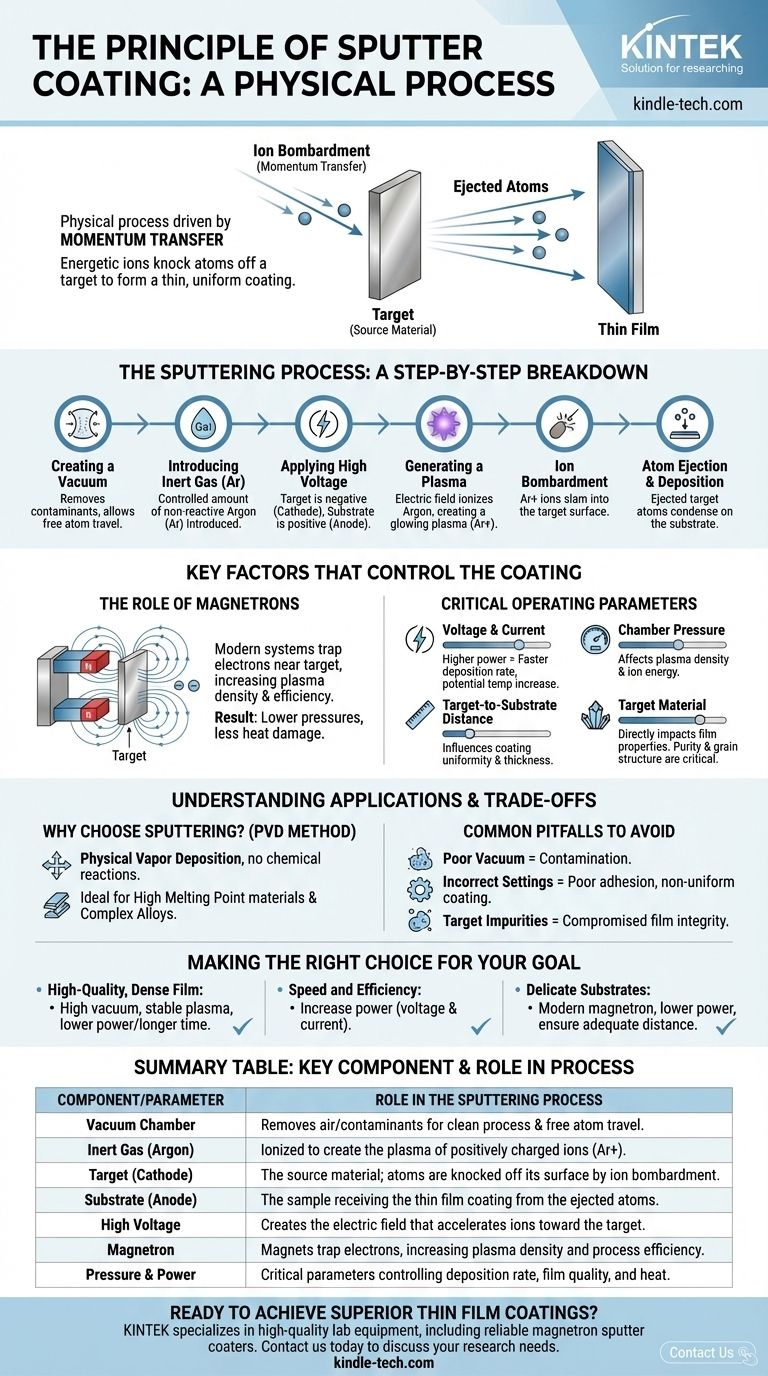
At its core, sputter coating is a physical process. It works by creating a plasma in a vacuum and using energetic ions from that plasma to physically knock atoms off a source material, known as the "target." These dislodged atoms then travel through the vacuum and deposit onto a sample, forming an exceptionally thin and uniform coating.
The fundamental principle is momentum transfer. Think of it as a subatomic-scale sandblasting process where individual gas ions are the projectiles that chip atoms off a target, which then build up layer-by-layer to form a new surface on your substrate.
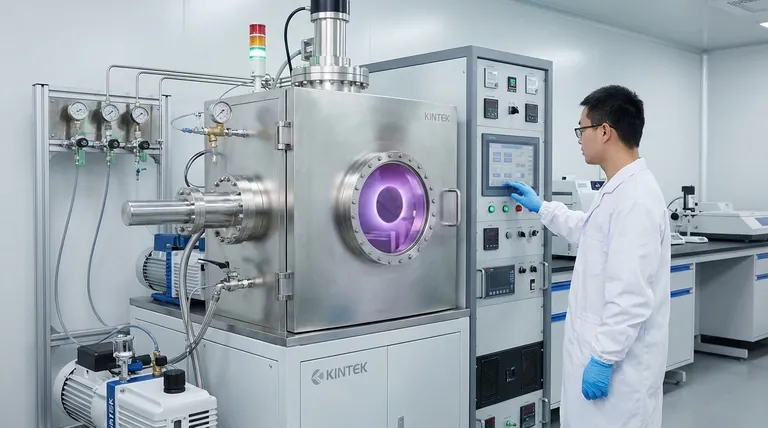

The Sputtering Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To truly understand the principle, it's best to walk through the sequence of events that occurs inside the sputter coater's vacuum chamber. Each step is critical for achieving a high-quality coating.
