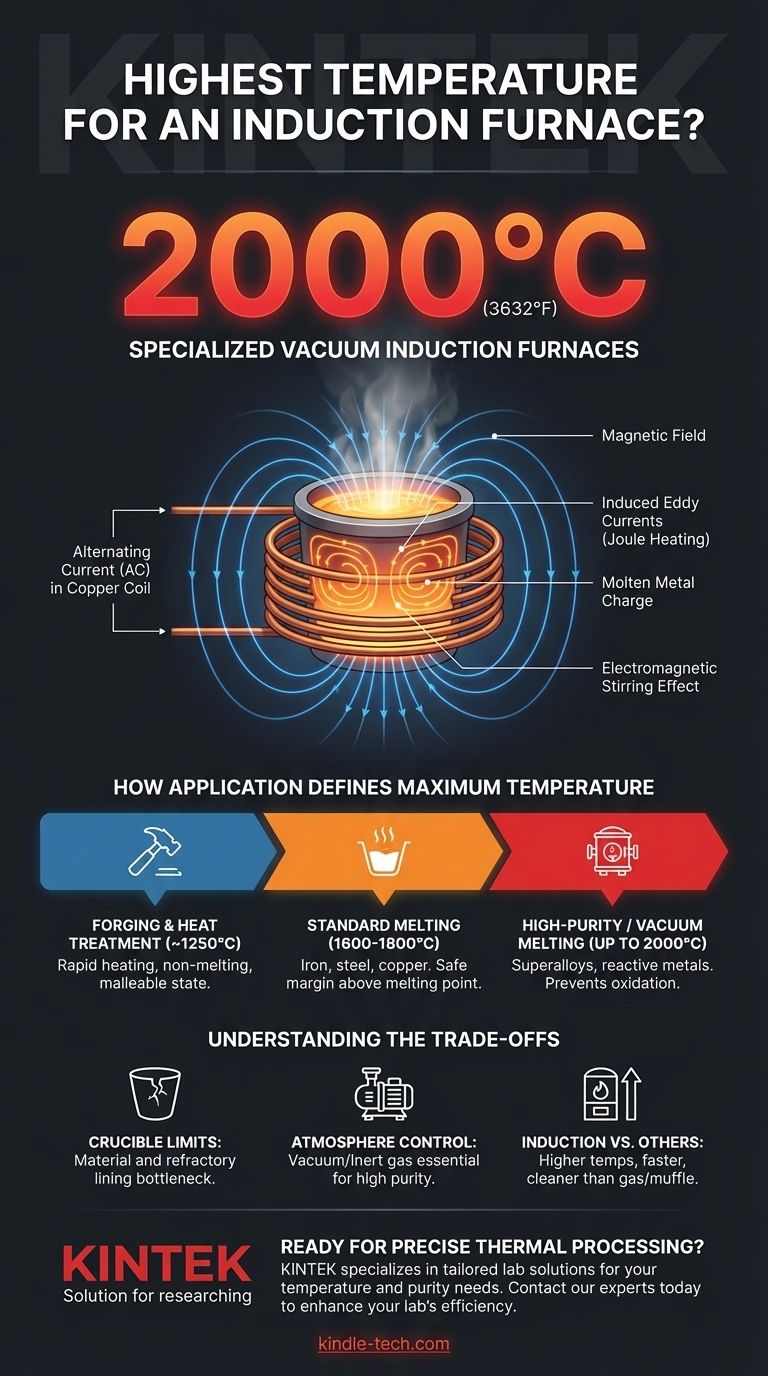
In practice, the highest temperature for a specialized induction furnace can reach up to 2000°C (3632°F). This capability, however, is not universal across all induction systems. The maximum achievable temperature depends heavily on the furnace's design, its operating environment (such as a vacuum), and the specific application it was built for, like melting or forging.
While a standard induction furnace reliably reaches 1600-1800°C, the true upper limit is defined by specialized equipment like vacuum induction furnaces. The core challenge isn't just generating heat, but managing it and ensuring the material being processed remains pure.
