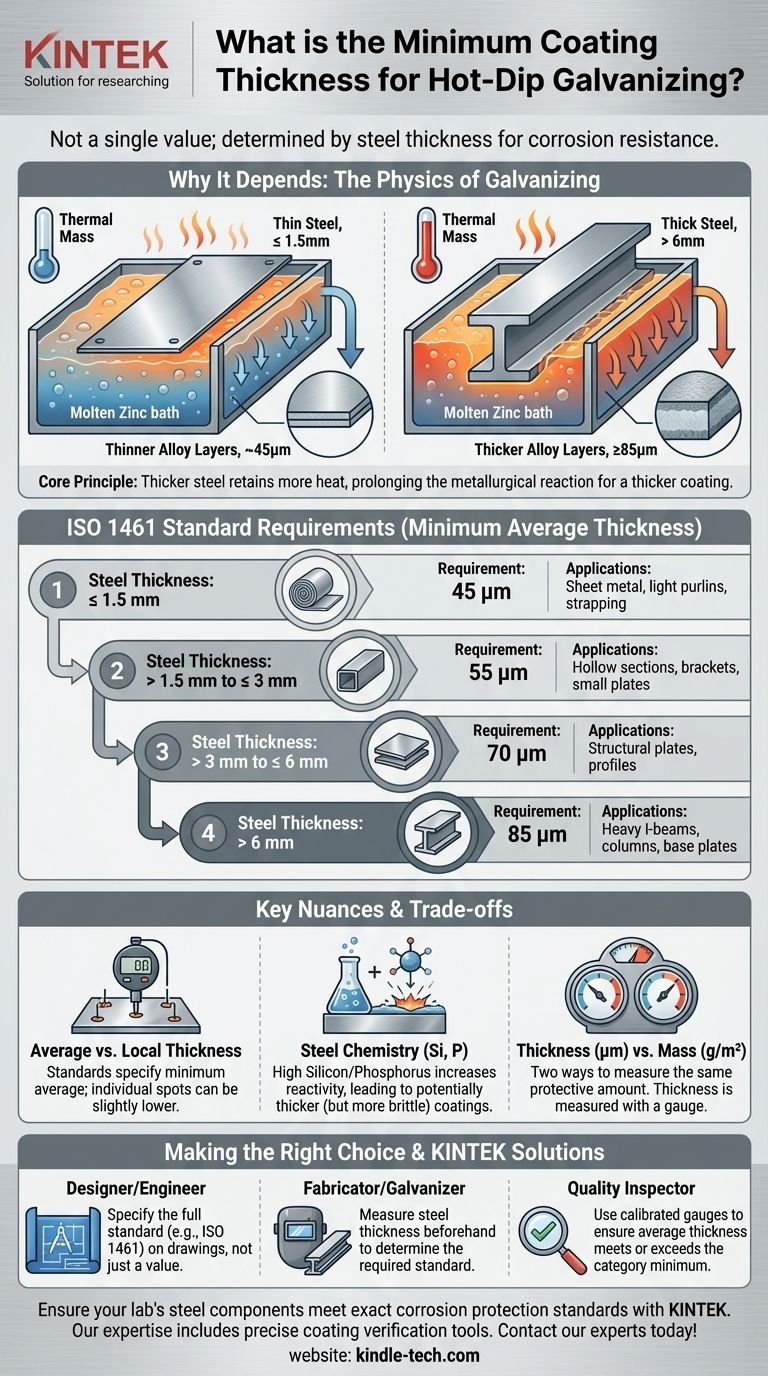
The minimum required coating thickness is not a single value; it is determined directly by the thickness of the steel part being protected. Industry standards mandate a thicker protective coating for heavier steel sections to ensure adequate corrosion resistance. For example, a thin steel sheet under 1.5 mm thick requires a minimum average coating of 45 micrometers (μm), while a thick structural beam over 6 mm requires at least 85 μm.
The core principle is that thicker steel retains more heat during the hot-dip galvanizing process. This increased heat allows the metallurgical reaction between the steel and zinc to proceed for longer, naturally forming a thicker and more robust protective coating.

Why Coating Thickness Depends on Steel Thickness
To ensure longevity and compliance, it's essential to understand the physics behind the specification. The relationship between steel and coating thickness is not arbitrary; it is a direct result of the hot-dip galvanizing process itself.
The Role of Thermal Mass
During hot-dip galvanizing, a steel article is submerged in a bath of molten zinc. The steel's thermal mass (its ability to store heat) is the most critical factor influencing the final coating thickness.
