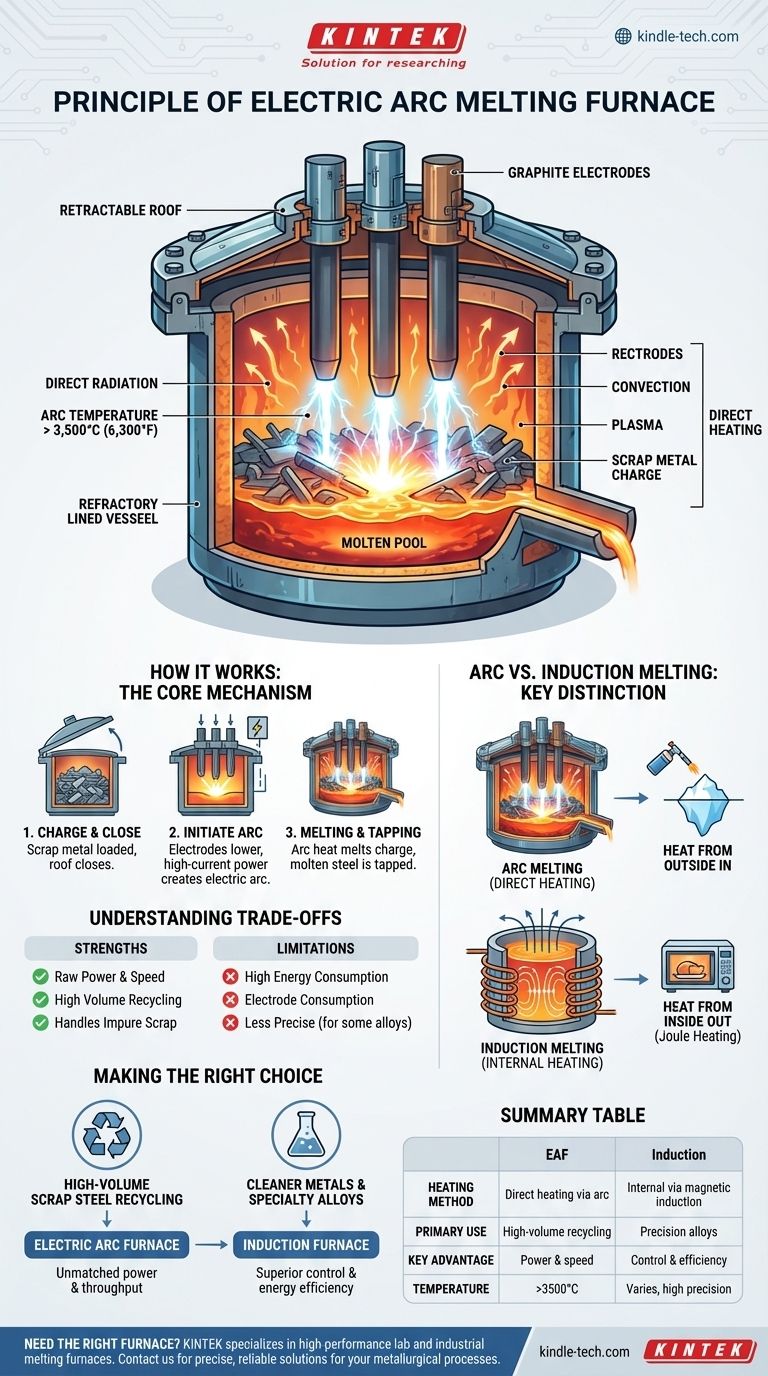
At its core, an electric arc furnace (EAF) operates on a simple but powerful principle: it uses the intense heat of a high-current electric arc to melt metals. Think of it as creating a controlled, continuous bolt of lightning inside a closed container. This arc forms between graphite electrodes and the metallic material (known as the "charge"), generating extreme temperatures that rapidly turn solid scrap into a molten liquid.
The critical distinction of an arc furnace is its method of direct heating. Unlike processes that heat metal from the outside or use magnetic fields, the EAF applies immense thermal energy directly to the charge via a plasma arc, making it exceptionally effective for high-volume melting.

