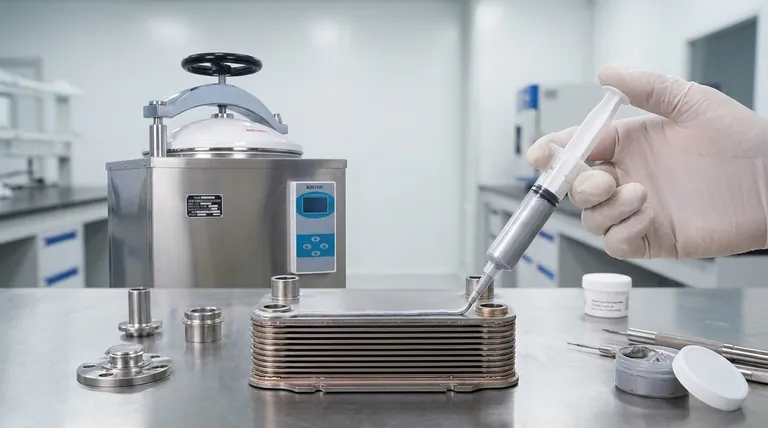
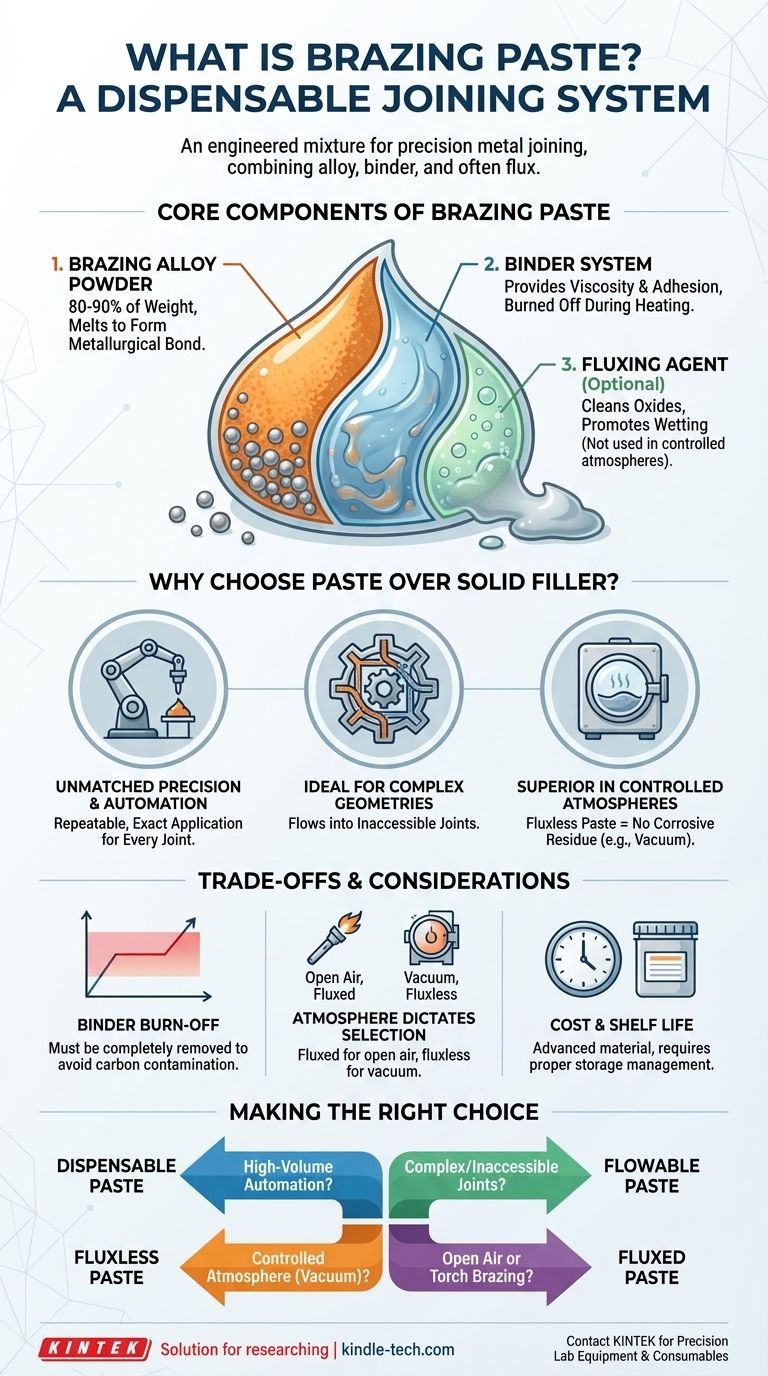
At its core, brazing paste is a precisely engineered, dispensable mixture used to join metal components. It consists of a fine metallic brazing alloy powder, a specialized binder system, and often a chemical flux, all suspended in a liquid carrier to create a smooth, paste-like consistency. This formulation allows for exact application and is critical for high-tech manufacturing.
Brazing paste is not merely a different form of filler metal; it is an integrated joining system. It combines the alloy, the application method, and often the flux into a single product, enabling levels of precision, automation, and repeatability that are impossible with solid wires or preforms.

