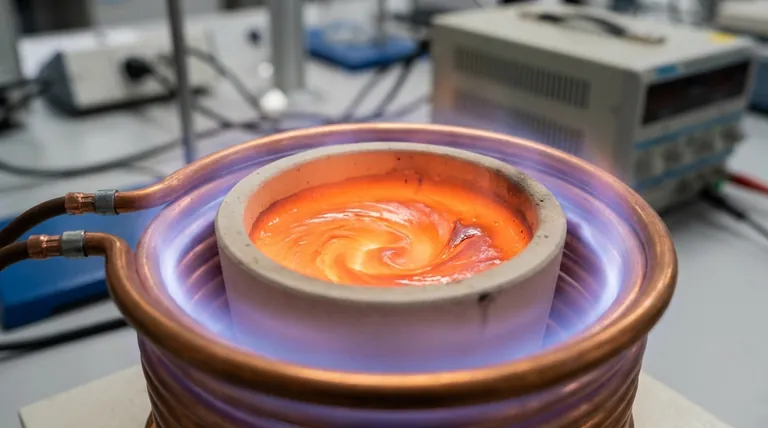
At its most fundamental level, an induction furnace works by using a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field to turn the metal inside the furnace into its own heat source. This process relies on two core physics principles: electromagnetic induction to create an electrical current in the metal, and the Joule effect, where the resistance to this current generates intense heat, causing the metal to melt from within.
An induction furnace is not a conventional oven that heats metal from the outside in. Instead, it transforms the conductive metal charge itself into the source of the heat, enabling rapid, clean, and highly controlled melting without direct contact.

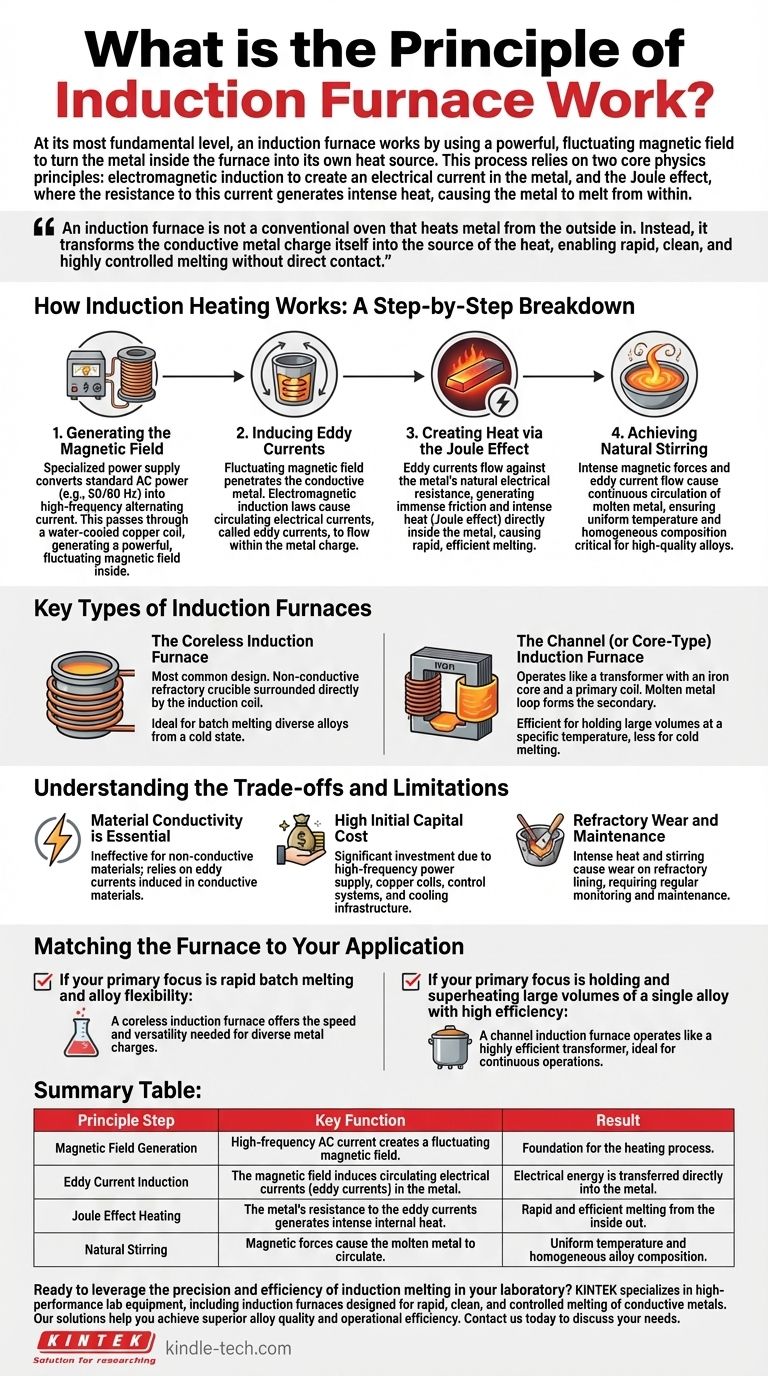
How Induction Heating Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To truly grasp the principle, it's helpful to break the process down into its sequential stages, from the power supply to the final molten product.
