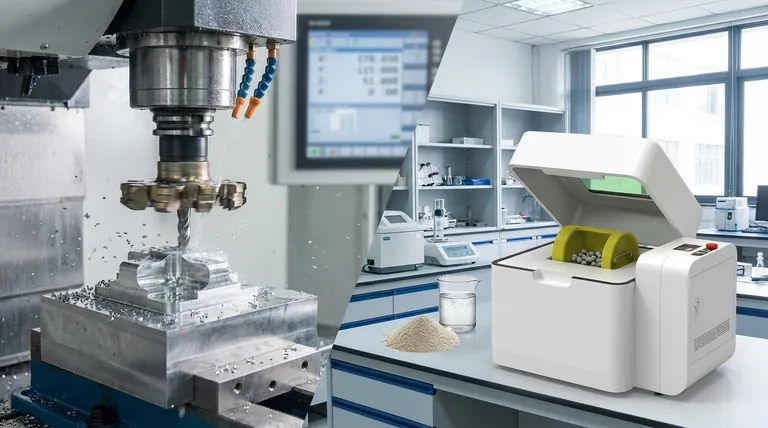
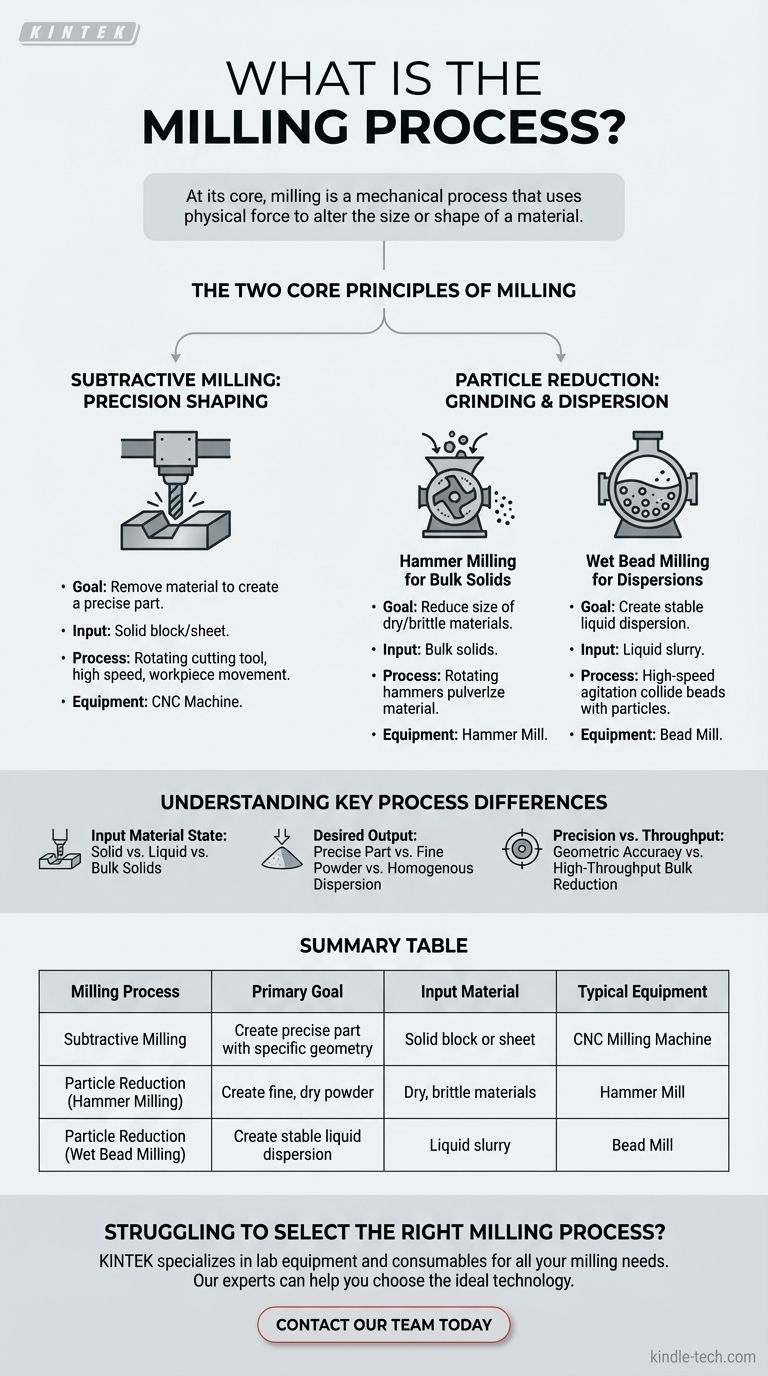
At its core, milling is a mechanical process that uses physical force to alter the size or shape of a material. While most often associated with subtractive manufacturing where a rotating tool cuts away material to shape a part, the term also applies to methods that break down particles into smaller sizes, such as in powders or liquid dispersions. The specific mechanics of the process change dramatically based on whether the goal is precision shaping or particle reduction.
