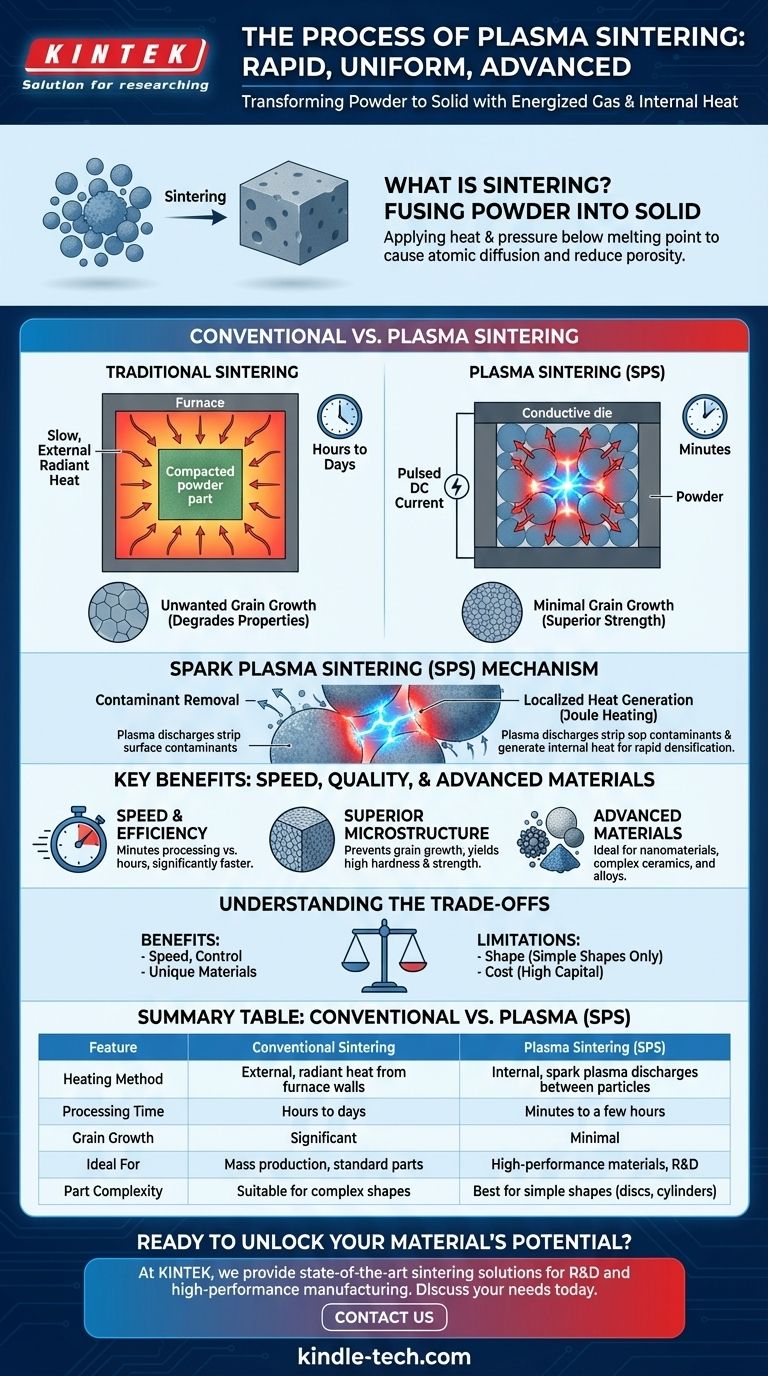
At its core, plasma sintering is an advanced manufacturing technique that uses an energized, ionized gas—known as plasma—to rapidly heat and fuse powdered materials into a solid, dense object. Unlike traditional sintering which relies on slow, external heating in a furnace, plasma sintering generates intense heat directly within the powder itself. This allows for significantly faster processing times and superior control over the final material's microstructure, with the most common method being Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS).
The fundamental difference between conventional and plasma sintering is not the goal, but the method of heating. While traditional sintering slowly heats a material from the outside-in, plasma sintering uses electrical energy to create plasma discharges between powder particles, heating them almost instantly from the inside-out.

The Foundation: Understanding Sintering's Goal
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a process that transforms a collection of loose powder into a solid, coherent mass. This is achieved by applying heat and pressure at a temperature below the material's melting point.
