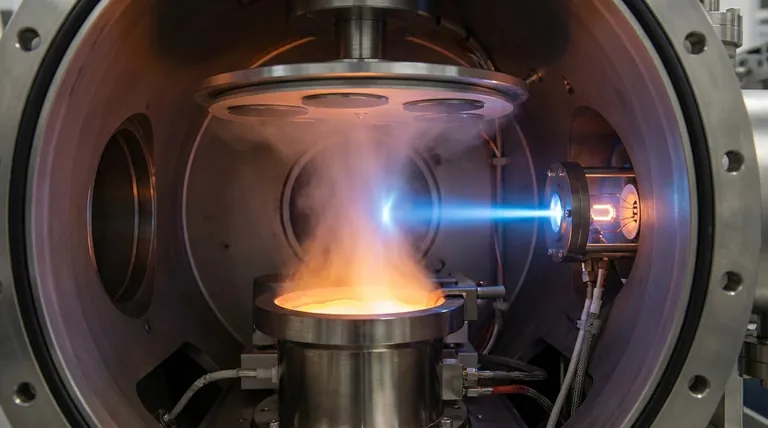
At its core, e-beam evaporation is a controlled process of energy conversion and phase transition. It uses a high-energy beam of electrons as a precision heating tool inside a high-vacuum chamber. This beam transfers its kinetic energy to a source material, causing intense, localized heating that vaporizes the material. These vaporized particles then travel in a straight line and condense onto a cooler substrate, forming an exceptionally pure and uniform thin film.
The fundamental physics involves converting electrical energy into a stream of high-kinetic-energy electrons. This beam then transfers that energy into thermal energy upon striking a source material, causing it to evaporate in a vacuum for clean, line-of-sight deposition onto a substrate.

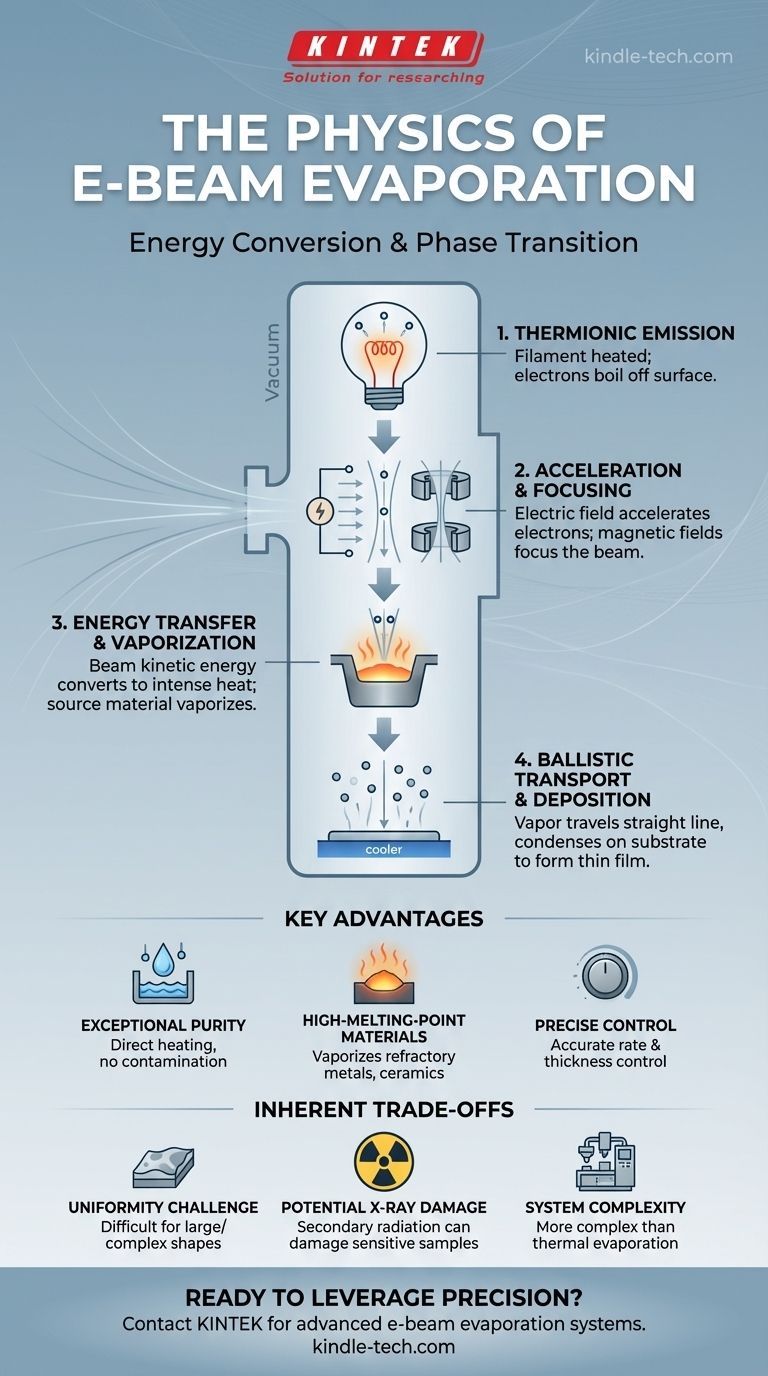
The Four Core Physical Stages
To truly understand e-beam evaporation, we must break it down into four distinct physical events that happen in sequence. Each stage is governed by fundamental principles of physics.
