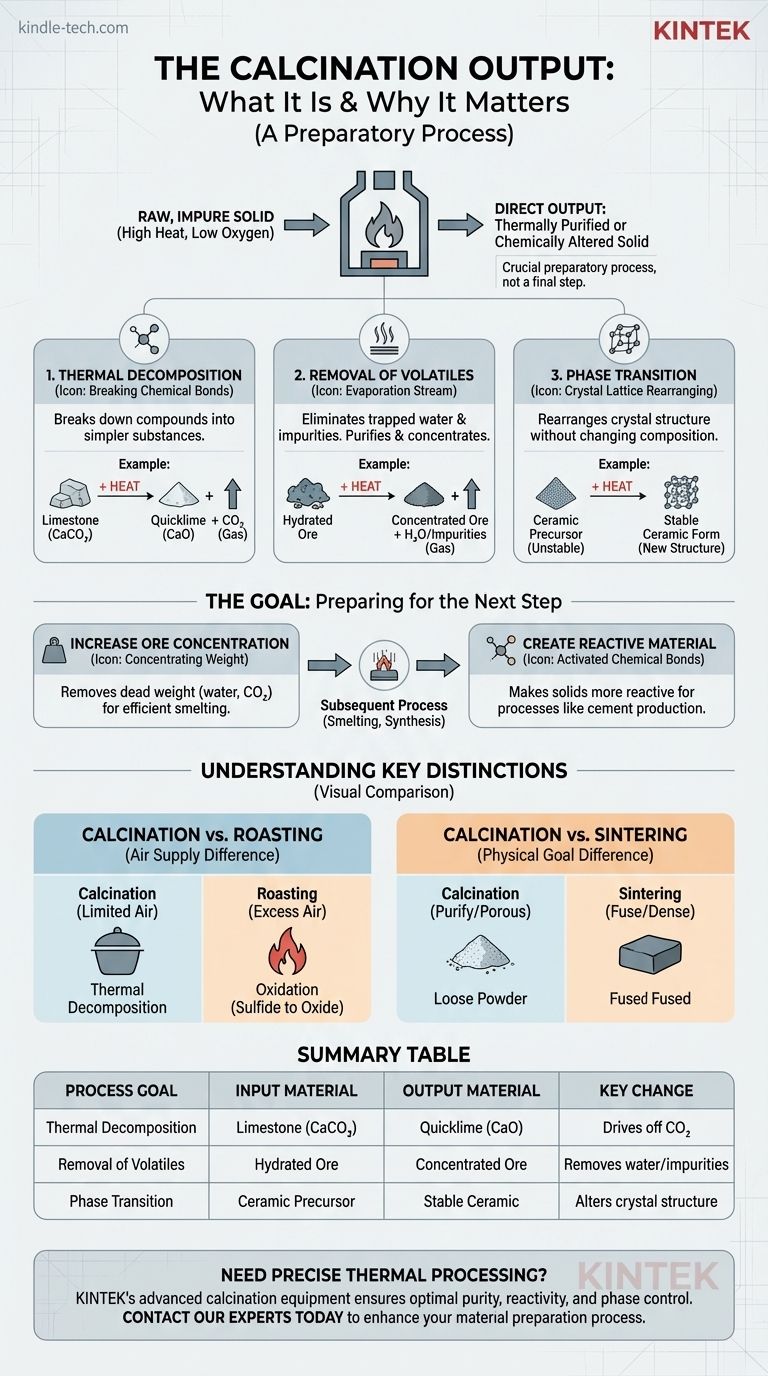
The direct output of calcination is a solid material that has been thermally purified or chemically altered. The process uses high heat in a low-oxygen environment to drive off volatile substances like water and carbon dioxide, decompose compounds, or change the material’s crystalline structure without melting it.
Calcination is not a final manufacturing step, but a crucial preparatory process. Its primary purpose is to transform a raw, impure solid into a more concentrated, stable, or reactive material that is optimized for a subsequent process like smelting or chemical synthesis.