Deconstructing Brazing Paste: The Core Components
To understand why brazing paste is so effective, you must first understand its three primary constituents and the role each one plays.
The Brazing Alloy Powder
This is the fundamental filler metal that melts and flows into the joint, creating the metallurgical bond. It typically comprises 80% to 90% of the paste's total weight.
The alloy itself is atomized into a fine, high-purity powder. The specific metal composition (e.g., aluminum, nickel, copper, or silver-based) is selected based on the parent metals being joined and the performance requirements of the final assembly.
The Binder System
The binder is a specialty organic compound that gives the paste its viscosity and adhesive properties. Its function is twofold.
First, it creates a stable suspension, ensuring the heavy metal powder doesn't separate from the liquid carrier. Second, it acts as a temporary glue, holding the powder particles in place on the part after application and before the assembly enters the furnace.
The Fluxing Agent (If Present)
Many brazing pastes contain a chemical flux. The flux becomes active during heating, cleaning oxides from the surfaces of the base metals and the alloy powder itself.
This cleaning action is essential for promoting wetting, which is the ability of the molten brazing alloy to flow smoothly and evenly across the joint surfaces.
Why Choose a Paste Over Solid Filler Metal?
Using a paste is a deliberate choice driven by the need for control and efficiency, particularly in demanding applications.
Unmatched Precision and Automation
Brazing paste is designed to be dispensed through automated equipment, such as syringes or pneumatic applicators. This allows for an exact, repeatable amount of filler metal to be applied to every joint, every time.
This level of control is crucial in industries like aerospace and electronics, where joint integrity is non-negotiable.
Ideal for Complex Geometries
Paste can be applied to intricate joints, internal channels, and other areas where placing a solid wire or shim would be physically impossible. Its flowable nature ensures the filler metal is present exactly where the bond is needed.
Superior Performance in Controlled Atmospheres
In processes like vacuum brazing, oxidation is eliminated by the environment itself. For these applications, a fluxless brazing paste is used.
This paste contains only the alloy powder and the binder. The absence of flux eliminates the risk of corrosive flux residue being trapped in the joint, which is a critical requirement for high-purity applications involving materials like titanium, nickel alloys, and advanced ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, using brazing paste requires a clear understanding of the process.
Binder Burn-Off is a Critical Step
The organic binder must be completely removed before the brazing alloy melts. This is achieved by programming a "burn-off" phase into the heating cycle, where the assembly is held at a temperature high enough to vaporize the binder but below the alloy's melting point.
Failure to remove the binder fully will introduce carbon contamination into the joint, leading to porosity and a catastrophic bond failure.
Atmosphere Dictates Paste Selection
The choice between a fluxed and a fluxless paste is not interchangeable. It is dictated entirely by the brazing process.
Using a fluxless paste for torch brazing in open air will result in a heavily oxidized, failed joint. Conversely, using a fluxed paste in a high-vacuum furnace can contaminate the furnace interior and is unnecessary.
Cost and Shelf Life
Brazing pastes are advanced materials and are typically more expensive than simple filler wire. Furthermore, the organic binders give the paste a defined shelf life, requiring proper storage and inventory management.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision to use brazing paste should be based on your manufacturing goals and the specific demands of your components.
- If your primary focus is high-volume automation and repeatability: A dispensable paste is the ideal choice, as it integrates seamlessly into automated production lines.
- If you are brazing complex joints or inaccessible areas: The flowable, adhesive nature of a paste allows you to apply filler metal precisely where it is needed most.
- If you are working in a controlled atmosphere (like a vacuum furnace): Select a fluxless paste to avoid flux residue and achieve the highest possible joint purity and strength.
- If you are brazing in open air or with a torch: You must use a paste that includes an appropriate fluxing agent to protect the joint from oxidation.
Ultimately, brazing paste transforms filler metal from a simple component into a sophisticated delivery system engineered to create flawless, repeatable joints.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Brazing Alloy Powder | Melts to form the metallurgical bond | 80-90% of paste weight; fine, high-purity powder |
| Binder System | Provides viscosity and adhesion | Holds paste in place; must be burned off during heating |
| Fluxing Agent | Cleans oxides for proper wetting | Optional; not used in vacuum or controlled atmosphere brazing |
Ready to achieve flawless, repeatable brazing results?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for precision brazing processes. Whether you are automating high-volume production or joining complex components in a controlled atmosphere, the right materials are critical to your success.
Our expertise can help you select the optimal brazing paste and associated equipment for your specific application, ensuring superior joint integrity and manufacturing efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your brazing operations and deliver the reliable performance your laboratory demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Laboratory Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer Lab Microcomputer Sterilizer
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
People Also Ask
- What are the requirements for an autoclave machine? Achieve Sterile Confidence for Your Lab
- What is a lab autoclave? Your Guide to Sterilization with Pressurized Steam
- What is the temperature effective for sterilization using autoclave? Achieve Sterile Conditions for Your Lab
- What to look for when buying an autoclave? A Guide to Selecting the Right Sterilization Technology
- How does the lab autoclave work? Achieve Complete Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam












