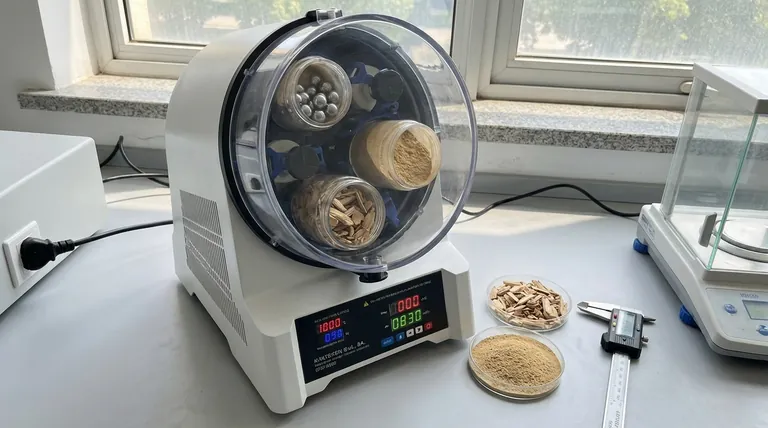
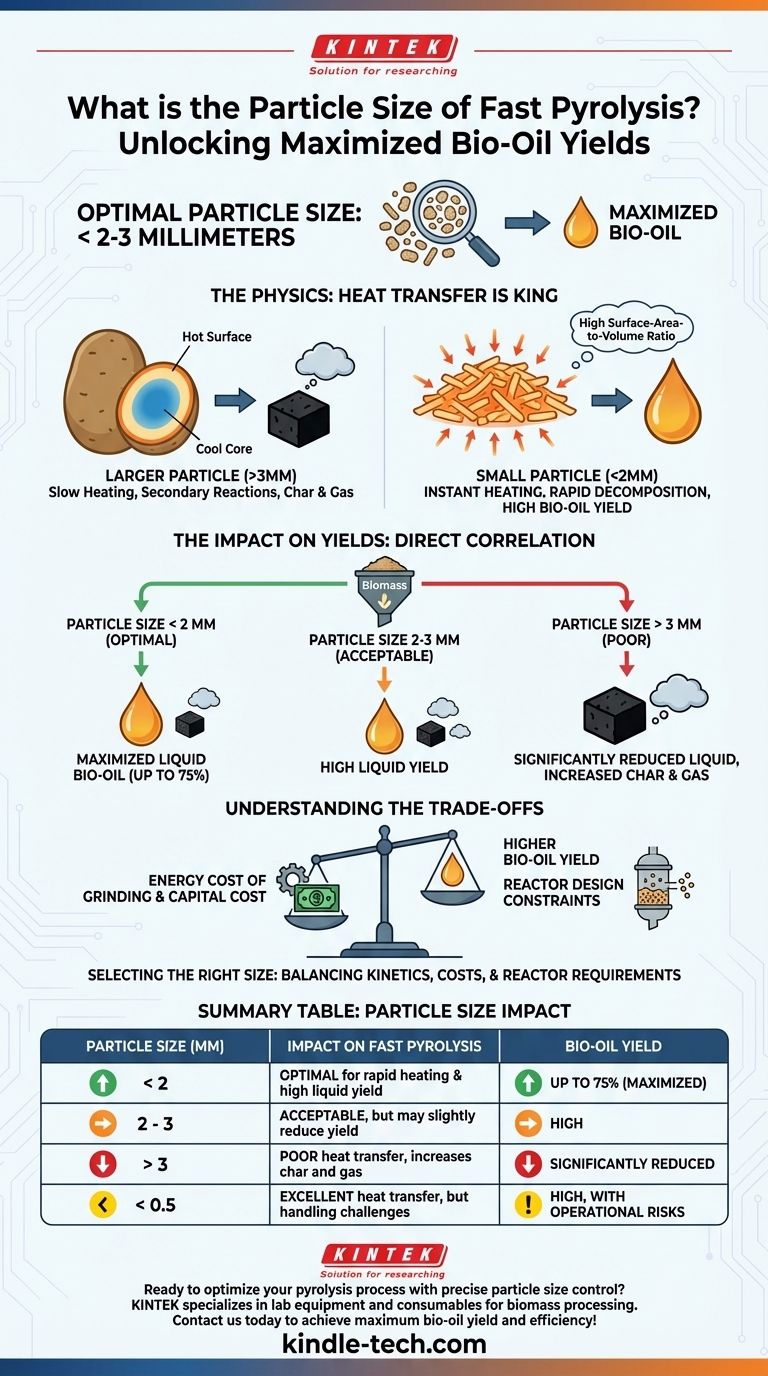
For optimal fast pyrolysis, the feedstock particle size must be very small, typically less than 2-3 millimeters in diameter. This is not a casual recommendation but a fundamental requirement dictated by the process's core objective: extremely rapid heat transfer to maximize the production of liquid bio-oil. Larger particles simply cannot heat up fast enough, which fundamentally changes the chemical reaction pathways and product yields.