Step 1: Creating a Vacuum
The entire process must occur in a vacuum chamber. Removing air and other contaminants is essential to prevent unwanted chemical reactions and to allow the sputtered atoms to travel freely from the target to the substrate.
Step 2: Introducing an Inert Gas
A small, controlled amount of an inert gas, almost always argon (Ar), is introduced into the chamber. Argon is used because it is heavy, non-reactive, and easily ionized.
Step 3: Applying High Voltage
A high DC voltage (hundreds to thousands of volts) is applied between two electrodes. The source material (target) is made the negative electrode (cathode), and the sample to be coated (substrate) is placed on or near the positive electrode (anode).
Step 4: Generating a Plasma
The strong electric field strips electrons from the argon atoms, creating a mixture of free electrons and positively charged argon ions (Ar+). This energized, glowing cloud of ions and electrons is the plasma.
Step 5: Ion Bombardment
The positively charged argon ions are powerfully accelerated by the electric field and slam into the negatively charged target surface. This is the key "sputtering" event.
Step 6: Atom Ejection and Deposition
When an argon ion strikes the target, it transfers its kinetic energy. If the energy is sufficient, it knocks one or more atoms loose from the target material. These ejected atoms travel in a straight line until they strike a surface, including the substrate, where they condense to form a thin film.
Key Factors That Control the Coating
The quality, thickness, and deposition speed of the coating are not accidental. They are the direct result of carefully controlled parameters that influence the sputtering process.
The Role of Magnetrons
Modern systems are almost always magnetron sputter coaters. They use powerful magnets placed behind the target.
These magnets trap the free electrons from the plasma in a magnetic field close to the target's surface. This dramatically increases the probability of these electrons colliding with and ionizing more argon atoms, creating a much denser, more stable plasma right where it's needed.
The result is a more efficient process that can operate at lower pressures and causes less heat damage to the substrate.
Critical Operating Parameters
Several variables must be managed to achieve the desired outcome:
- Voltage and Current: Higher power generally leads to a faster deposition rate but can also increase the temperature.
- Chamber Pressure: The amount of argon gas affects the density of the plasma and the energy of the bombarding ions.
- Target-to-Substrate Distance: This distance influences the uniformity and thickness of the final coating.
- Target Material: The type of material being sputtered directly impacts the properties of the resulting film. Purity and grain structure are critical.
Understanding the Applications and Trade-offs
Sputtering is not the only way to create a thin film, but its physical nature gives it distinct advantages and makes it ideal for specific applications.
Why Choose Sputtering?
Sputtering is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method. Unlike chemical vapor deposition (CVD), it doesn't rely on chemical reactions.
This makes it exceptionally versatile. It is one of the best methods for depositing materials with very high melting points or for creating complex alloys that are difficult to evaporate using other techniques.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The quality of the final film is highly sensitive to process control. A poor vacuum can lead to contamination, while incorrect power or pressure settings can result in poor adhesion or a non-uniform coating with undesirable grain size.
Furthermore, the quality of the sputter target itself is paramount. Impurities or non-uniform grain size in the target will be directly transferred to the thin film, compromising its integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" sputtering parameters are defined entirely by your objective. Adjusting the key variables allows you to tailor the process to your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is a high-quality, dense film: Prioritize achieving a high vacuum level and maintaining a stable plasma, often using lower power over a longer duration.
- If your primary focus is speed and efficiency: Increase the power (voltage and current) to accelerate ion bombardment and the rate of atom ejection from the target.
- If your primary focus is coating a delicate, heat-sensitive substrate: Use a modern magnetron system at lower power settings and ensure adequate distance between the target and the substrate to minimize heat transfer.
Ultimately, mastering sputter coating is about understanding how these controlled physical interactions produce a desired material outcome.
Summary Table:
| Key Component/Parameter | Role in the Sputtering Process |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Removes air/contaminants for a clean process and free atom travel. |
| Inert Gas (Argon) | Ionized to create the plasma of positively charged ions (Ar+). |
| Target (Cathode) | The source material; atoms are knocked off its surface by ion bombardment. |
| Substrate (Anode) | The sample receiving the thin film coating from the ejected atoms. |
| High Voltage | Creates the electric field that accelerates ions toward the target. |
| Magnetron | Magnets trap electrons, increasing plasma density and process efficiency. |
| Pressure & Power | Critical parameters controlling deposition rate, film quality, and heat. |
Ready to achieve superior thin film coatings for your laboratory?
Understanding the principle of sputter coating is the first step. Implementing it effectively requires the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable magnetron sputter coaters designed for precise control over deposition parameters.
Whether your goal is high-purity coatings for sensitive substrates or efficient deposition of complex alloys, our solutions are tailored to meet your specific research and production needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our sputter coaters can enhance your lab's capabilities and deliver the consistent, high-quality results you demand.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















