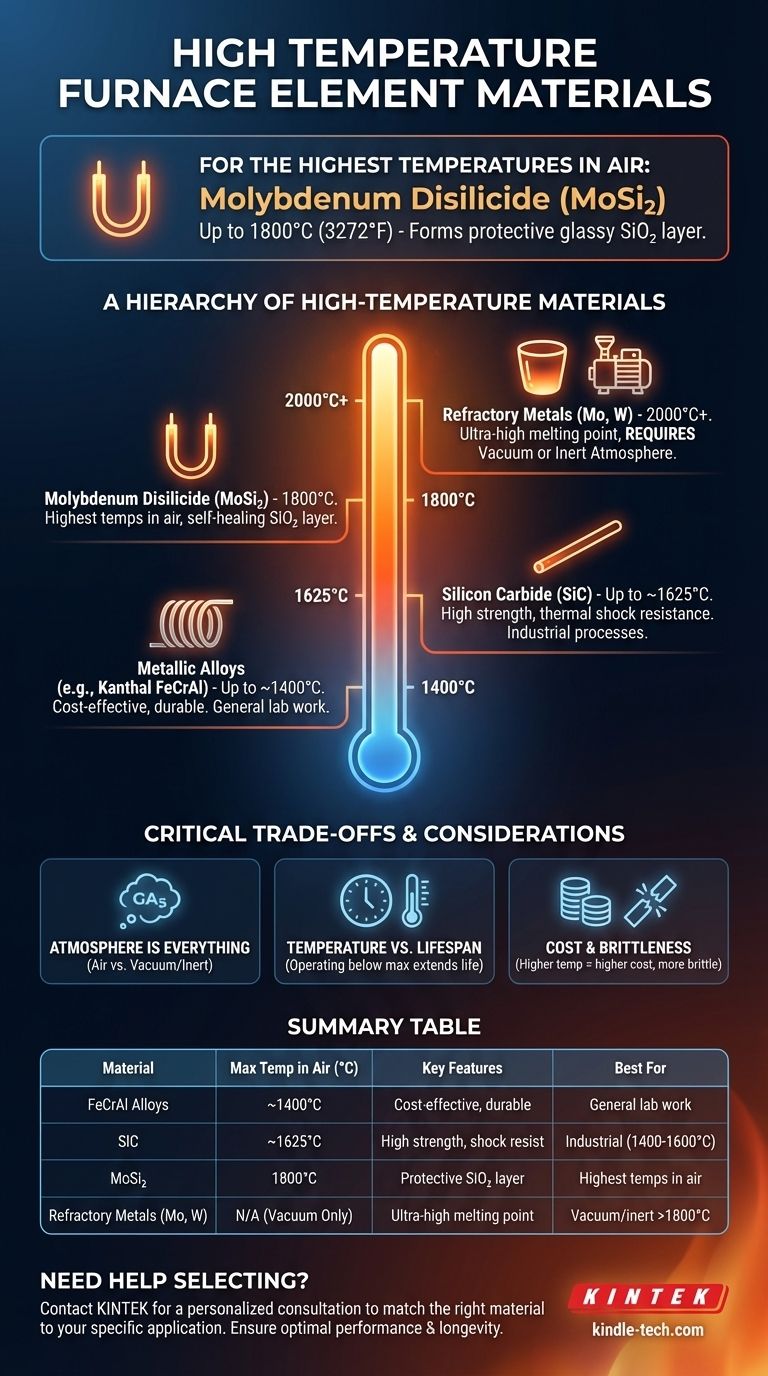
For the highest temperature applications in an air atmosphere, the heating element material of choice is molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂). This advanced ceramic composite is capable of achieving stable working temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F) by forming a protective glassy layer on its surface that prevents rapid oxidation.
The selection of a furnace heating element is not about finding a single "best" material, but about matching the material's properties—specifically its temperature limit and atmospheric compatibility—to the precise requirements of your application.

What Defines a High-Performance Heating Element?
Before comparing specific materials, it's crucial to understand the properties that engineers seek when designing heating elements for extreme environments. The ideal material must perform reliably under intense thermal and electrical stress.
High Melting Point & Oxidation Resistance
The most fundamental requirement is that the element must not melt or degrade at its operating temperature. In furnaces that operate in air, oxidation resistance is paramount, as oxygen will aggressively attack most materials at high temperatures.
Stable Electrical Resistivity
The element's electrical resistance is what generates heat (I²R heating). This resistance must be stable and predictable across the temperature range to allow for precise and repeatable temperature control.
Mechanical Strength and Form
A heating element must maintain its shape and structural integrity when hot. Materials that become soft, sag, or grow brittle can lead to premature failure and create an electrical short circuit inside the furnace chamber.
