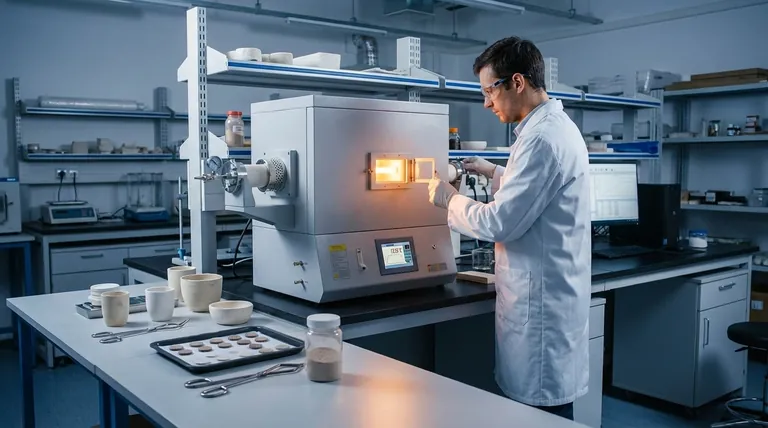
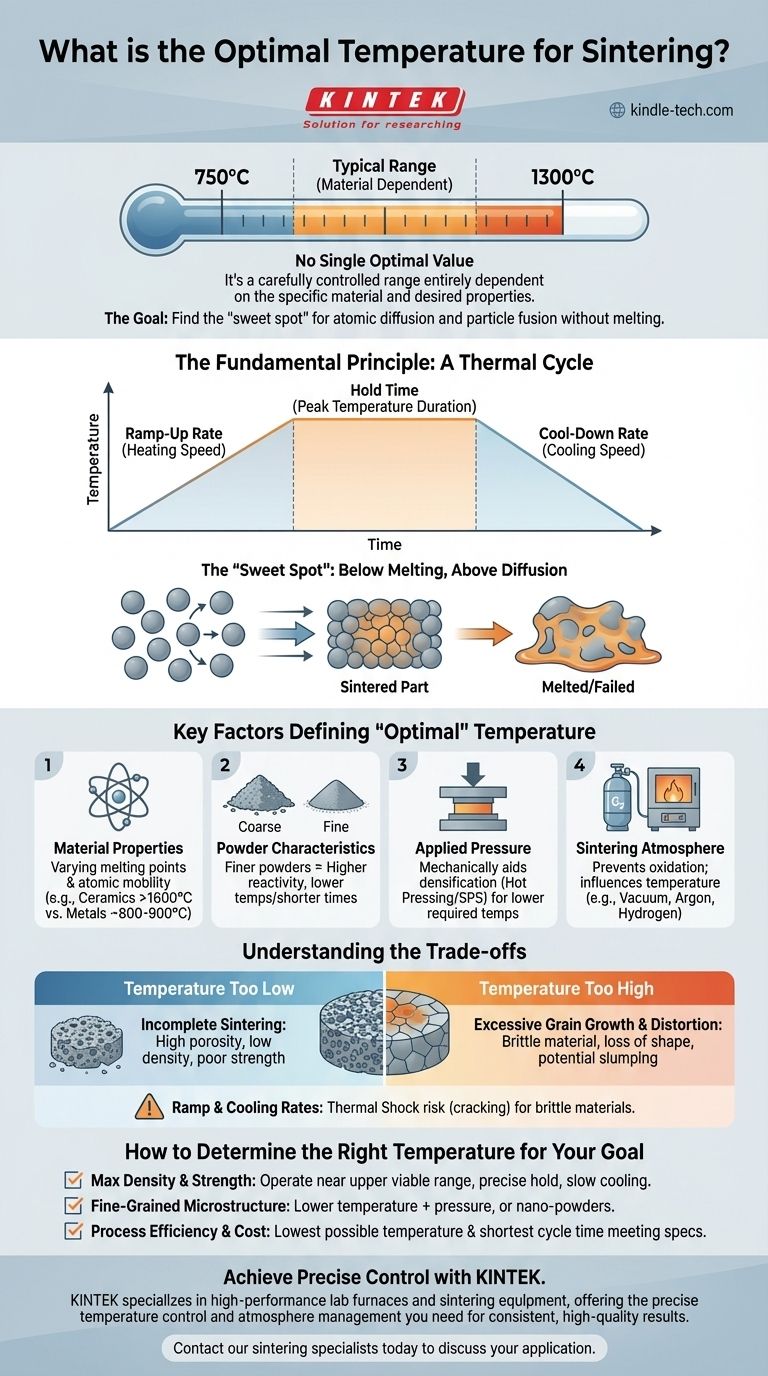
The optimal temperature for sintering does not exist as a single value. Instead, it is a carefully controlled range, typically between 750°C and 1300°C, that is entirely dependent on the specific material being processed and the final properties you aim to achieve. The goal is to find the "sweet spot" that promotes atomic diffusion and particle fusion without melting the material.
The concept of an "optimal temperature" is a misnomer. The true goal is to implement an optimal thermal process—a full cycle of heating, holding, and cooling—that is precisely tailored to your material's properties, your equipment's capabilities, and your desired outcome.

