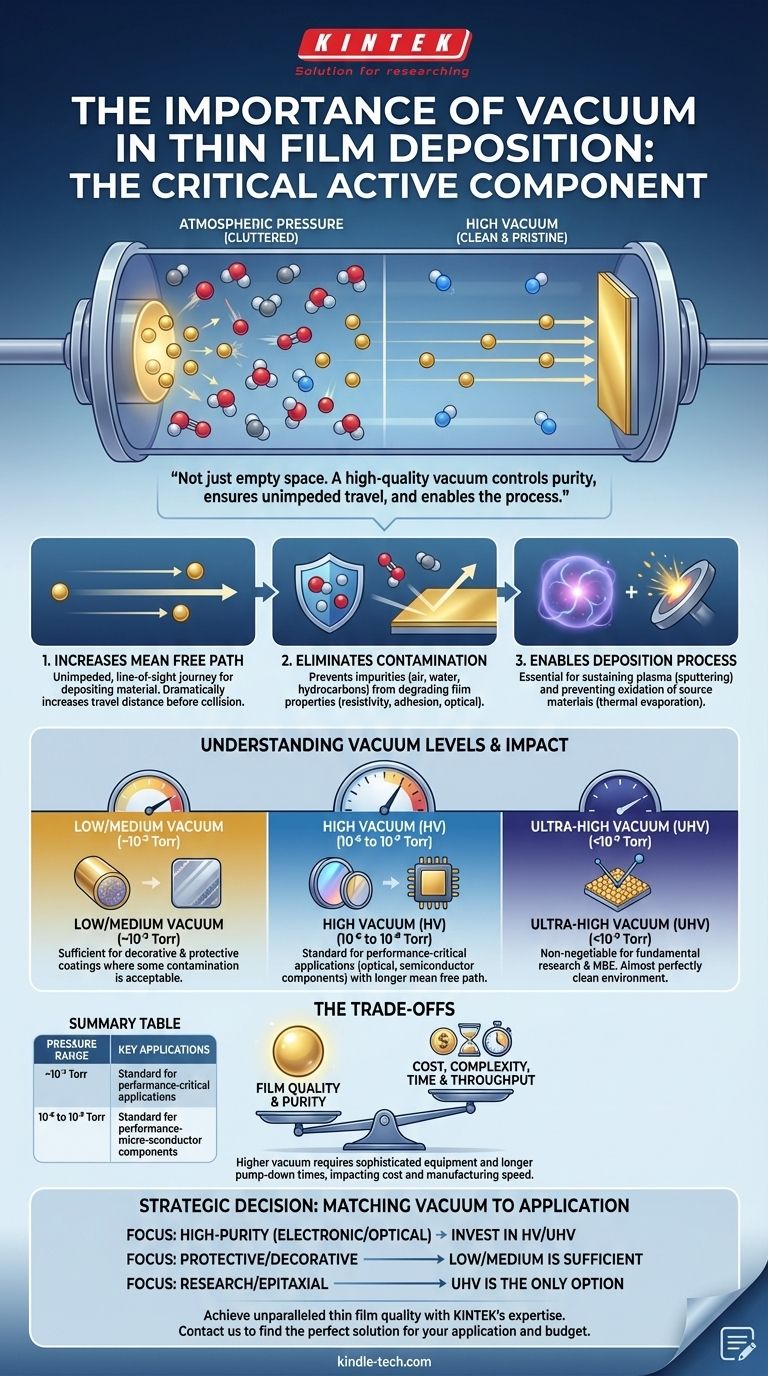
In thin film deposition, the vacuum is not just an empty space; it is the single most critical active component of the process. A high-quality vacuum is essential for controlling the purity of the deposited film, ensuring particles travel unimpeded from the source to the substrate, and enabling the entire physical process to occur reliably. Without it, creating high-performance, functional thin films would be impossible.
The fundamental purpose of a vacuum in thin film deposition is to remove all other atoms and molecules from the chamber. This creates a pristine and predictable environment, ensuring the final film is composed purely of the intended material and has the required structural integrity.

The Fundamental Roles of Vacuum in Deposition
To understand why vacuum is so crucial, we must look at how it solves three distinct physical challenges inherent in building a film one atomic layer at a time.
Increasing the Mean Free Path
The mean free path is the average distance a particle can travel before it collides with another particle. In the air around us, this distance is incredibly short—nanometers.