Heat Retention and Reaction Time
A thick, heavy steel section has a much higher thermal mass than a thin, light one. It takes longer to heat up to the temperature of the zinc bath and, crucially, cools down much more slowly once removed.
This extended cooling period allows more time for the diffusion reaction between the molten zinc and the iron in the steel to occur, building up thicker intermetallic alloy layers.
Formation of Protective Alloy Layers
The galvanized coating is not just a layer of zinc sitting on top of the steel. It is a series of zinc-iron alloy layers that are metallurgically bonded to the steel substrate, with a final outer layer of pure zinc. The thickness of these tough, abrasion-resistant alloy layers is what provides the majority of the long-term protection.
Understanding the Standard Specification
The requirements you are seeing are based on international standards like ISO 1461 or regional equivalents like ASTM A123. These standards categorize minimum coating thickness based on the thickness of the steel being galvanized.
For Steel ≤ 1.5 mm Thick
The required minimum average thickness is 45 μm. This applies to thin-gauge materials like sheet metal, light purlins, or steel strapping.
For Steel > 1.5 mm to ≤ 3 mm Thick
The requirement increases to 55 μm. This is a common category for components like hollow structural sections (HSS), brackets, and smaller plates.
For Steel > 3 mm to ≤ 6 mm Thick
The minimum average thickness is 70 μm. This covers a wide range of common structural steel plates and profiles used in construction and manufacturing.
For Steel > 6 mm Thick
The requirement is 85 μm. This applies to heavy structural steel, such as large I-beams, columns, and thick base plates, which require the most robust corrosion protection due to their application and long design life.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Simply knowing the numbers in the table is not enough. A true expert must understand the critical distinctions that affect real-world application and inspection.
Average vs. Local Thickness
The standards specify a minimum average thickness, calculated from a number of measurements taken across the surface. They also permit individual spot measurements, or local thickness, to be slightly lower than the average, but not by more than a set amount. This accounts for minor variations in the coating process.
The Impact of Steel Chemistry
The chemical composition of the steel itself can have a dramatic effect on the coating. Steels with higher levels of silicon (Si) and phosphorus (P) are more reactive with zinc.
This can result in coatings that are much thicker than the minimum requirement. While this sounds good, a very thick coating can sometimes be more brittle and may require special handling.
Thickness (μm) vs. Mass (g/m²)
The standards provide requirements in both thickness (micrometers) and coating mass (grams per square meter). These are simply two different ways of measuring the same outcome. Thickness is measured with a magnetic gauge, while mass is a way to express the amount of zinc applied over a given surface area.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, you must align your actions with your role in the project lifecycle.
- If you are a designer or engineer: Specify the coating by referencing the full standard (e.g., "Hot-dip galvanize to ISO 1461") on your drawings rather than just a single thickness value.
- If you are a fabricator or galvanizer: Always measure the thickness of your steel components before galvanizing to identify which standard requirement you are obligated to meet.
- If you are a quality inspector: Use a properly calibrated electronic thickness gauge to take measurements on representative surfaces and calculate the average, ensuring it meets or exceeds the minimum for that part's steel thickness category.
By understanding the direct link between steel thickness and coating requirements, you can confidently specify and verify protective coatings that guarantee compliance and deliver long-term performance.
Summary Table:
| Steel Thickness (mm) | Minimum Average Coating Thickness (μm) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| ≤ 1.5 | 45 μm | Sheet metal, light purlins, strapping |
| > 1.5 to ≤ 3 | 55 μm | Hollow sections, brackets, small plates |
| > 3 to ≤ 6 | 70 μm | Structural plates, profiles |
| > 6 | 85 μm | Heavy I-beams, columns, base plates |
Ensure your lab's steel components meet exact corrosion protection standards with KINTEK. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables includes precise coating verification tools and solutions tailored to laboratory environments. Whether you're designing, fabricating, or inspecting, KINTEK provides the reliable equipment and support needed for compliance and long-term performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific lab coating requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Filter Testing Machine FPV for Dispersion Properties of Polymers and Pigments
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- How does a three-electrode electrolytic cell function? Precision Testing for 8620 Steel in Corrosive Environments
- What role does a water-jacketed electrolytic cell play in variable-temperature electrochemical corrosion measurements?
- How is a high-precision electrolytic cell used to evaluate metal corrosion resistance? Validate DCT Results Accurately
- What is the volume range of the coating evaluation electrolytic cell? A Guide to Choosing the Right Size
- What are the advantages of a flat electrochemical cell for corrosion? Achieve Precise Pitting & Crevice Analysis


















