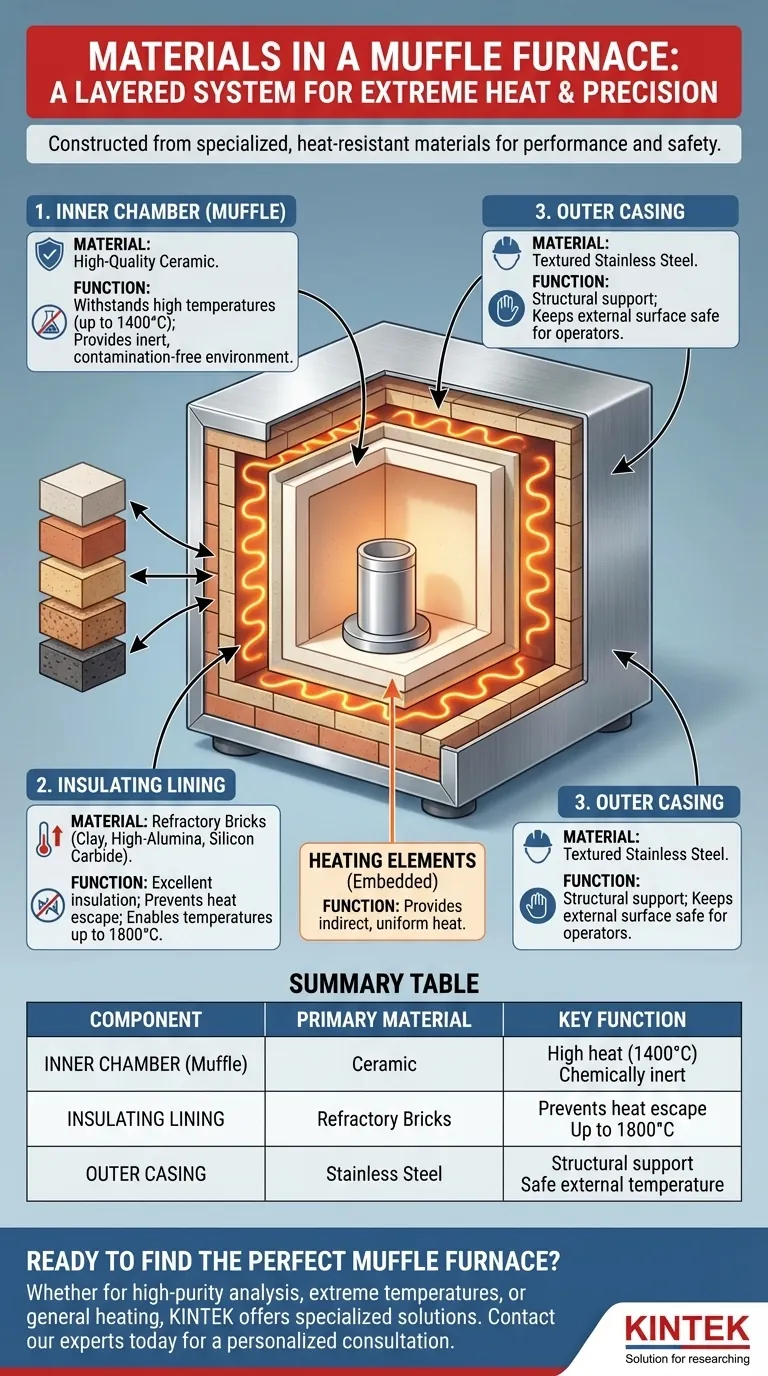
At its core, a muffle furnace is constructed from a combination of specialized, heat-resistant materials. The inner chamber, or "muffle," is made of ceramic to withstand high temperatures and isolate the sample. This chamber is then surrounded by an insulating lining of refractory bricks, all of which is contained within a durable outer casing, typically made of stainless steel.
A muffle furnace is not made of a single material, but is a layered system. Each material is selected for its specific role in containing extreme heat, insulating the chamber, and providing structural integrity, ensuring both performance and safety.

The Core Components and Their Materials
To understand a muffle furnace, you must understand its layered construction. Each layer serves a distinct and critical purpose, from the innermost chamber that holds the sample to the external housing that protects the user.
