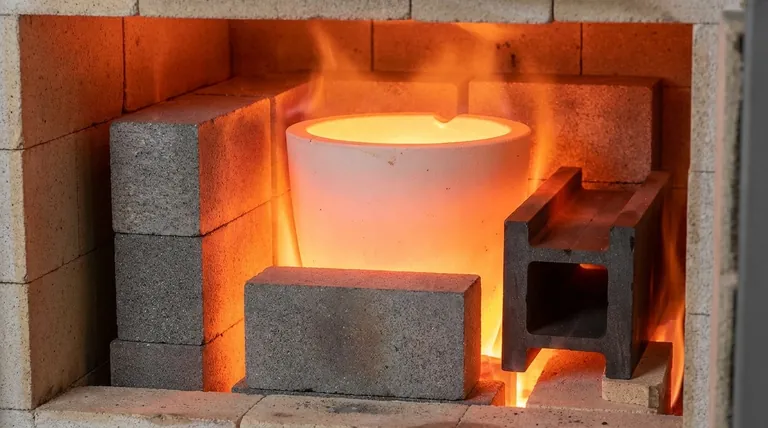
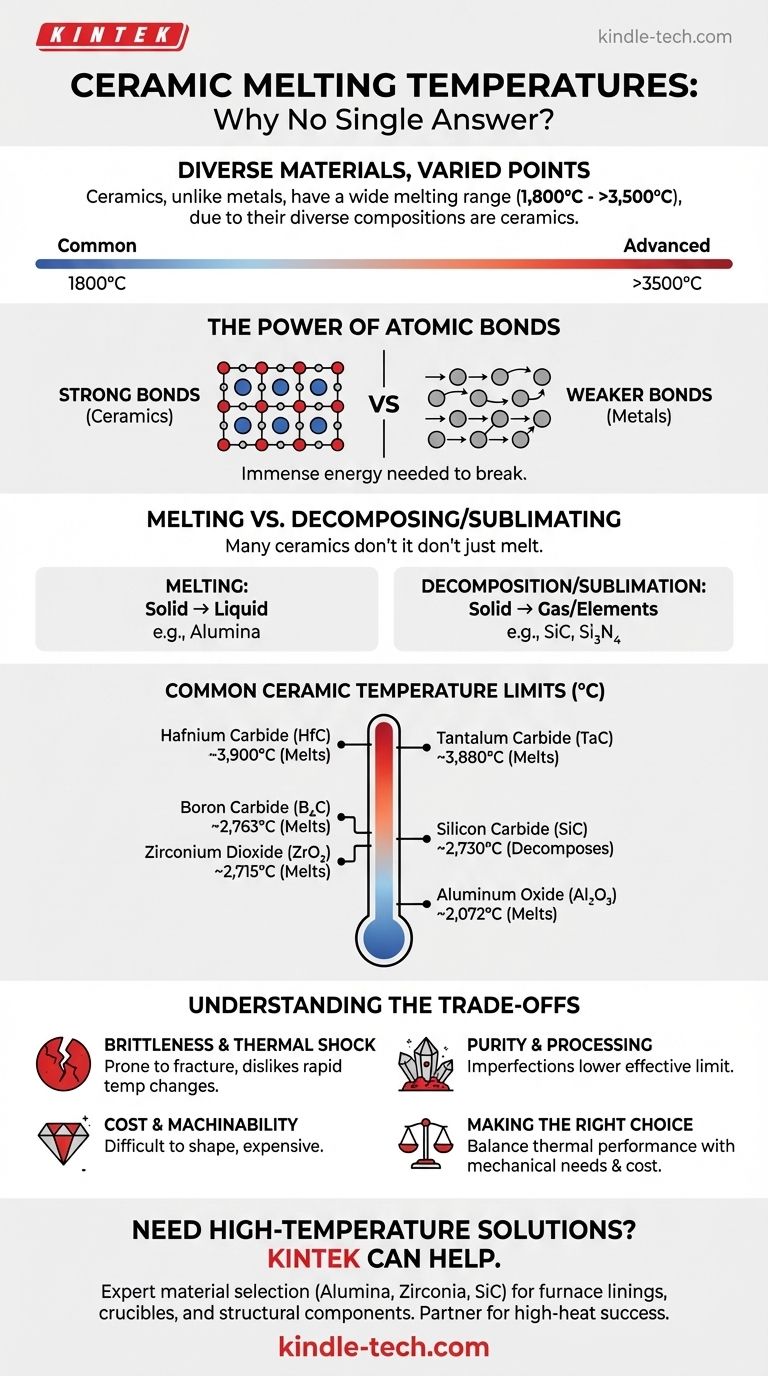
Unlike a pure metal, ceramics do not have a single melting temperature. As a broad class of inorganic, non-metallic materials, their melting points vary dramatically based on their specific chemical composition and atomic structure, ranging from around 1,800 °C (3,272 °F) for common types to well over 3,500 °C (6,332 °F) for advanced, exotic compositions.
The core reason for the high heat resistance of ceramics lies in their powerful atomic bonds. Unlike the weaker metallic bonds in metals, the strong ionic and covalent bonds within a ceramic's crystal lattice require immense thermal energy to break apart, resulting in exceptionally high melting points.

