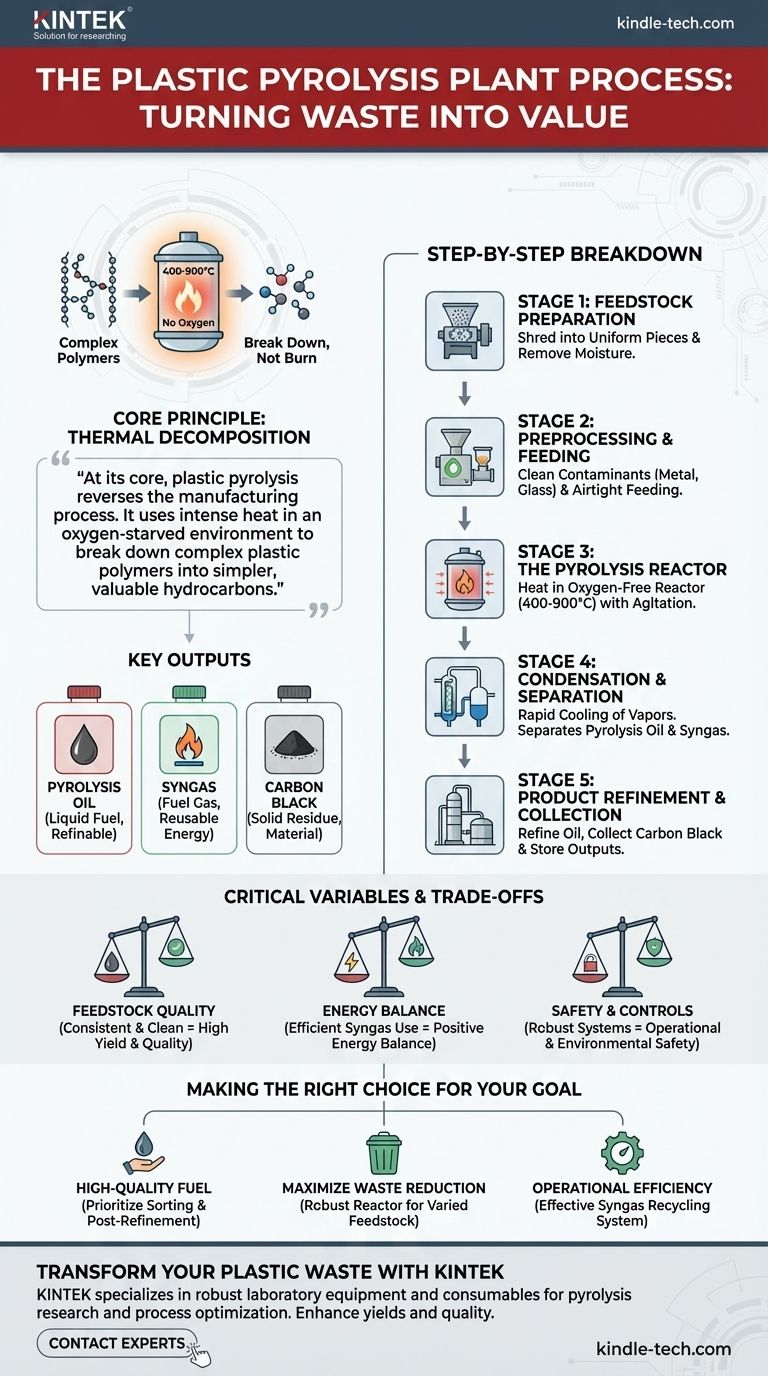
The plastic pyrolysis process is a multi-stage thermal conversion technique designed to chemically decompose waste plastic into valuable outputs. It begins with rigorous preparation of the raw plastic, followed by heating it to high temperatures in a sealed, oxygen-free reactor, and concludes with the separation and refinement of the resulting products: pyrolysis oil, syngas, and carbon black.
At its core, plastic pyrolysis reverses the manufacturing process. It uses intense heat in an oxygen-starved environment to break down complex plastic polymers into simpler, valuable hydrocarbons, rather than burning them.