How an Electric Arc Furnace Works: The Core Mechanism
The operation of an EAF is a process of converting electrical energy into thermal energy with brutal efficiency. It is the workhorse of modern steel recycling for this reason.
The Key Components
An EAF consists of a refractory-lined vessel to contain the heat, a retractable roof for loading scrap, and massive graphite electrodes. These electrodes can be several feet in diameter and are the terminals that will deliver the electrical power.
Initiating the Arc
The process begins by loading the furnace with the charge, which is typically scrap steel. The roof is closed, and the electrodes are lowered until they are just above the metal. A massive power supply sends a high-current, high-voltage charge through the electrodes.
Generating Immense Heat
When the electricity attempts to jump the gap between the electrode tip and the scrap metal, it ionizes the air, creating a sustained electric arc. This arc is a channel of plasma with temperatures that can exceed 3,500°C (6,300°F).
This intense heat is transferred to the metal in two primary ways:
- Direct radiation from the incredibly bright arc.
- Convection from the superheated gases inside the furnace.
The Melting Process
This overwhelming thermal energy rapidly melts the scrap metal, creating a pool of molten liquid at the bottom of the furnace. The process continues until the entire charge is melted, at which point alloying agents can be added to achieve the desired chemical composition before the molten steel is tapped from the furnace.
The Key Distinction: Arc vs. Induction Melting
To truly understand the arc furnace principle, it is helpful to contrast it with the other common electrical melting method: the induction furnace. They both use electricity, but in fundamentally different ways.
Direct Heating: The Arc Furnace
As established, the EAF is a direct heating method. The heat is generated outside the metal (in the arc) and then transferred to the metal. It is analogous to using a massive, incredibly hot blowtorch to melt an iceberg.
Internal Heating: The Induction Furnace
An induction furnace works by internal heating. An alternating current flows through a coil, creating a powerful, rapidly reversing magnetic field. This field induces strong electrical currents, called eddy currents, directly inside the metal charge.
The metal's own electrical resistance causes these eddy currents to generate heat—a principle known as Joule heating. The metal effectively heats itself from the inside out, with no external arc or flame.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a melting technology is a decision driven by scale, material, and cost. Each method has distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Strengths of the Arc Furnace
The EAF's primary advantage is its raw power and speed. It is exceptionally good at melting large volumes of scrap steel, even material that is not perfectly clean. This makes it the dominant technology for large-scale steel mills focused on recycling.
Common Pitfalls and Limitations
The main trade-offs for an EAF include extremely high energy consumption and the ongoing cost of replacing the graphite electrodes, which are consumed during the melting process. The violent nature of the arc is also very loud and can be less precise for creating specialized, high-purity alloys compared to induction melting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on the material you are processing and your operational objectives.
- If your primary focus is high-volume scrap steel recycling: The electric arc furnace is the unmatched industry standard for its sheer power and throughput capacity.
- If your primary focus is melting cleaner metals or creating precise specialty alloys: An induction furnace offers superior control, cleanliness, and energy efficiency for these more sensitive applications.
Understanding the fundamental difference between the EAF's direct arc heating and the induction furnace's internal magnetic heating is the key to selecting the right tool for your metallurgical goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Arc Melting Furnace | Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct heating via electric arc | Internal heating via magnetic induction |
| Primary Use | High-volume scrap steel recycling | Precise specialty alloys, cleaner metals |
| Key Advantage | Raw power and high throughput | Superior control and energy efficiency |
| Temperature Range | Exceeds 3500°C (6300°F) | Varies, typically high precision |
Need the right furnace for your lab or production facility? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including melting furnaces tailored for research and industrial applications. Whether you're recycling metals or developing advanced alloys, our expertise ensures you get the precise, reliable equipment you need. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your metallurgical processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a sputtering system? Achieve Unmatched Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is RF magnetron sputtering? A Guide to Depositing Insulating Thin Films
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What are sputtering systems used for? A Guide to Advanced Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the types of induction melting furnace? Coreless, Channel, and VIM Explained



















