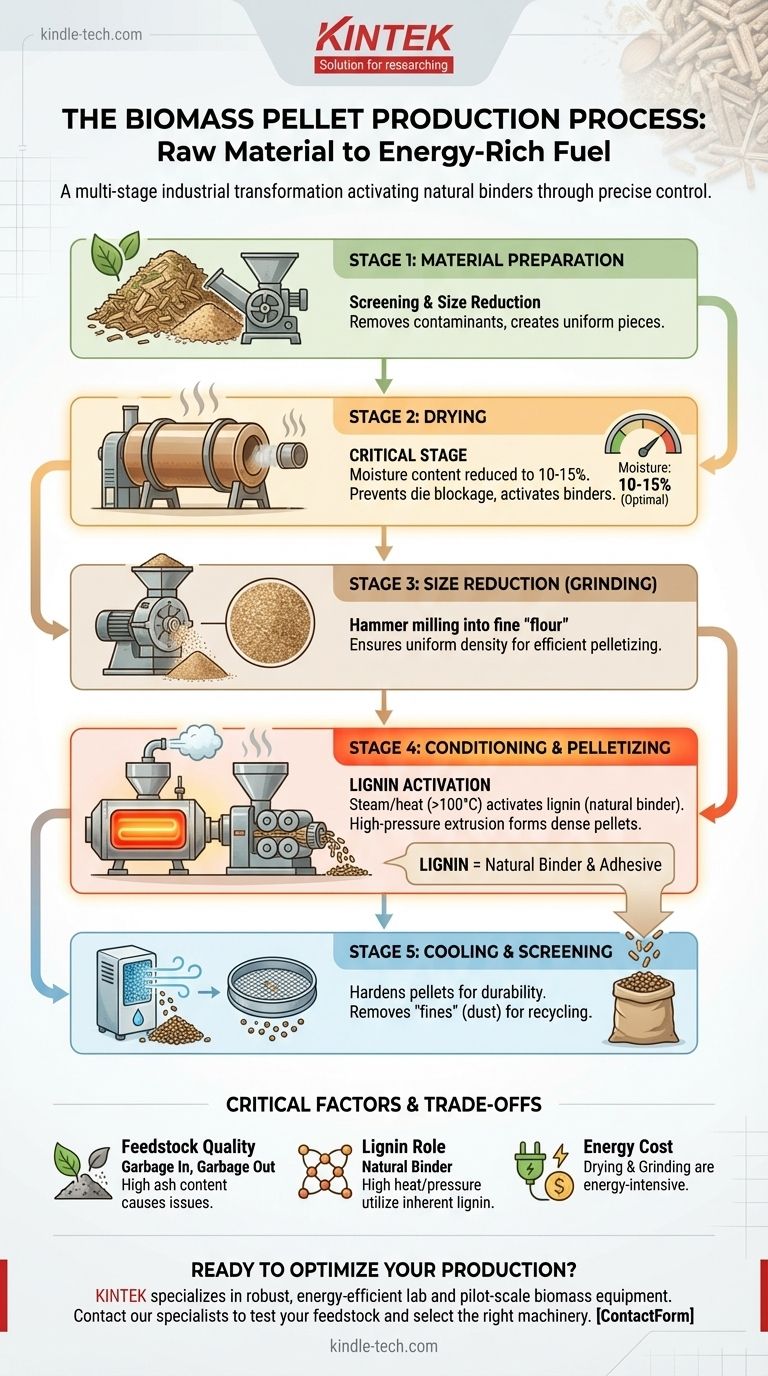
In essence, making biomass pellets is a multi-stage industrial process that transforms raw, low-density organic material into a uniform, dense, and energy-rich solid fuel. The core of this transformation involves finely grinding the feedstock, controlling its moisture content to a precise level, and then forcing it through a die under extreme pressure and heat. This process activates the natural binders within the biomass itself, creating a stable and compact pellet.
The key to understanding pellet production is realizing it's not just a mechanical process, but a chemical and physical transformation. Success hinges on meticulously controlling two variables: moisture content and particle size, which allows the natural lignin in the biomass to act as a binding agent.
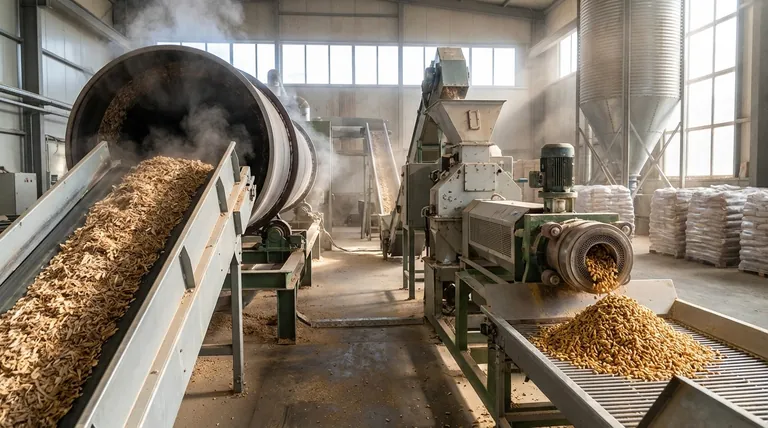

The Core Stages of Pellet Production
The journey from raw biomass—such as wood chips, sawdust, or agricultural residue—to a finished pellet follows a clear, sequential path. Each stage is designed to prepare the material for the next, ensuring a high-quality final product.