A Hierarchy of High-Temperature Materials
No single element material covers all applications. They exist in a clear hierarchy, with each type occupying a specific niche based on its maximum temperature and atmospheric compatibility.
The Workhorse: Metallic Alloys (up to ~1400°C)
For many standard high-temperature applications, iron-chromium-aluminum alloys (like Kanthal FeCrAl) are the standard. They are durable, relatively inexpensive, and perform reliably in air.
These alloys form a protective aluminum oxide layer, but this layer breaks down as temperatures approach their upper limit, leading to element failure.
The Mid-Range Performer: Silicon Carbide (up to ~1625°C)
Silicon Carbide (SiC) represents the next step up. It is a ceramic material known for its high strength and excellent thermal shock resistance.
SiC elements are self-supporting and can be used in air or inert atmospheres, making them common in industrial heat treating, glass production, and semiconductor manufacturing.
The High-Temperature Champion: Molybdenum Disilicide (up to 1800°C)
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) is the material specified for the most demanding applications in oxidizing (air) atmospheres.
When heated above 1000°C, a MoSi₂ element forms a thin, non-porous layer of quartz (SiO₂). This self-healing glassy layer is what protects the underlying material from catastrophic oxidation, allowing it to reach extreme temperatures.
Beyond Air: Refractory Metals (2000°C+)
For temperatures exceeding 1800°C or for processes that require a strictly controlled vacuum or inert gas (like Argon or Nitrogen), different materials are needed.
Refractory metals like Molybdenum and Tungsten have exceptionally high melting points but will instantly vaporize in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures. They are therefore restricted to vacuum or inert/reducing atmosphere furnaces.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing an element involves balancing performance, longevity, and cost. Misunderstanding these trade-offs is a common cause of furnace failure and unexpected expenses.
Atmosphere Is Everything
The single most important factor beyond temperature is the furnace atmosphere. An element designed for air, like MoSi₂, will fail in certain reducing atmospheres. A Tungsten element designed for a vacuum will be destroyed in seconds if operated in air.
Temperature vs. Lifespan
Operating any heating element at its absolute maximum rated temperature will drastically shorten its lifespan. For better longevity and reliability, it is common practice to select an element material with a maximum temperature rating significantly higher than the intended working temperature.
Cost and Brittleness
There is a direct correlation between temperature rating and cost. MoSi₂ elements are significantly more expensive than FeCrAl alloys. Furthermore, ceramic-based elements like SiC and MoSi₂ are brittle at room temperature and require careful handling during installation and maintenance to prevent breakage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application dictates the correct material. The goal is to choose the most cost-effective option that provides a safe operating margin for your required temperature and atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is general lab work up to 1400°C: Iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys provide the best balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is industrial processes between 1400°C and 1600°C: Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a robust, reliable, and well-established choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures in an air atmosphere: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) is the definitive industry standard.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperatures above 1800°C in a vacuum or inert atmosphere: Refractory metals like Molybdenum or Tungsten are essential.
Understanding these distinct material capabilities is the key to selecting a furnace that is not only effective but also reliable for its intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temp in Air (°C) | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| FeCrAl Alloys | ~1400°C | Cost-effective, durable | General lab work up to 1400°C |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | ~1625°C | High strength, thermal shock resistance | Industrial processes (1400-1600°C) |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | 1800°C | Forms protective SiO₂ layer | Highest temps in air atmosphere |
| Refractory Metals (Mo, W) | 2000°C+ | Ultra-high melting point | Vacuum/inert atmospheres above 1800°C |
Need help selecting the perfect heating element for your furnace? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab equipment and consumables. Our experts will help you match the right material—whether it's MoSi₂, SiC, or FeCrAl—to your specific temperature, atmosphere, and application requirements. Ensure optimal performance and longevity for your lab processes. Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the technical advantages of using graphite rods? Boost Precision in 1200°C High-Temperature Operations
- Is tungsten the most heat resistant material? It depends on your application's environment.
- How does the placement of K-type or R-type thermocouples affect temperature control? Ensure Precise Pyrolysis Results
- Is graphite good heating element? Discover Its Superior Performance in High-Temperature Vacuum Furnaces
- What is the most efficient type of heating element? It’s About Heat Transfer, Not Generation
- What factors affect the resistance of a heating element? Master the 4 Key Variables for Precise Thermal Design
- Can tungsten be used as a heating element? Unlocking Extreme Heat for High-Temperature Applications
- What is the maximum temperature for a heating element? A Guide to Material Limits & Lifespan



