The Inner Chamber (The Muffle)
The heart of the furnace is the muffle, a box-like inner chamber. This component is almost always made from a high-quality ceramic material.
The choice of ceramic is deliberate. It can withstand constant high temperatures, often up to 1400°C, without melting or degrading. Critically, it also provides a chemically inert environment, preventing the sample from being contaminated by the heating elements or fuel combustion byproducts.
The Insulating Lining
Surrounding the ceramic muffle is a thick lining of refractory materials. These are materials specifically designed to resist heat and provide excellent insulation.
Common refractory materials include clay brick, high-alumina brick, silicon carbide, and refractory concrete. The primary job of this layer is to prevent heat from escaping, which ensures the furnace operates efficiently and can reach its maximum temperature, sometimes as high as 1800°C.
The Heating Elements
The heating elements are embedded between the ceramic muffle and the refractory lining. This design is fundamental to how a muffle furnace works.
By enclosing the elements, the furnace provides indirect heat. This prevents direct contact between the heating source and the sample, which is essential for ensuring uniform heating and preventing contamination.
The Outer Casing
The entire internal assembly is housed within a casing made of textured stainless steel sheets. This outer shell provides structural support and protects the internal components. More importantly, thanks to the effective refractory insulation, it keeps the external surface at a safe temperature for operators.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Material Choices
The specific materials used in a muffle furnace are chosen based on its intended temperature range and application. Not all furnaces are built alike, and these differences have practical implications.
Not All Refractories Are Equal
The choice of refractory brick directly impacts the furnace's maximum operating temperature. A furnace using standard clay brick will have a lower temperature limit than one built with high-alumina or silicon carbide bricks, which are reserved for more demanding, higher-temperature processes.
The Critical Role of the Muffle
The ceramic muffle's primary function is to isolate the sample. This is non-negotiable for sensitive scientific applications like determining the ash content of a polymer or heat-treating a material in a controlled atmosphere where purity is paramount.
Thermal Shock and Durability
Both ceramic and refractory materials can be susceptible to thermal shock—cracking caused by rapid temperature changes. This is a key operational constraint. High-quality furnaces use materials engineered to better withstand this stress, but users must still follow proper heating and cooling protocols to extend the furnace's life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the material construction allows you to select the right tool for your specific task and use it effectively.
- If your primary focus is high-purity analysis (e.g., ashing): The integrity of the ceramic muffle is your most critical feature, as it guarantees sample isolation.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature metal treatment (e.g., annealing or sintering): The furnace's refractory lining (e.g., high-alumina) is key, as it determines the ability to reach and sustain temperatures up to 1800°C.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory heating: A standard furnace combining a ceramic muffle with a reliable refractory brick insulation offers the best balance of performance and versatility.
By appreciating how these materials work together, you can better match the equipment's capabilities to your specific technical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Material | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Inner Chamber (Muffle) | Ceramic | Withstands high heat (up to 1400°C); provides a chemically inert, contamination-free environment. |
| Insulating Lining | Refractory Bricks (e.g., clay, high-alumina, silicon carbide) | Prevents heat escape; enables higher temperatures (up to 1800°C) and efficient operation. |
| Outer Casing | Stainless Steel | Provides structural support and maintains a safe external temperature for operators. |
Ready to find the perfect muffle furnace for your lab's specific needs?
Whether your priority is high-purity analysis, extreme temperature applications, or general laboratory heating, the right material construction is critical for performance, safety, and accurate results.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select a muffle furnace with the ideal ceramic, refractory, and steel components to match your technical requirements and budget.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and ensure your lab has the right tool for the job!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How hot does a furnace get in Celsius? From 1100°C to 1800°C for Your Lab Needs
- What is a muffle furnace used to estimate? A Key Tool for Precise Ash Determination
- Where is a muffle furnace used? Essential for Clean, High-Temperature Processing
- What are the applications of muffle furnaces? Essential Tools for High-Temperature Processes
- Which material is used in a muffle furnace? The Key to High-Temperature Performance and Purity



