The Fundamental Principle of Sintering Temperature
To understand how to select the right temperature, you must first grasp the core mechanism of sintering. It is a balancing act between encouraging atomic movement and preventing structural failure.
The "Sweet Spot": Below Melting, Above Diffusion
Sintering works by heating a material to a temperature where its atoms become mobile enough to diffuse across the boundaries of individual particles, causing them to fuse together. This process reduces the empty space (porosity) between particles, resulting in a denser, stronger final part.
This temperature must be high enough to energize the atoms but must remain safely below the material's melting point. If the material liquefies, you lose all structural shape and control, resulting in a failed process.
It's a Thermal Cycle, Not a Single Temperature
Focusing only on the peak temperature is a common mistake. The entire temperature profile is critical for success and includes three distinct phases:
- Ramp-Up Rate: The speed at which you heat the material.
- Hold Time: The duration you maintain the peak sintering temperature.
- Cool-Down Rate: The speed at which you cool the material back down.
Each of these stages significantly influences the final quality, microstructure, and integrity of the component.
Key Factors That Define "Optimal" Temperature
The ideal temperature for your process is a variable dependent on several interconnected factors. Changing one often requires adjusting another.
The Material's Intrinsic Properties
This is the most significant factor. Different materials have vastly different melting points and atomic mobility. A ceramic like alumina requires a much higher sintering temperature (e.g., >1600°C) than a copper alloy (e.g., ~800-900°C).
Powder Characteristics (Grain Size)
The size of the initial powder particles plays a crucial role. Finer powders, with their higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, are more reactive and can be sintered effectively at lower temperatures or for shorter times compared to coarser powders.
Applied Pressure
Techniques like Hot Pressing or Spark Plasma Sintering apply external pressure during the heating cycle. This pressure mechanically aids in densification, which can often allow you to achieve the desired density at a significantly lower temperature than in pressureless sintering.
Sintering Atmosphere
The gas environment inside the furnace (e.g., vacuum, inert gas like argon, or a reactive gas like hydrogen) is critical. It prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, which can inhibit the sintering process and degrade the material's final properties. The atmosphere can influence the required temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing temperature is about managing competing risks. Pushing the boundaries in either direction has clear consequences.
Temperature Too Low: Incomplete Sintering
If the temperature is not high enough or the hold time is too short, atomic diffusion will be insufficient. This results in a part with high porosity, low density, and poor mechanical strength. The particles have not fully bonded.
Temperature Too High: Grain Growth and Distortion
Exceeding the ideal temperature, even if below the melting point, can cause excessive grain growth. While the part may be dense, oversized grains can often make the material more brittle. If you get too close to the melting point, you risk slumping, distortion, or partial melting, destroying the component's dimensional accuracy.
Ramp and Cooling Rates: Thermal Shock
Heating or cooling the part too quickly can introduce internal stresses due to thermal gradients. For many materials, especially brittle ceramics, this can lead to cracking and catastrophic failure.
How to Determine the Right Temperature for Your Goal
There is no universal formula. You must define your primary objective and adjust your thermal process accordingly.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: You will likely need to operate near the upper end of the material's viable sintering range, with precise control over hold times and a slow cooling rate.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fine-grained microstructure: Consider using a lower temperature combined with pressure-assisted techniques or starting with nano-sized powders to achieve densification without excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and cost: The goal is to find the lowest possible temperature and shortest cycle time that still meets the minimum quality and density specifications for your application.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about understanding and controlling the entire thermal process to achieve your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Optimal Temperature |
|---|---|
| Material Type | Dictates base temperature range (e.g., ceramics vs. metals). |
| Powder Grain Size | Finer powders enable lower sintering temperatures. |
| Applied Pressure | Pressure-assisted methods can significantly lower required temperature. |
| Sintering Atmosphere | Influences temperature by preventing oxidation or enabling reactions. |
Achieve precise control over your sintering process with KINTEK.
Determining the optimal thermal cycle is critical for achieving the desired density, strength, and microstructure in your lab materials. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and sintering equipment, offering the precise temperature control and atmosphere management you need for consistent, high-quality results.
Whether you're working with advanced ceramics, metal alloys, or other powdered materials, our experts can help you select the right equipment to master your sintering parameters.
Contact our sintering specialists today to discuss your specific application and how we can support your research and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Will THC distillate dissolve in water? Unlocking the Science of Water-Soluble Cannabis
- What kind of carbide is used for end mills? Tungsten Carbide for Superior Performance
- Is biomass an efficient source of energy? A Deep Dive into Its Strategic Role in Renewable Power
- Is KBr used in FTIR? The Essential Guide to Solid Sample Analysis
- Which is better carbon or graphite? Choose the Right Material for Your Application
- What is the difference between melting and sintering temperatures? A Guide to Material Processing Methods
- What are the three steps in the sintering cycle? Master the Process for Stronger Parts
- What are the benefits of plastic pyrolysis? Turning Waste into Valuable Fuel and Feedstock



