What Changes During Calcination?
Calcination achieves its goal by inducing specific physical and chemical changes in a material through carefully controlled heating. The output is defined by which of these transformations occurs.
Thermal Decomposition
This is the most common objective of calcination. The heat breaks down a chemical compound into two or more simpler substances.
A classic example is the production of lime from limestone. Heating calcium carbonate (CaCO3) drives off carbon dioxide (CO2), leaving behind calcium oxide (CaO), or quicklime.
Removal of Volatile Fractions
Calcination is highly effective at removing volatile impurities that are trapped within the solid. This purifies and concentrates the desired material.
This includes removing physically absorbed water (drying) and, more importantly, chemically bonded water molecules from hydrated minerals, a process known as dehydration.
Inducing a Phase Transition
Sometimes, the goal isn't to change the chemical composition but to alter the material's internal crystal structure, or phase.
Heating a material can cause its atoms to rearrange into a different, often more stable or useful, crystalline form. This is a common step in the production of specific types of ceramics and catalysts.
The Goal: Preparing Materials for the Next Step
Understanding the output of calcination requires seeing it as a means to an end. The resulting solid is rarely the final product but is now ready for a more demanding industrial application.
Increasing Ore Concentration
In metallurgy, calcination is used to process ores before smelting. By driving off water from hydrated oxides or carbon dioxide from carbonate ores, the process removes dead weight.
This significantly increases the percentage of metal in the ore, making the subsequent, energy-intensive smelting process more efficient and cost-effective.
Creating a More Reactive Material
The calcined product is often more chemically reactive than the original raw material.
The lime (calcium oxide) produced from calcining limestone is a key ingredient in cement manufacturing precisely because it reacts readily with other components. The original limestone does not.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
To truly grasp what calcination produces, it is critical to distinguish it from similar high-temperature processes that have different goals and outputs.
Calcination vs. Roasting
The key difference is the presence of air. Calcination occurs in the absence or limited supply of air to cause thermal decomposition.
Roasting, by contrast, is heating in an excess of air. Its purpose is to induce oxidation, typically converting metal sulfide ores into metal oxides.
Calcination vs. Sintering
These processes have opposite physical goals. Calcination aims to purify or decompose a material, often making it more porous or powdery.
Sintering uses heat to fuse small particles together into a single, solid piece, increasing its strength and density without melting it.
Applying Calcination Effectively
The desired output dictates how and when you should use this process. Your choice depends entirely on the starting material and your ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is producing lime or cement: Use calcination for the thermal decomposition of limestone (calcium carbonate) into lime (calcium oxide).
- If your primary focus is preparing a metal ore for smelting: Apply calcination to remove water or carbon dioxide, thereby concentrating the desired metal oxide.
- If your primary focus is developing specific material properties: Use calcination to precisely control the phase transition and crystal structure of your raw material, a common practice in ceramics and catalyst production.
Ultimately, calcination is the foundational heat treatment process for purifying and preparing solid materials for their final application.
Summary Table:
| Process Goal | Input Material | Output Material | Key Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Decomposition | Limestone (CaCO₃) | Quicklime (CaO) | Drives off CO₂ |
| Removal of Volatiles | Hydrated Ore | Concentrated Ore | Removes water/impurities |
| Phase Transition | Ceramic Precursor | Stable Ceramic | Alters crystal structure |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials? KINTEK's advanced calcination equipment is engineered for laboratories and industrial applications, ensuring optimal purity, reactivity, and phase control for ores, ceramics, and chemical precursors. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your material preparation process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature for activated carbon regeneration? Key Ranges from 220°C to 900°C
- What is the temperature of a carbon regeneration kiln? Mastering the 750-800°C Reactivation Process
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process
- What temperature is a carbon regeneration kiln? Master the 650°C-800°C Range for Optimal Results



















