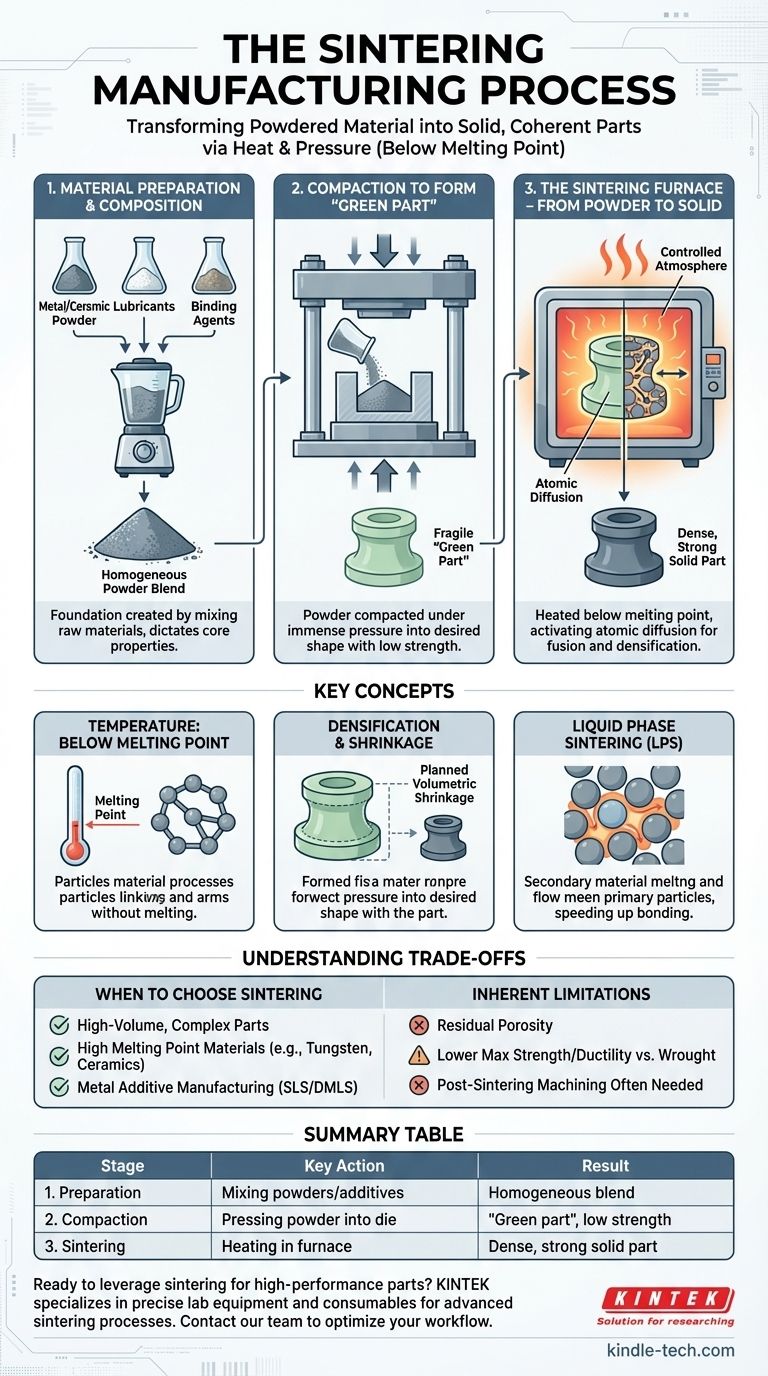
At its core, sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms powdered material into a solid, coherent mass using heat and pressure. It crucially operates at a temperature below the material's melting point, relying on atomic diffusion to fuse particles together, rather than fully melting and recasting the substance. This method is fundamental for creating parts from metals and ceramics, especially those with very high melting points.
Sintering is not about melting; it's about solid-state bonding. The primary goal is to use thermal energy to encourage individual powder particles to fuse, reducing porosity and creating a strong, unified component from a compacted powder shape.

The Three Core Stages of Sintering
The sintering process can be broken down into three distinct and critical stages. The quality and properties of the final part are determined by the precise control executed at each step.
Stage 1: Material Preparation and Composition
Before any heating or pressing occurs, the foundation of the part is created by selecting and mixing the raw materials.
This involves choosing the primary metal or ceramic powder, which dictates the final part's core properties like strength, hardness, and thermal resistance. Common choices include iron, nickel, copper, and refractory metals like tungsten, as well as various engineering ceramics.
Additives are then mixed in. Lubricants are often included to improve powder flow and reduce friction during compaction, while binding agents provide initial strength to the pre-sintered part.
