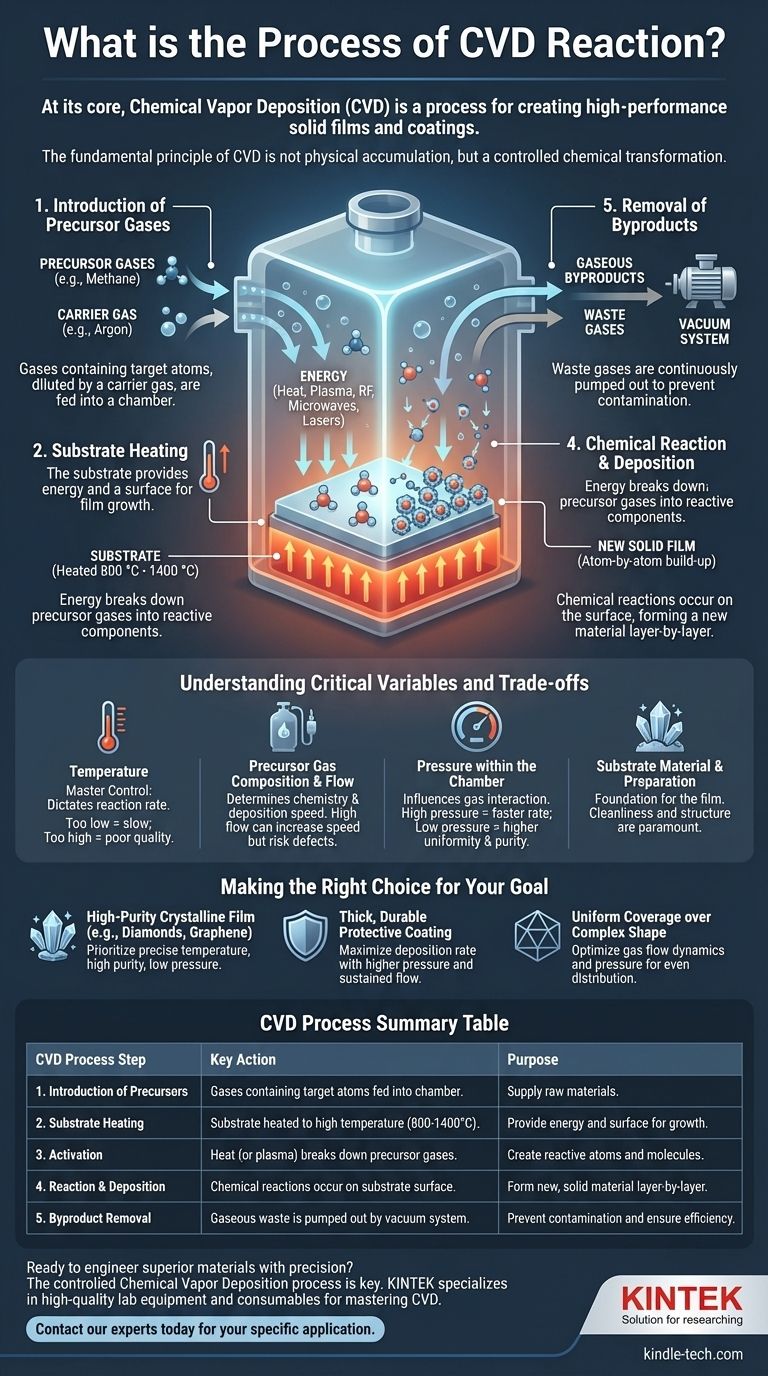
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process for creating high-performance solid films and coatings. It works by introducing reactive gases into a chamber where they interact with a heated surface, known as a substrate. This high-temperature environment triggers a chemical reaction, causing the gases to decompose and deposit a new solid material, layer by layer, directly onto the substrate's surface.
The fundamental principle of CVD is not physical accumulation, but a controlled chemical transformation. It uses energy to break down stable precursor gases into reactive components that then build a new, solid material atom-by-atom on a prepared surface.
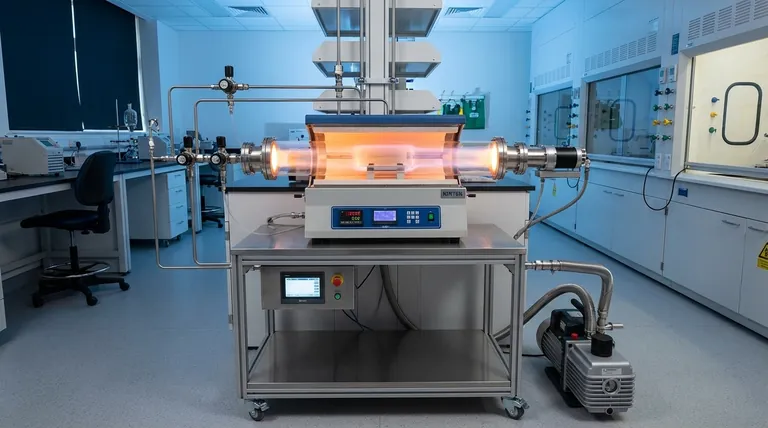

A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the CVD Process
To truly understand CVD, we must look at it as a sequence of carefully controlled events. Each step is critical for the formation of a high-quality, uniform film.