1. Generating the Magnetic Field
It all begins with a specialized power supply. This unit converts standard mains frequency AC power (e.g., 50/60 Hz) into a higher frequency alternating current.
This high-frequency current is then passed through a hollow copper coil, often water-cooled, that surrounds the crucible holding the metal. The flow of this current generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field inside the coil.
2. Inducing Eddy Currents
This fluctuating magnetic field penetrates the conductive metal placed inside the crucible. According to the laws of electromagnetic induction, the changing magnetic field induces circulating electrical currents within the metal.
These induced currents are known as eddy currents. They flow in closed loops within the metal charge, much like eddies in a stream of water.
3. Creating Heat via the Joule Effect
The metal itself has a natural electrical resistance. As the powerful eddy currents are forced to flow through the metal against this resistance, they generate immense friction at a molecular level.
This friction manifests as heat—a phenomenon known as the Joule effect. Because the heat is generated directly inside the metal, the melting process is extremely fast and efficient.
4. Achieving Natural Stirring
A significant secondary benefit of this process is an inherent stirring action. The intense magnetic forces and the flow of eddy currents cause the molten metal to circulate continuously.
This natural stirring ensures a highly uniform temperature and a homogenous chemical composition throughout the melt, which is critical for producing high-quality alloys.
Key Types of Induction Furnaces
While the underlying principle is the same, the physical design of the furnace can vary significantly based on the application.
The Coreless Induction Furnace
This is the most common design. It consists of a non-conductive refractory crucible surrounded directly by the induction coil.
It is highly versatile and ideal for melting materials from a cold state in batches. Its flexibility allows for the production of many different types of alloys.
The Channel (or Core-Type) Induction Furnace
This design operates much more like a traditional transformer. It has an iron core with a primary induction coil wound around it.
A loop of molten metal forms the secondary component. Heat is generated within this loop and circulates into a larger bath of metal. These furnaces are exceptionally efficient for holding large volumes of molten metal at a specific temperature, but less suited for cold melting.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
The induction method offers incredible advantages, but it is not without its specific requirements and challenges.
Material Conductivity is Essential
The entire principle hinges on the material being electrically conductive. Induction heating is ineffective for non-conductive materials like ceramics or dry refractories, as eddy currents cannot be induced within them.
High Initial Capital Cost
The required components—including the high-frequency power supply, copper coils, control systems, and cooling infrastructure—make induction furnaces a significant capital investment compared to some traditional fuel-fired furnaces.
Refractory Wear and Maintenance
The intense heat and the constant stirring action of the molten metal can lead to wear on the refractory lining of the crucible. This requires regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure furnace integrity and safety.
Matching the Furnace to Your Application
The choice between induction furnace types depends entirely on the operational goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid batch melting and alloy flexibility: A coreless induction furnace offers the speed and versatility needed for diverse metal charges.
- If your primary focus is holding and superheating large volumes of a single alloy with high efficiency: A channel induction furnace operates like a highly efficient transformer, ideal for continuous operations.
Understanding this principle of internal heat generation is the key to leveraging the precision, speed, and efficiency of induction technology.
Summary Table:
| Principle Step | Key Function | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Field Generation | High-frequency AC current creates a fluctuating magnetic field. | Foundation for the heating process. |
| Eddy Current Induction | The magnetic field induces circulating electrical currents (eddy currents) in the metal. | Electrical energy is transferred directly into the metal. |
| Joule Effect Heating | The metal's resistance to the eddy currents generates intense internal heat. | Rapid and efficient melting from the inside out. |
| Natural Stirring | Magnetic forces cause the molten metal to circulate. | Uniform temperature and homogeneous alloy composition. |
Ready to leverage the precision and efficiency of induction melting in your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for rapid, clean, and controlled melting of conductive metals. Our solutions help you achieve superior alloy quality and operational efficiency.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss how an induction furnace can transform your metal processing workflow and meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