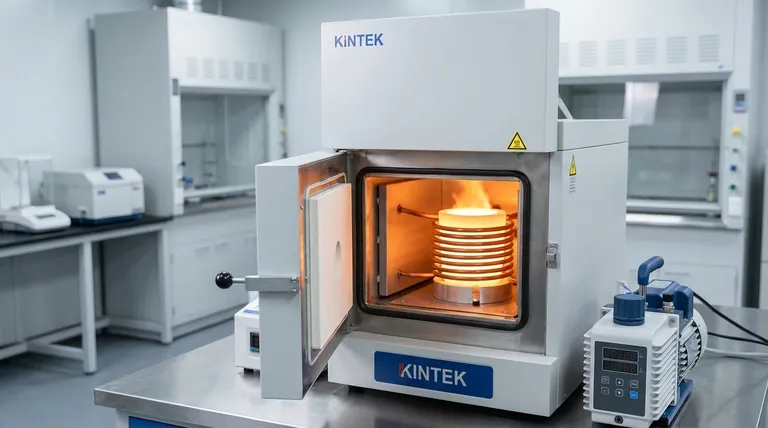

How Application Defines Maximum Temperature
The term "induction furnace" covers a range of equipment designed for different tasks. The temperature requirement for simply heating a billet for forging is vastly different from that needed to melt a high-temperature alloy.
For Standard Melting Operations
Most industrial induction furnaces are used for melting metals like iron, steel, and copper. For these applications, a maximum temperature of around 1600°C to 1800°C is both sufficient and typical. This range provides a safe margin above the melting points of common alloys.
For Forging and Heat Treatment
When heating metal for forging, the goal is to make it malleable, not to melt it. Induction forging heaters are designed to rapidly bring materials to temperatures of approximately 1250°C. Exceeding this temperature is unnecessary and can damage the metal's properties.
For High-Purity and Specialty Metals
The highest temperatures are achieved in Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnaces. By operating in a vacuum, these systems prevent the metal from reacting with oxygen and other atmospheric gases. This is critical for producing high-purity superalloys or processing reactive metals, allowing them to safely reach temperatures up to 2000°C.
The Principle Behind Induction Heating
Understanding how an induction furnace works clarifies why it can achieve such high temperatures so efficiently. It does not rely on external burners or heating elements.
Direct and Instantaneous Heat
An induction furnace uses a powerful alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field around the metallic material (the "charge") placed inside the crucible. This magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal itself.
Resistance Creates Temperature
The metal's natural electrical resistance causes it to heat up as these eddy currents flow through it—a principle called Joule heating. Because the heat is generated inside the material, the process is extremely fast, clean, and precisely controllable compared to traditional fuel-fired furnaces.
The Stirring Effect
A unique advantage of this process is the natural electromagnetic stirring that occurs in the molten metal. This ensures the temperature and chemical composition remain remarkably uniform throughout the melt, leading to higher-quality end products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving extreme temperatures with an induction furnace involves significant technical and financial considerations. The theoretical maximum temperature is often limited by practical constraints.
Crucible and Refractory Limits
The molten metal is held in a crucible, which must withstand the extreme temperature and potential chemical reactions. The crucible material and the refractory lining of the furnace itself often represent the real-world temperature bottleneck, not the induction coil's power.
Atmosphere Control is Key
As temperatures rise, metals become highly reactive with the air. A standard "open-air" furnace is unsuitable for high-temperature alloys. The added complexity and cost of a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere is a necessary trade-off for achieving temperatures near 2000°C and maintaining material purity.
Induction vs. Other Furnaces
Compared to gas or muffle furnaces, which typically top out between 1100°C and 1400°C, induction offers a clear temperature advantage. It provides faster heating, higher efficiency, and a cleaner operating environment without combustion byproducts. However, the initial equipment cost is generally higher.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" furnace is the one that meets your specific material and process requirements without unnecessary complexity or cost.
- If your primary focus is melting standard steels, iron, or aluminum: A conventional coreless induction furnace with a range of 1650-1800°C is the industry standard and most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is preparing metals for forging or forming: A lower-temperature induction heater designed for around 1250°C will provide the rapid, precise heating you need.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity superalloys or melting reactive metals: A vacuum induction furnace capable of reaching 2000°C is the only suitable option.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's capability to your specific temperature and purity requirements is the key to a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Application | Typical Maximum Temperature | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Melting (Steel, Iron) | 1600°C - 1800°C | Cost-effective for common alloys |
| Forging & Heat Treatment | ~1250°C | Rapid heating without melting |
| High-Purity/Vacuum Melting | Up to 2000°C | Essential for superalloys & reactive metals |
Ready to find the perfect induction furnace for your specific temperature and purity needs?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for laboratories requiring precise thermal processing. Whether you are melting standard alloys or developing high-purity superalloys, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our induction furnaces can enhance your lab's efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications



