Stage 1: Thermionic Emission - Generating Electrons
The process begins not with the beam, but with the creation of free electrons. A filament, typically made of tungsten, is heated to a very high temperature.
This intense heat provides enough thermal energy to the electrons within the filament to overcome the material's work function—the energy barrier that normally keeps them bound to the atom. This process of "boiling" electrons off a hot surface is called thermionic emission.
Stage 2: Acceleration and Focusing - Creating the Beam
Once freed, the electrons are subjected to a strong electric field created by a high-voltage difference (often several kilovolts) between the heated filament (cathode) and an anode.
This powerful electric field accelerates the negatively charged electrons toward the positive potential, causing them to gain a tremendous amount of kinetic energy. Magnetic fields are then used to bend the trajectory of this electron beam and focus it with high precision onto a small spot within a crucible.
Stage 3: Energy Transfer and Vaporization - The Key Interaction
This is the central event. The focused, high-energy electron beam strikes the surface of the source material held in a water-cooled copper hearth.
Upon impact, the kinetic energy of the electrons is rapidly converted into thermal energy within the material. The energy delivered is so intense and concentrated that it heats the material far beyond its melting and boiling points, causing it to sublimate or evaporate into a vapor.
Stage 4: Ballistic Transport and Deposition - The Final Journey
This entire process occurs within a high-vacuum chamber. The vacuum is critical because it removes most air molecules, creating a long mean free path for the vaporized atoms.
This means the evaporated particles travel in straight, uninterrupted lines—a state known as ballistic transport. When these particles reach the cooler substrate positioned above the source, they lose their thermal energy and condense onto its surface, forming a dense, solid thin film.
Why This Physics Matters: Key Advantages
The underlying physics of the process directly leads to its primary advantages in materials science and manufacturing.
Achieving Exceptional Purity
The electron beam heats only the source material itself. The water-cooled hearth it sits in remains cool, preventing the crucible material from outgassing or alloying with the source. This direct, targeted heating is the reason e-beam evaporation produces films of extremely high purity.
Deposition of High-Melting-Point Materials
The energy density of an electron beam is incredibly high. This allows it to easily vaporize materials with very high melting points, such as refractory metals (titanium, tungsten) and dielectric ceramics (silicon dioxide, titanium oxide), which are difficult or impossible to evaporate with other methods.
Precise Rate and Thickness Control
The intensity of the electron beam can be controlled with great precision by adjusting the filament current and accelerating voltage. This gives operators fine control over the evaporation rate, which in turn allows for the deposition of films with highly accurate and repeatable thicknesses, often on the scale of nanometers.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
No physical process is without its limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is key to using the technology effectively.
The Challenge of Uniformity
Because the vapor source is small and deposition is "line-of-sight," achieving a perfectly uniform film thickness over a large or complex-shaped substrate can be challenging. This often requires complex substrate holders that rotate during deposition to average out the coating distribution.
Potential for X-ray Damage
The impact of high-energy electrons (several keV) on a material inevitably generates X-rays. For sensitive substrates, such as certain electronic components or biological samples, this secondary radiation can cause damage and must be accounted for.
System Complexity
The components required—a high-voltage power supply, magnetic steering coils, a high-vacuum system, and an electron gun—make e-beam evaporators significantly more complex and expensive than simpler methods like thermal evaporation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision to use e-beam evaporation is driven by the specific requirements of the final film.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-melting-point materials like refractory metals or ceramics: E-beam evaporation is often the superior or only choice due to its ability to deliver highly concentrated energy.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity for optical or electronic applications: The direct heating mechanism of e-beam evaporation minimizes contamination, making it the ideal process.
- If your primary focus is simply coating a robust substrate with a low-melting-point metal like aluminum: A less complex and more cost-effective method, such as thermal evaporation, may be sufficient for your needs.
Understanding these physical principles allows you to leverage the precise power of e-beam evaporation for the most demanding thin-film applications.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Physical Process | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Thermionic Emission | Free electrons are "boiled" off a hot filament. |
| 2 | Acceleration & Focusing | Electrons gain kinetic energy and are focused into a beam. |
| 3 | Energy Transfer & Vaporization | Beam's kinetic energy converts to heat, vaporizing the source material. |
| 4 | Ballistic Transport & Deposition | Vaporized atoms travel in a straight line and condense into a thin film. |
Ready to leverage the precision of e-beam evaporation in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including advanced e-beam evaporation systems. Our solutions are designed for researchers and engineers who require the highest purity films and the capability to work with refractory materials. We provide the tools for unparalleled control over deposition rate and thickness, critical for cutting-edge applications in semiconductors, optics, and materials science.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your thin-film processes and help you achieve your research and production goals.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