Stage 2: Compaction to Form the "Green Part"
Once the powder is prepared, it is compacted into the desired shape. This is typically done by pouring the powder into a die and applying immense pressure.
The result of this stage is a fragile, pre-sintered component known as a "green part." It has the required shape and dimensions but possesses very low mechanical strength, similar to a tightly packed sandcastle.
This compaction step is critical for establishing the initial density and ensuring uniform particle contact, which is essential for successful bonding in the next stage.
Stage 3: The Sintering Furnace – From Powder to Solid
The green part is carefully placed into a high-temperature furnace with a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation. The thermal cycle is the heart of the sintering process.
The part is heated to a specific temperature, always remaining just below the primary material's melting point. It is held at this temperature for a set duration.
During this time, thermal energy activates atomic diffusion. Atoms migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles, causing the particles to fuse and bond together. Pores between the particles shrink or close up, and the part becomes significantly denser and stronger.
Finally, the part is cooled in a controlled manner to solidify into a single, unified mass with its final mechanical properties.
Key Concepts that Define the Process
Understanding the underlying principles of sintering is crucial for leveraging it effectively. The process is more than just "baking" a powder; it's a sophisticated materials science technique.
The Role of Temperature: Below the Melting Point
The defining characteristic of sintering is that no large-scale melting occurs. The temperature is high enough to make the atoms mobile but not so high that the material loses its shape and becomes a liquid.
Think of it as a crowd of people linking arms to form a single, connected unit, rather than all of them melting into a single puddle. This allows for the creation of complex shapes from materials that are extremely difficult or impossible to melt and cast.
Densification and Shrinkage
As the particles fuse and the voids between them are eliminated, the part densifies. This process is accompanied by a predictable volumetric shrinkage.
This shrinkage is not a defect but a planned aspect of the process. The initial die and green part must be designed slightly larger than the final desired dimensions to account for this change. Precise control of the powder composition and sintering cycle ensures this shrinkage is consistent and repeatable.
Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS)
In some cases, the process can be accelerated by introducing a small amount of a secondary material with a lower melting point. This technique is called Liquid Phase Sintering.
During heating, this additive melts and flows into the pores between the solid primary particles. The liquid acts as a transport medium, dramatically speeding up the diffusion and bonding process, leading to faster and more complete densification.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sintering is a powerful tool, but it is not universally optimal. Acknowledging its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
When to Choose Sintering
Sintering excels in the high-volume production of small, geometrically complex parts where the cost of machining from solid stock would be prohibitive. It is also the go-to method for processing materials with exceptionally high melting points, such as tungsten, molybdenum, and advanced ceramics, which cannot be practically manufactured via casting.
Furthermore, sintering is a cornerstone of metal additive manufacturing, including Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), where a laser provides the thermal energy to fuse powder layer by layer.
Inherent Limitations: Porosity and Strength
While the goal is to reduce porosity, most sintered parts retain some level of microscopic voids. This residual porosity means a sintered component may not achieve the same maximum strength or ductility as a part machined from a fully dense wrought billet or a forged piece.
However, this porosity can also be a feature. It is intentionally leveraged to create self-lubricating bearings (where oil is held in the pores) and filters.
Post-Processing and Finishing
Achieving very tight tolerances may require post-sintering machining. For hard ceramic parts, this can involve specialized and costly processes using diamond tools. In some applications, sintered metal parts are joined to other components through brazing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a manufacturing process requires aligning its capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production of complex metal parts: Sintering is a leading candidate, but you must design the tooling to precisely account for material shrinkage.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing parts from high-melting-point materials like ceramics or refractory metals: Sintering is often the most practical or even the only viable method available.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material strength and zero porosity for a critical structural component: Consider alternative methods like forging or machining from solid billet, as the inherent porosity of sintering may be a limiting factor.
- If your primary focus is creating a component with controlled porosity, such as a filter or self-lubricating bearing: Sintering is the ideal process, as it allows you to engineer the porous structure directly.
By understanding these core principles, you can effectively leverage sintering to create robust and intricate components where other methods fall short.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Mixing primary powder with lubricants/binders | Homogeneous powder blend |
| 2. Compaction | Pressing powder into a die under high pressure | "Green part" with shape but low strength |
| 3. Sintering | Heating in a controlled atmosphere furnace | Dense, strong solid part via atomic diffusion |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's high-performance parts?
KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced sintering processes. Whether you are working with high-melting-point metals, ceramics, or developing new materials, our reliable furnaces and tools ensure consistent, high-quality results. Let our experts help you optimize your sintering workflow.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What conditions does a vacuum hot press provide for Al2O3/ZrO2 sintering? Achieve 1550°C and 30 MPa Densification
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics



