The heat encourages atoms to move, or diffuse, across the boundaries of individual powder particles. This atomic movement effectively fuses the particles together, reducing the empty space (porosity) between them and creating a dense, solid part.
The Conventional Sintering Process
In a traditional furnace, a compacted powder part (often called a "green part") is placed inside and slowly heated. The heat radiates from the furnace walls, gradually penetrating the part.
This process is often slow, taking many hours or even days. The prolonged exposure to high temperatures is necessary to ensure the entire part reaches the required temperature for atoms to diffuse and for the part to become fully dense.
Key Limitations of the Traditional Method
The primary drawback of conventional sintering is its speed. The long heating cycles are not only time-consuming but can also lead to a critical problem: unwanted grain growth.
As the material is held at high temperatures, the small crystalline grains within it tend to merge and grow larger. This can degrade the material's mechanical properties, such as its strength and hardness.
How Plasma Changes the Game: The Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) Mechanism
Introducing Plasma: The Fourth State of Matter
Plasma is often called the fourth state of matter. It is a gas that has been energized to the point where its atoms become ionized, creating a highly conductive and reactive environment. Think of it as a controlled, microscopic version of lightning.
The Role of Plasma in Sintering
In the most common method, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), the powder is placed in a conductive die, typically made of graphite. A high-amperage, pulsed direct current (DC) is then passed through the die and the powder itself.
This creates momentary spark plasma discharges in the microscopic gaps between the powder particles. These plasma sparks have two critical effects: they strip away contaminants from the particle surfaces and generate intense, localized heat precisely at the particle-to-particle contacts.
The Result: Rapid and Uniform Densification
Because the heat is generated internally and exactly where it is needed, the powder consolidates with incredible speed, often in a matter of minutes. This direct, efficient heating is known as Joule heating.
The overall temperature of the furnace and the bulk of the material can remain lower than in conventional sintering, and the time at peak temperature is drastically reduced. This prevents the undesirable grain growth, preserving the fine microstructure of the starting powder.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Key Advantage: Speed and Microstructure Control
The single greatest benefit of plasma sintering is the combination of speed and quality. Processing times are reduced from hours to minutes, and the ability to avoid grain growth allows for the creation of materials with exceptionally fine grains, leading to superior hardness and strength.
Key Advantage: Processing Advanced Materials
SPS is particularly effective for consolidating materials that are difficult to sinter conventionally. This includes nanomaterials, whose unique properties are lost if grain growth occurs, and advanced ceramics or composites.
The Primary Limitation: Shape and Scale
The main constraint of SPS is geometric complexity. The process relies on passing a current through a simple die, so it is best suited for producing simple shapes like discs, cylinders, and blocks. Creating large or intricate parts is significantly more challenging than with other methods like 3D printing or metal injection molding.
The Cost Factor
SPS systems are more complex and carry a higher capital cost than traditional sintering furnaces. This makes the technology better suited for high-value applications in research and advanced manufacturing rather than the mass production of simple components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a sintering method, your final objective is the most important factor.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of standard parts: Conventional sintering remains a robust and scalable choice.
- If your primary focus is creating high-performance materials with superior strength: Plasma sintering (SPS) is the ideal technology for achieving high density while preserving a fine-grained microstructure.
- If your primary focus is rapid research and development of new alloys or composites: The speed of plasma sintering makes it an unparalleled tool for quickly iterating and testing new material formulations.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference in the heating mechanism is the key to selecting the right technology to achieve your material performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Conventional Sintering | Plasma Sintering (SPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | External, radiant heat from furnace walls | Internal, spark plasma discharges between particles |
| Processing Time | Hours to days | Minutes to a few hours |
| Grain Growth | Significant due to prolonged high temperatures | Minimal due to rapid processing |
| Ideal For | Cost-effective mass production of standard parts | High-performance materials, nanomaterials, R&D |
| Part Complexity | Suitable for complex shapes | Best for simple shapes (discs, cylinders) |
Ready to unlock the potential of plasma sintering for your advanced materials?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing state-of-the-art lab equipment, including advanced sintering solutions, to meet the demanding needs of research and high-performance manufacturing. Whether you are developing new alloys, working with nanomaterials, or seeking superior material properties, our expertise can help you achieve rapid, precise densification.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your R&D and enhance your material performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts



















