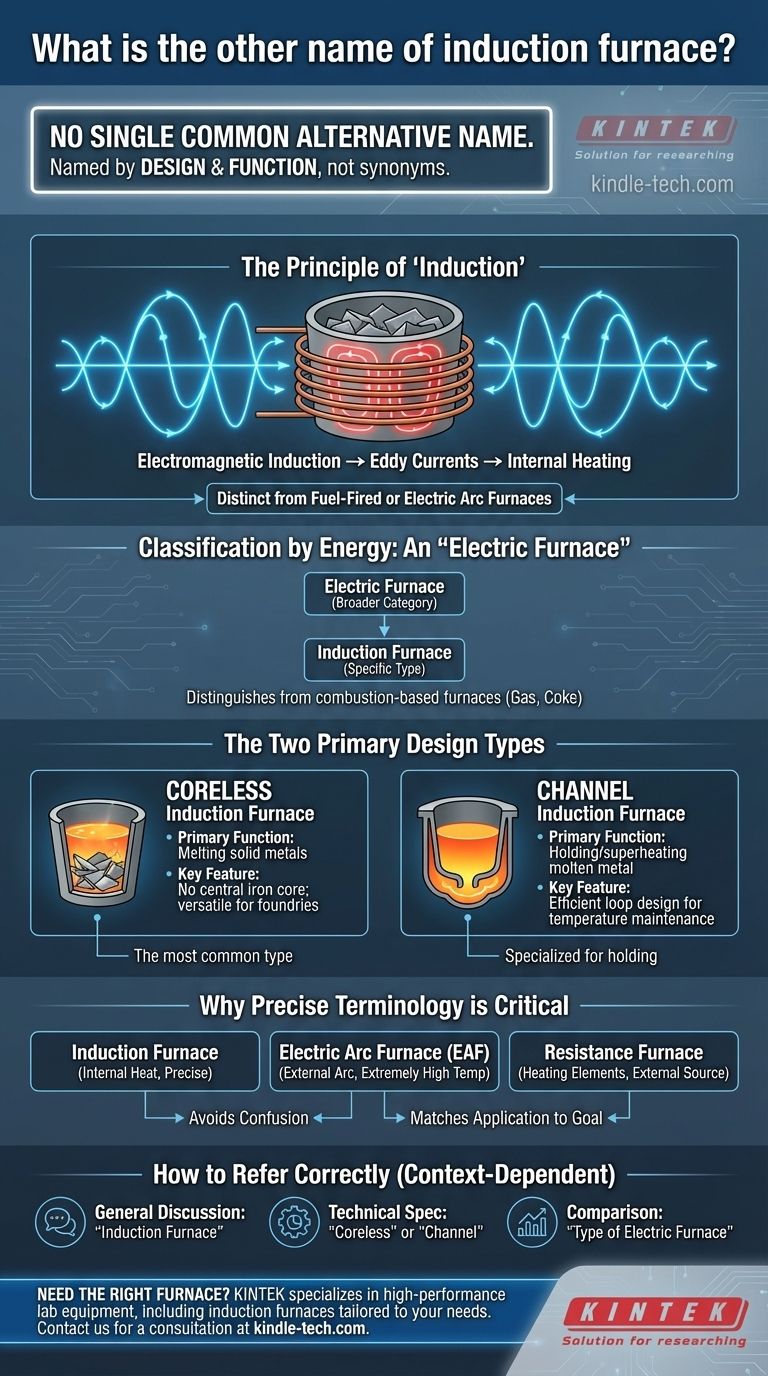
In short, an induction furnace does not have a single common alternative name. Instead, it is typically referred to by its specific type, such as a coreless induction furnace or a channel induction furnace. These terms describe the furnace's design and principle of operation rather than serving as a direct synonym.
The term "induction furnace" is already highly specific to its heating method. Any other names you encounter are less likely to be synonyms and more likely to be classifications describing its specific design, its energy source, or its role within a foundry.

Understanding the Name: Function Over Synonym
The name "induction furnace" directly describes how it works. This focus on its unique operating principle is why a simple, alternative name hasn't become common.
The Principle of "Induction"
An induction furnace uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to generate heat directly within the metal. An alternating current flows through a copper coil, creating a powerful magnetic field. This field "induces" eddy currents within the metal charge, and the metal's natural electrical resistance causes it to heat up and melt, much like a pan heats on an induction cooktop.
This method is distinct from other furnaces that burn fuel or use an electric arc to generate heat externally.
Classification by Energy: An "Electric Furnace"
While not a synonym, an induction furnace is a primary type of electric furnace. This broader category distinguishes it from furnaces that use combustible fuels like gas or coke. When discussing industrial heating methods, it is accurate to refer to it as a type of electric furnace.
The Two Primary Design Types
The most common "other names" you will hear for an induction furnace are actually references to its two main construction types. The distinction is critical for engineering and operational purposes.
The Coreless Induction Furnace
This is the most common design, especially for melting solid metals in foundries. It consists of a non-conductive crucible surrounded by the water-cooled induction coil. Because it has no central iron core, it is called a coreless furnace. For many, this is the default image of an induction furnace.
The Channel Induction Furnace
A channel furnace has a distinct "channel" or loop of molten metal that passes through an induction coil assembly. This design is highly efficient for holding already-molten metal at a specific temperature or for superheating it, but it is less suited for melting cold scrap from a solid state.
Why Precise Terminology is Critical
Using the correct term is essential for clear communication in technical and industrial settings. Referring to a furnace by its specific type avoids costly misunderstandings.
Differentiating from Other Electric Furnaces
Calling an induction furnace simply an "electric furnace" can create confusion. This broad category also includes Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF), which melt metal using an extremely high-temperature arc, and resistance furnaces, which use heating elements. Each has vastly different applications, costs, and metallurgical effects.
Matching the Furnace to the Application
The choice between a coreless and a channel furnace depends entirely on the goal. Coreless furnaces are versatile for melting a wide range of metals from a solid state. Channel furnaces are more specialized, acting like a high-efficiency holding vessel. Specifying the type is crucial for process design and equipment procurement.
How to Refer to an Induction Furnace Correctly
Your choice of terminology should be guided by your context and your audience.
- If your primary focus is a general discussion: Using "induction furnace" is the clearest and most universally understood term.
- If your primary focus is technical specification: You must specify the design, such as "coreless induction furnace" for melting or "channel induction furnace" for holding.
- If your primary focus is comparing heating methods: You can refer to it as a type of "electric furnace" to contrast it with fuel-fired alternatives.
Ultimately, clarity is achieved by describing the furnace by its unique and powerful method of heating: induction.
Summary Table:
| Design Type | Primary Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Coreless Induction Furnace | Melting solid metals | No central iron core; versatile for foundries |
| Channel Induction Furnace | Holding/superheating molten metal | Efficient loop design for temperature maintenance |
Need the right furnace for your lab or foundry?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces tailored to your specific melting or holding needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect coreless or channel furnace to optimize your process efficiency and results.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- What is the core role of a vacuum hot press furnace in composites? Master Precision Bonding and Densification
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?
- Why is it essential to maintain a high vacuum state during hot press sintering? Optimize SiCp/2024Al Quality



