The central principle of fast pyrolysis is to heat biomass so quickly that it decomposes into valuable vapors before it has a chance to turn into char. Small particle size is the most critical factor in achieving this necessary speed of heat transfer.

The Physics Behind Particle Size: Heat Transfer is King
Fast pyrolysis is defined by its extreme process conditions. Understanding the physics of how particles behave under these conditions is key to understanding why size is so critical.
The Goal: Rapid Heating, Short Residence Time
The entire process is engineered to achieve heating rates of over 1000°C per second. The goal is to get the biomass to a reaction temperature of around 500°C in less than two seconds. This rapid heating cracks the solid biomass structure directly into vapor-phase molecules.
Why Small Particles Heat Faster
A small particle has a very high surface-area-to-volume ratio. Think of the difference between cooking a whole potato versus cooking shredded potatoes. The shreds cook almost instantly because heat can penetrate the entire volume of each small piece at once.
This high ratio ensures that heat from the reactor (e.g., hot sand in a fluidized bed) is transferred into the core of the particle almost instantaneously.
Avoiding Secondary Reactions
If a particle is too large, its surface gets hot while its core remains cool. This temperature gradient is disastrous for bio-oil yield.
The hot surface begins to pyrolyze, but the vapors must travel through the cooler, unreacted core of the particle. This journey allows for undesirable secondary reactions, where the valuable vapors re-polymerize into low-value char and non-condensable gases.
The Impact of Particle Size on Yields
The choice of particle size has a direct and predictable impact on the final distribution of products: liquid, solid (char), and gas.
Maximizing Liquid Bio-oil
Years of research have confirmed that particle sizes below 2 mm are directly correlated with the highest liquid bio-oil yields, which can reach up to 75% by weight. This is the "sweet spot" where heat transfer is fast enough to suppress char-forming side reactions.
The Problem with Larger Particles (> 3 mm)
Once particle size exceeds about 3 mm, the process is no longer true fast pyrolysis. Heat transfer becomes limited by the particle's own thermal conductivity, leading to the temperature gradients discussed earlier. The result is a significant drop in liquid yield and a corresponding increase in char and gas production.
The Effect of Ultra-Fine Particles (< 0.5 mm)
While excellent for heat transfer, extremely fine particles can introduce engineering challenges. They can be difficult to handle, pose a dust explosion risk, and can be easily carried out of the reactor with the product vapors (a phenomenon called elutriation), complicating separation and cleanup.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the ideal particle size is not just a scientific decision; it is an economic and engineering one involving critical trade-offs.
The Energy Cost of Grinding
Reducing biomass from its initial form (e.g., wood chips) to sub-2mm particles is an energy-intensive process. Size reduction (milling, grinding, and drying) is a major contributor to both the capital cost (equipment) and operational cost (electricity) of a biomass conversion plant.
Reactor Design Constraints
The type of pyrolysis reactor also dictates the acceptable particle size range. For instance, fluidized bed reactors, a common choice for fast pyrolysis, require a specific particle size distribution to ensure the solids behave like a fluid. Particles that are too large will not fluidize, while particles that are too fine will be blown out of the bed.
Feedstock Variability
The ideal size is also influenced by the feedstock itself. Low-density, porous materials like agricultural straws may tolerate slightly larger particle sizes than dense hardwoods, as heat can penetrate their structure more easily.
Selecting the Right Particle Size for Your Process
Your specific goal will determine the optimal balance between ideal reaction kinetics and practical operational constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil yield: You must use finely ground feedstock, aiming for an average particle size below 2 mm and minimizing the fraction above 3 mm.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost: You may investigate using slightly larger particles to reduce grinding energy, but you must accept and quantify the resulting penalty in lower liquid yield and higher char production.
- If you are designing for a specific reactor: The particle size distribution must first satisfy the hydrodynamic requirements of your reactor (e.g., fluidization velocity), which will define the window you must operate within.
Ultimately, controlling particle size is one of the most powerful levers for managing the product distribution and economic viability of a fast pyrolysis system.
Summary Table:
| Particle Size (mm) | Impact on Fast Pyrolysis | Bio-Oil Yield |
|---|---|---|
| < 2 | Optimal for rapid heating and high liquid yield | Up to 75% (Maximized) |
| 2 - 3 | Acceptable, but may slightly reduce yield | High |
| > 3 | Poor heat transfer, increases char and gas | Significantly Reduced |
| < 0.5 | Excellent heat transfer, but handling challenges | High, but with operational risks |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process with precise particle size control? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for biomass processing, helping you achieve maximum bio-oil yield and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and let our experts guide you to the right solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the working principle of planetary ball mill? Unlock High-Energy Grinding for Nanoscale Results
- What are the parameters of a planetary ball mill? Master Speed, Time, and Media for Perfect Grinding
- What are the effects of ball milling? A Deep Dive into Mechanical Alloying and Material Transformation
- What is the principle of planetary ball mill? Achieve Rapid, High-Energy Grinding for Your Materials
- How does a planetary mill work? Harnessing High-Energy Impact for Nano-Grinding



