Why There Is No Single Answer
The question "What is the melting temperature of ceramics?" is like asking "What is the top speed of a vehicle?" The answer depends entirely on whether you are discussing a bicycle, a family car, or a jet aircraft. Ceramics are a diverse category of materials, not a single substance.
The Critical Role of Atomic Bonds
The defining characteristic of a ceramic is its atomic structure. Atoms are held together by extremely strong covalent (shared electrons) or ionic (transferred electrons) bonds.
These bonds are far more rigid and require significantly more energy to disrupt than the metallic bonds found in metals. This fundamental difference in bond strength is why ceramics, as a class, vastly outperform metals in high-temperature environments.
Melting vs. Decomposing
A crucial distinction for technical ceramics is that many do not "melt" in the conventional sense. At extreme temperatures, some materials will decompose into their constituent elements or sublimate (turn directly from a solid to a gas) before they ever reach a liquid state at atmospheric pressure.
For example, Silicon Carbide (SiC) decomposes at around 2,730 °C, and Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) sublimes at approximately 1,900 °C. For engineering purposes, this decomposition or sublimation temperature is the material's effective upper-temperature limit.
Melting Points of Common Technical Ceramics
To provide a practical reference, it's best to look at the melting points of specific, widely used technical ceramics. These materials are chosen for their predictable and exceptional performance under stress.
Oxide Ceramics: The Workhorses
These are ceramics based on metallic oxides. They are the most common type of advanced ceramic due to their stability and relatively lower cost.
- Aluminum Oxide (Alumina, Al₂O₃): ~2,072 °C (3,762 °F)
- Zirconium Dioxide (Zirconia, ZrO₂): ~2,715 °C (4,919 °F)
- Magnesium Oxide (Magnesia, MgO): ~2,852 °C (5,166 °F)
Non-Oxide Ceramics: Extreme Performance
These materials are formed from compounds of non-oxide elements and offer superior hardness, strength, and thermal shock resistance, often at a higher cost.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Decomposes at ~2,730 °C (4,946 °F)
- Boron Carbide (B₄C): Melts at ~2,763 °C (5,005 °F)
- Tantalum Carbide (TaC): Melts at ~3,880 °C (7,016 °F)
- Hafnium Carbide (HfC): Melts at ~3,900 °C (7,052 °F)
Understanding the Trade-offs
A high melting point is only one part of the story. When selecting a ceramic for a high-temperature application, you must consider the practical limitations and trade-offs.
Brittleness and Thermal Shock
The same strong, rigid atomic bonds that give ceramics their high melting points also make them brittle. Unlike metals, which can bend and deform, ceramics tend to fracture catastrophically when their stress limit is exceeded. They are also susceptible to thermal shock—cracking caused by rapid temperature changes.
Purity and Processing
The theoretical melting point of a ceramic is for a pure, perfectly formed crystal. In reality, manufacturing processes introduce impurities, porosity, and grain boundaries (the interfaces between crystal grains). These imperfections can act as weak points, lowering the material's effective maximum service temperature and mechanical strength.
Cost and Machinability
High-performance ceramics are inherently difficult and expensive to produce. Their extreme hardness means that once they are fired into their final shape, they can only be machined with highly specialized diamond grinding tools, adding significant cost and complexity to any project.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires balancing thermal performance against mechanical requirements and cost.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective performance for high-heat structural components: Alumina is often the most balanced and widely used choice.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature resistance for applications like furnace linings or crucibles: Zirconia and Magnesia provide a step up in thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is resisting abrasion, chemical attack, or thermal shock at high temperatures: Non-oxide ceramics like Silicon Carbide are the superior, albeit more expensive, option.
Ultimately, choosing the right ceramic requires understanding that its value lies not in a single number, but in its specific profile of properties.
Summary Table:
| Ceramic Material | Type | Melting/Decomposition Point (°C) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Oxide (Alumina) | Oxide | ~2,072 °C | Cost-effective, widely used for structural components |
| Zirconium Dioxide (Zirconia) | Oxide | ~2,715 °C | Excellent thermal stability for furnace linings |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Non-Oxide | Decomposes at ~2,730 °C | Superior abrasion and thermal shock resistance |
| Hafnium Carbide (HfC) | Non-Oxide | ~3,900 °C | Extreme temperature performance for specialized applications |
Need High-Temperature Ceramic Solutions for Your Laboratory?
Choosing the right ceramic material is critical for your high-temperature applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing premium lab equipment and consumables, including advanced ceramic components tailored to your specific thermal and mechanical requirements.
Our experts can help you:
- Select the optimal ceramic material for your temperature range and application needs
- Source high-purity alumina, zirconia, silicon carbide, and other technical ceramics
- Ensure reliable performance in furnace linings, crucibles, and high-heat structural components
Let KINTEK be your partner in high-temperature success. Contact our technical specialists today to discuss your ceramic requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of dry ashing? Avoid Inaccurate Results with Better Alternatives
- What is the optimal temperature for ashing in a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise and Efficient Results
- What is the temperature of a muffle furnace for ash determination? Key Insights for Accurate Results
- What are the disadvantages of wet ashing? Key Safety & Contamination Risks
- What is the body structure of a furnace? Unlocking the Dual-Layer Design for Superior Thermal Control



