For deposition to work, atoms of the source material must travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate. By creating a vacuum, we remove most of the air and water molecules, dramatically increasing the mean free path. This ensures an unimpeded, line-of-sight journey for the depositing material.
Eliminating Contamination and Unwanted Reactions
A deposition chamber at atmospheric pressure is filled with nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, and hydrocarbons. If these particles are present during deposition, they will be incorporated into the growing film as impurities.
This contamination degrades the film's properties in several ways. It can alter electrical resistivity, change optical absorption characteristics, and create stress that leads to poor adhesion and film failure. Pre-cleaning substrates and achieving a high vacuum removes these contaminants, ensuring the film's purity and performance.
Enabling the Deposition Process Itself
Many deposition techniques simply cannot function without a vacuum. In processes like sputtering, a low-pressure environment is required to ignite and sustain a stable plasma.
In thermal evaporation, the vacuum prevents the hot filament and source material from instantly oxidizing and burning out upon heating. The vacuum provides the inert environment necessary for these physical processes to occur as intended.
Understanding Vacuum Levels and Their Impact
Not all vacuums are created equal. The required level of vacuum—measured by how low the pressure is—depends entirely on the sensitivity of the final film.
Low to Medium Vacuum (~10⁻³ Torr)
This level of vacuum removes the bulk of the air but leaves significant residual gas. It is often sufficient for processes where some contamination is acceptable, such as applying simple decorative or protective metallic coatings.
High Vacuum (HV) (10⁻⁶ to 10⁻⁹ Torr)
High vacuum is the standard for most performance-critical applications. It provides a much longer mean free path and significantly lower contamination levels, making it essential for creating high-quality optical filters, semiconductor interconnects, and other precise electronic components.
Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV) (<10⁻⁹ Torr)
UHV creates an almost perfectly clean environment, where the mean free path can be measured in kilometers. This is non-negotiable for fundamental surface science research, molecular beam epitaxy (MBE), and the manufacturing of devices where even a single atomic impurity can cause failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While a better vacuum leads to a better film, pursuing it comes with practical consequences that must be balanced against the project's goals.
Cost and Complexity
Achieving higher vacuum levels requires more sophisticated and expensive equipment. A system capable of UHV needs multiple stages of pumps (like turbomolecular and cryogenic pumps), superior chamber materials, and complex monitoring gauges, all of which dramatically increase cost.
Time and Throughput
The lower the target pressure, the longer it takes to pump down the chamber. Reaching UHV can take hours or even days, often requiring a high-temperature "bake-out" procedure to force trapped water molecules off the chamber walls. This significantly reduces manufacturing throughput.
Process Constraints
The need for a high vacuum places limits on the materials you can use. Substrates and fixtures must be made of low-outgassing materials (like stainless steel instead of plastics) to avoid introducing contaminants back into the vacuum environment.
Matching the Vacuum to Your Application
The right vacuum level is a strategic decision that balances the need for film quality against practical constraints like time and budget.
- If your primary focus is high-purity electronic or optical films: You must invest in a High Vacuum (HV) or Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV) system to prevent contamination that degrades performance.
- If your primary focus is protective or decorative coatings: A low or medium vacuum is likely sufficient and far more cost-effective, as minor impurities are less critical to the film's mechanical function.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or epitaxial growth: An Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV) environment is the only option to achieve the required atomic-level control and pristine surfaces.
Ultimately, controlling the vacuum is synonymous with controlling the quality, purity, and performance of your final thin film.
Summary Table:
| Vacuum Level | Pressure Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low/Medium Vacuum | ~10⁻³ Torr | Decorative & protective coatings |
| High Vacuum (HV) | 10⁻⁶ to 10⁻⁹ Torr | Optical filters, semiconductor components |
| Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV) | <10⁻⁹ Torr | Surface science, molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) |
Achieve unparalleled thin film quality with KINTEK's expertise.
Selecting the right vacuum system is critical to your project's success. Whether you are developing high-purity electronic films, durable protective coatings, or conducting fundamental research, the vacuum environment dictates your film's properties and performance.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum systems tailored for thin film deposition. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between vacuum level, cost, and throughput to find the perfect solution for your specific application and budget.
Contact us today to discuss your thin film deposition needs and ensure your process is built on a foundation of quality and reliability. Reach out via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures
- What is the speed of PECVD? Achieve High-Speed, Low-Temperature Deposition for Your Lab
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems



