The term "milling" describes two fundamentally different objectives achieved through mechanical force. It can refer to the precise, subtractive shaping of a solid object with a cutting tool, or it can describe the grinding and size reduction of particles within a solid or liquid medium.

The Two Core Principles of Milling
Understanding milling requires separating the process into two distinct categories based on the intended outcome: shaping an object or reducing particle size.
Subtractive Milling: Precision Shaping
This is the most common interpretation of milling, often performed on a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine.
The primary goal here is to remove material from a solid block, known as a workpiece, to create a part with specific geometric features. A multi-toothed cutting tool rotates at high speed while the workpiece is moved relative to it.
Particle Reduction: Grinding and Dispersion
This category of milling is not about creating a single shaped object, but about breaking down a bulk material into much smaller particles.
The objective is to reduce particle size through impact, collision, and attrition. This is critical in industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing.
A Closer Look at Key Milling Methods
Each principle is executed using highly specialized equipment designed for a specific type of material and a specific end result.
Cutting Mills for Manufacturing
This method uses a variety of rotating tools with different diameters and hardnesses to cut away material.
The high rotational speed of the cutting tool is essential for achieving a clean, smooth surface finish on the final part. This process is fundamental to creating metal, plastic, and wood components.
Wet Bead Milling for Dispersions
This process is designed for particle reduction within a liquid medium. The material is mixed into a liquid slurry and fed into a chamber filled with small grinding "beads."
An agitator moves the beads at high speed, causing them to collide with the material particles. This shatters agglomerates and fractures particles, creating a fine, stable, and homogenous liquid dispersion, such as in paints, inks, or pharmaceutical suspensions.
Hammer Milling for Bulk Solids
A hammer mill reduces the size of dry or brittle materials. Material is fed into a chamber where rapidly rotating hammers strike it repeatedly.
The particles are pulverized by the repeated impacts until they are small enough to pass through a screen at the bottom of the mill. This method is valued for its high throughput and is common in agriculture and recycling.
Understanding Key Process Differences
Choosing the correct milling process is impossible without first defining the state of your starting material and your final goal. The methods are not interchangeable.
Input Material State
The physical form of your material dictates the appropriate process. Subtractive milling requires a solid block or sheet. Wet bead milling requires a liquid slurry. Hammer milling is designed for bulk solids, such as grains, minerals, or waste material.
Desired Output
Your end goal is the most critical factor. If you need a finished part with precise dimensions, subtractive milling is the only option. If you need a fine powder from a bulk solid, you need a hammer mill. If your goal is a stable liquid dispersion with nano-sized particles, wet bead milling is the correct choice.
Precision vs. Throughput
These processes operate on different scales of precision and speed. CNC milling is a slow, highly precise process focused on geometric accuracy. In contrast, hammer milling is a high-throughput process designed for bulk reduction where exact particle geometry is less important than overall size.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
To select the right technology, you must first define your objective with absolute clarity.
- If your primary focus is creating a precise physical part from a solid block: You require subtractive milling, typically using a CNC milling machine.
- If your primary focus is creating a fine, dry powder from a bulk material: You need a particle reduction process like hammer milling.
- If your primary focus is creating a homogenous liquid mixture with suspended micro- or nano-sized particles: You must use a dispersion method like wet bead milling.
Understanding these fundamental distinctions allows you to select the precise milling technology required to achieve your material processing objective.
Summary Table:
| Milling Process | Primary Goal | Input Material | Typical Equipment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subtractive Milling | Create a precise part with specific geometry | Solid block or sheet (metal, plastic) | CNC Milling Machine |
| Particle Reduction (Hammer Milling) | Create a fine, dry powder from bulk solids | Dry, brittle materials (grains, minerals) | Hammer Mill |
| Particle Reduction (Wet Bead Milling) | Create a stable liquid dispersion | Liquid slurry (paints, inks, suspensions) | Bead Mill |
Struggling to select the right milling process for your material?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for all your milling needs. Whether you require precision shaping or particle size reduction, our experts can help you choose the ideal technology to enhance your product quality and processing efficiency.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) milling jars recommended for sulfide electrolytes? Ensure Purity in Li6PS5Cl Synthesis
- Why are silicon nitride or zirconia preferred for milling iodo-vanadate-lead precursors? Ensure High Purity Results
- Why is a ball mill jar lined with Y-ZrO2 required for Na3PS4 synthesis? Ensuring Purity in Sulfide Electrolytes



















