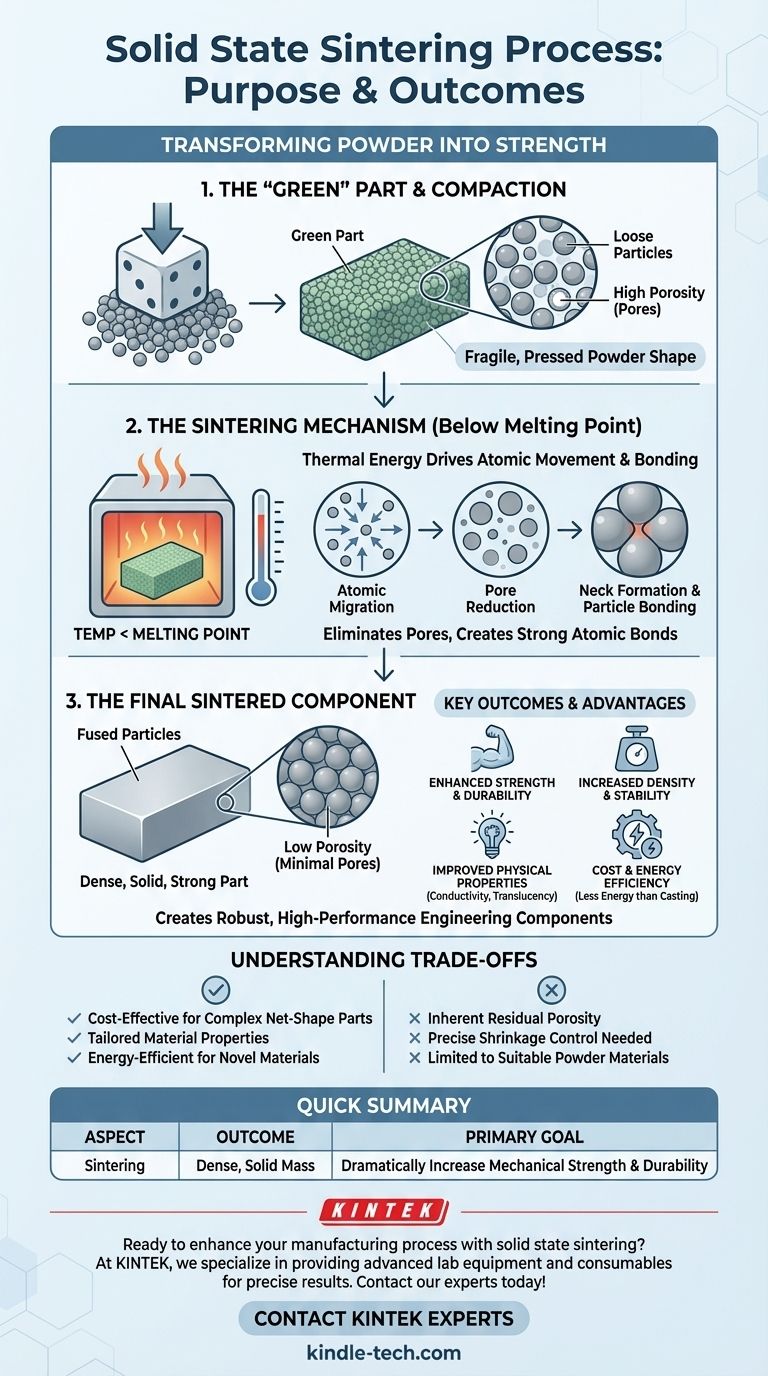
The primary purpose of the solid state sintering process is to transform a compacted powder into a dense, solid mass, significantly increasing its mechanical strength and stability. This is accomplished by applying heat at a temperature below the material's melting point, causing the individual particles to bond together.
At its core, sintering is the crucial step that converts a fragile, pressed-powder shape—known as a "green" part—into a strong, stable, and functional engineering component by eliminating internal pores and creating powerful atomic bonds between particles.

From Powder to Part: The Sintering Mechanism
Sintering isn't just about heating a material; it's a carefully controlled process that fundamentally changes its internal structure and properties. It typically follows a compaction stage, where the process begins.
Starting with a "Green" Part
Before sintering, a blended powder is pressed into a desired shape using a die. This compacted, but still fragile, piece is called a "green" part. While it holds its shape, it has low strength and high porosity.
The Role of Thermal Energy
The green part is then placed in a furnace and heated to a temperature below its melting point. This thermal energy doesn't melt the material but instead gives the atoms enough mobility to move and rearrange themselves.
Driving Down Porosity
The primary goal of this atomic movement is to reduce the overall energy of the system. The most efficient way to do this is by eliminating the empty spaces, or pores, between the powder particles.
Creating Atomic Bonds
As the atoms migrate and the pores shrink, the individual particles fuse at their contact points. This creates strong atomic bonds, effectively transforming the collection of loose particles into a single, unified, and dense mass.
Key Outcomes and Advantages
This transformation from a powder compact to a solid body yields several critical benefits, making sintering a cornerstone of modern manufacturing in ceramics and powder metallurgy.
Enhanced Mechanical Strength
The most significant outcome is a dramatic increase in strength and durability. The final sintered component can withstand mechanical stresses that the green part could not, allowing it to be used in applications like gears, bearings, and structural components.
Increased Density and Stability
By minimizing porous spaces, sintering significantly increases the part's density. This new, dense structure is dimensionally stable and less susceptible to environmental factors.
Improved Physical Properties
The reduced porosity and unified structure also enhance other material properties. Sintering can improve thermal and electrical conductivity, and in the case of certain ceramics, it can even increase translucency.
Cost and Energy Efficiency
Because the material is never fully melted, sintering consumes far less energy than casting processes. This makes it a highly cost-effective method for producing complex parts in high volumes with minimal waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process has inherent characteristics that must be managed to achieve desired results.
Inherent Porosity
It is often difficult to eliminate 100% of the porosity through sintering alone. Some residual porosity may remain, which can impact the ultimate strength compared to a component made from fully melted and solidified material.
Precise Shrinkage Control
As the pores are eliminated, the component shrinks. This shrinkage is predictable but must be precisely accounted for during the initial design of the compaction tooling to ensure the final part meets dimensional specifications.
Material Suitability
The process is best suited for materials that can be readily formed into powders. The complexity of the part is also a consideration, as the initial powder must be able to fill the die cavity evenly during the compaction stage.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing a manufacturing process depends entirely on your end goal. Sintering offers unique advantages for specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of complex net-shape parts: Sintering is an ideal choice for creating components like gears, sprockets, and pulleys with high precision and minimal need for secondary machining.
- If your primary focus is creating materials with tailored properties: Sintering allows you to precisely control density and microstructure to enhance qualities like thermal conductivity, electrical resistance, or translucency in ceramics.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency or advanced composites: Low-temperature sintering techniques enable the creation of novel materials that cannot be formed through traditional high-temperature melting processes.
Ultimately, sintering provides a powerful and versatile method for transforming simple powders into robust, high-performance components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Transform compacted powder into a dense, solid mass |
| Key Benefit | Dramatically increases mechanical strength and durability |
| Process | Heating below melting point to fuse particles via atomic diffusion |
| Main Advantage | Cost-effective production of complex, high-performance parts |
| Ideal For | Manufacturing gears, bearings, and components with tailored properties |
Ready to enhance your manufacturing process with solid state sintering?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to achieve precise and reliable sintering results. Whether you are developing new materials or producing high-volume components, our solutions help you create stronger, denser parts efficiently.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability



