Introduction of Precursor Gases
The process begins by feeding one or more gases, known as precursors, into a reaction chamber. These gases contain the specific atoms required for the final film (e.g., methane for a carbon film).
Often, these precursors are mixed with a carrier gas, which is an inert gas like argon. This helps to dilute the reactants and control their flow and distribution within the chamber.
The Role of the Substrate
Inside the chamber is the substrate—the material to be coated. This isn't a passive component; it is actively heated to a precise, high temperature, often between 800 °C and 1400 °C.
The substrate serves two purposes. First, its high temperature provides the necessary energy to initiate the chemical reaction. Second, it provides the physical surface for the nucleation and growth of the new film.
Activation via Energy
Heat is the primary energy source in most CVD processes. When the precursor gases contact the hot substrate, they gain enough thermal energy for their chemical bonds to break.
In some advanced CVD methods, other energy sources like RF plasma, microwaves, or lasers are used to help ionize the gases. This breaks them down into more reactive radicals, allowing the process to occur at lower temperatures.
The Chemical Reaction and Deposition
Once the precursor gases are broken down into reactive atoms and molecules, they diffuse across the substrate's surface.
A series of chemical reactions occurs directly on this surface. These reactions reassemble the constituent atoms into a new, stable, solid material, forming a thin film that adheres strongly to the substrate. In many cases, the substrate surface itself acts as a catalyst, facilitating these reactions.
Removal of Byproducts
The chemical reactions that form the desired film also create unwanted gaseous byproducts.
These waste gases are continuously removed from the chamber by a vacuum system. This step is crucial to prevent them from contaminating the film and to allow the deposition reaction to proceed efficiently.
Understanding the Critical Variables and Trade-offs
The quality, thickness, and structure of a CVD-grown film are not accidental. They are the direct result of meticulously controlling several process variables. Understanding these trade-offs is key to mastering the technique.
Temperature as the Master Control
The substrate temperature is the most critical variable in the entire process. It directly dictates the rate of the chemical reactions.
Too low a temperature results in a slow or non-existent reaction. Too high a temperature can lead to poor film quality or unwanted gas-phase reactions away from the substrate.
Precursor Gas Composition and Flow
The type and concentration of precursor gases determine the chemistry of the final film. The flow rate at which these gases are introduced is also critical.
A high flow rate can increase the deposition speed, but if it's too fast, the reactants may not have enough time to react on the surface properly, leading to defects.
Pressure within the Chamber
The pressure inside the reaction chamber influences how the gas molecules travel and interact.
Higher pressures can increase deposition rates but may reduce the uniformity of the coating. Lower pressures often yield more uniform, higher-purity films but at a slower rate.
Substrate Material and Preparation
The substrate is the foundation of the film. Its own chemical makeup can influence the reaction, sometimes acting as a catalyst, as seen when growing graphene on copper.
Furthermore, the cleanliness and crystalline structure of the substrate surface are paramount, as any imperfection can be propagated into the growing film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling the CVD process is about balancing these variables to achieve a specific outcome. Your primary objective will dictate your approach.
- If your primary focus is creating a high-purity crystalline film (like diamonds or graphene): You must prioritize precise control over substrate temperature, precursor purity, and low chamber pressures.
- If your primary focus is applying a thick, durable protective coating: You will likely use higher pressures and sustained precursor flow rates to maximize the deposition rate.
- If your primary focus is achieving uniform coverage over a complex shape: Your main challenge is optimizing the gas flow dynamics and pressure to ensure reactants reach all surfaces evenly.
By understanding these core process steps and their controlling variables, you can effectively harness Chemical Vapor Deposition to engineer materials from the atom up.
Summary Table:
| CVD Process Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Introduction of Precursors | Gases containing target atoms are fed into a chamber. | To supply the raw materials for the film. |
| 2. Substrate Heating | The substrate is heated to a high temperature (800-1400°C). | To provide energy for the reaction and a surface for growth. |
| 3. Activation | Heat (or plasma) breaks down the precursor gases. | To create reactive atoms and molecules. |
| 4. Reaction & Deposition | Chemical reactions occur on the substrate surface. | To form a new, solid material layer-by-layer. |
| 5. Byproduct Removal | Gaseous waste is pumped out by a vacuum system. | To prevent contamination and ensure reaction efficiency. |
Ready to engineer superior materials with precision?
The controlled Chemical Vapor Deposition process is key to creating high-performance films for semiconductors, protective coatings, and advanced materials like graphene. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables—from reactors to precursor gases—that your laboratory needs to master CVD.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect CVD solution for your research and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method



