Stage 1: Material Preparation
Before any processing can begin, the raw feedstock must be prepared. This involves screening out contaminants like rocks, metal, and dirt that could damage the machinery.
For larger materials like logs or wood scraps, an initial size reduction is performed using a chipper or shredder. This creates more manageable, uniformly-sized pieces for the subsequent drying stage.
Stage 2: Drying
This is arguably the most critical and energy-intensive stage. Raw biomass often has a moisture content of 40-60%, which is far too high for pelletization. The material is fed into large industrial dryers, typically rotary drum dryers, to reduce moisture to a target range of 10-15%.
If the material is too wet, the water will turn to steam in the pellet die, blocking it and halting production. If it's too dry, there won't be enough moisture to help activate the binders, resulting in brittle pellets that crumble.
Stage 3: Size Reduction (Grinding)
Once dried, the biomass is not yet fine enough for pelleting. It is passed through a hammer mill, which pulverizes the material into a fine, consistent "flour" or powder.
This uniform, small particle size is essential. It ensures every part of the material is exposed to the same pressure and heat in the pellet mill, leading to a dense and homogenous pellet.
Stage 4: Conditioning and Pelletizing
The finely ground material enters a conditioner, where steam or hot water is injected. This adds a small amount of heat and moisture, making the biomass more pliable and beginning to activate the lignin—a natural polymer within the plant cell walls that acts as a glue.
From the conditioner, the hot, moist material is fed into the pellet mill. Here, rollers force the material through the holes of a thick steel die. The immense pressure and friction generate intense heat (often over 100°C), which fully plasticizes the lignin and binds the particles together into dense, compressed pellets.
Stage 5: Cooling and Screening
Pellets exit the die hot, soft, and still releasing steam. They are immediately transferred to a cooler, where ambient air is drawn over them. This process is vital for cooling and hardening the pellets, making them durable for transport and storage.
Finally, the cooled pellets are passed over a screen to sift out any fine particles or dust created during the process. These "fines" are typically recycled back into the production line to minimize waste. The finished, screened pellets are then ready for bagging or bulk storage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Simply having the right machinery is not enough. The quality of the final pellet and the efficiency of the operation depend on several interconnected factors.
The Critical Role of Feedstock
The principle of "garbage in, garbage out" applies directly to pellet production. The type and quality of the raw biomass significantly impact the final product and the process itself.
High ash content in the feedstock (from dirt or bark) will result in high-ash pellets, which can create maintenance issues (clinkers) in the boilers or stoves where they are burned.
Lignin is the Natural Binder
The entire process is designed to leverage the natural lignin present in wood and most plant matter. High pressure and heat cause the lignin to soften and act as a natural adhesive, binding the biomass particles together as the pellet cools.
While some low-lignin feedstocks (like certain agricultural straws) may require adding external binders, high-quality wood pellets rely solely on this intrinsic property.
Energy Consumption is a Major Cost
Drying and grinding are extremely energy-intensive processes. The cost of running the dryers, chippers, and hammer mills constitutes a significant portion of the total production cost.
This creates a major operational incentive to source feedstock that is as dry and clean as possible to reduce the energy load on the drying and preparation equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the process allows you to prioritize based on your specific objectives, whether you are a producer, investor, or large-scale consumer.
- If your primary focus is producing premium-grade pellets: Concentrate on sourcing clean, low-ash feedstock and invest in precise moisture control systems.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational costs: Secure a supply of low-moisture raw material to dramatically reduce the energy consumed during the drying phase.
- If your primary focus is achieving high throughput: Ensure your grinding and drying equipment is robust and correctly sized, as these stages are common production bottlenecks.
Ultimately, biomass pellet production is a refined process of turning inconsistent raw material into a consistent, valuable, and standardized energy product.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Material Preparation | Screening & Size Reduction | Remove contaminants and create uniform pieces for drying. |
| 2. Drying | Reduce moisture to 10-15% | Critical for activating natural binders and preventing die blockage. |
| 3. Grinding | Hammer milling into fine powder | Ensures uniform density and efficient pellet formation. |
| 4. Pelletizing | High-pressure extrusion through a die | Heat and pressure activate lignin to bind particles into solid pellets. |
| 5. Cooling & Screening | Hardening and dust removal | Produces durable, stable pellets ready for storage and transport. |
Ready to Optimize Your Biomass Pellet Production?
Whether your goal is to produce premium-grade pellets, minimize operational costs, or achieve high throughput, the right equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in robust, energy-efficient lab and pilot-scale equipment for biomass processing—from precise dryers and hammer mills to reliable pellet mills.
Let our experts help you test your feedstock, optimize your process, and select the right machinery to create a consistent, high-value energy product.
Contact our biomass specialists today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can power your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of a single punch tablet press machine? A Guide to Precision Lab-Scale Production
- What is tablet pressing in pharmaceutical industry? The Core Process for Producing Solid Oral Dosage Forms
- What is the use of tablet press? Transforming Powder into Precise, Uniform Tablets
- What is the function of rotary tablet press? High-Speed, High-Volume Tablet Production
- How does a flat die pellet mill work? A Complete Guide to Small-Scale Pellet Production
- What are the steps of tablet production by direct compression? Streamline Your Manufacturing Process
- What is the difference between a rotary tablet press and a single tablet punch press? A Guide to Choosing the Right Machine
- What is the process of pelleting biomass? Transform Raw Biomass into High-Value, Energy-Dense Fuel



