The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition
The success of a pyrolysis plant hinges on a single chemical principle: breaking down materials with heat in the absence of oxygen.
How Pyrolysis Works
Pyrolysis is fundamentally thermal cracking. Inside the reactor, plastic is heated to temperatures between 400-900°C.
This intense heat, combined with the lack of oxygen, prevents the plastic from combusting. Instead, the long polymer chains that make up the plastic vibrate and break apart into smaller, lighter molecules.
These smaller molecules vaporize into a hot gas, which is then collected for processing.
The Three Key Outputs
The process is designed to separate the decomposed plastic into three distinct and usable streams.
- Pyrolysis Oil: The primary output. This is a liquid hydrocarbon mixture, similar to crude oil, created when the hot vapor is cooled and condensed. It can be used as an industrial fuel or further refined.
- Syngas (Synthesis Gas): A non-condensable gas rich in hydrogen and methane. It is typically captured and reused to power the pyrolysis reactor itself, reducing the plant's external energy consumption.
- Carbon Black (Char): A solid, carbon-rich residue left behind in the reactor. This material can be used as a soil amendment, a solid fuel, or as a raw material for products like activated carbon.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Plant Process
A commercial pyrolysis plant is a carefully orchestrated system with several distinct stages.
Stage 1: Feedstock Preparation
The process begins long before the plastic enters the reactor. Waste plastic must be shredded into small, uniform pieces.
This increases the surface area, allowing for more efficient and even heat transfer during pyrolysis. The material is also dried to remove any moisture, which can hinder the process and reduce oil quality.
Stage 2: Preprocessing and Feeding
Before entering the reactor, the shredded plastic is cleaned to separate non-plastic contaminants like metal, glass, or dirt.
This step is critical for protecting the equipment and ensuring the purity of the final products. The clean, dry feedstock is then fed into the reactor through an airtight system to prevent oxygen from entering.
Stage 3: The Pyrolysis Reactor
This is the heart of the plant. Inside the sealed, oxygen-free reactor, the prepared plastic is heated to the target temperature.
The material is continuously agitated to ensure uniform heating, causing it to break down and vaporize into the hydrocarbon gas mixture.
Stage 4: Condensation and Separation
The hot gas mixture exits the reactor and enters a cooling system. Here, the temperature is lowered rapidly.
The condensable components of the gas turn into liquid pyrolysis oil, which is collected. The remaining non-condensable syngas is piped away to be used as fuel for the plant's burners.
Stage 5: Product Refinement and Collection
The raw pyrolysis oil may undergo distillation and purification to remove impurities and improve its grade, making it suitable for a wider range of applications.
Simultaneously, the solid carbon black is safely removed from the reactor, cooled, and stored for dispatch.
Understanding the Critical Variables and Trade-offs
The theoretical process is straightforward, but real-world performance depends heavily on managing key variables.
The Challenge of Feedstock Quality
The single biggest variable is the quality of the incoming plastic waste. Mixed plastic types, high moisture content, and contamination levels directly impact the yield and quality of the pyrolysis oil.
A consistent, clean feedstock will produce a consistent, high-quality oil. Poorly sorted waste results in lower yields and requires more intensive purification.
Energy Balance and Efficiency
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process. A plant's profitability often depends on its ability to create a positive energy balance.
Highly efficient plants are designed to capture and burn nearly all the produced syngas to heat the reactor, significantly reducing their reliance on external fuel sources.
Safety and Environmental Controls
Operating at high temperatures and pressures with flammable materials requires robust safety and control systems.
Proper management of emissions and safe handling of the oil and gas outputs are essential for both operational safety and environmental compliance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The design and operational focus of a pyrolysis plant should align with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality fuel: Prioritize advanced feedstock sorting systems and invest in post-pyrolysis oil distillation and purification technologies.
- If your primary focus is maximizing waste reduction: Design for a robust reactor that can handle a more varied (but still pre-processed) plastic stream, accepting a potential trade-off in oil quality.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Emphasize a plant design with a highly effective syngas recycling system to minimize external energy costs.
Ultimately, mastering the interplay between feedstock quality and process control is the key to deploying a successful plastic pyrolysis system.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Primary Output |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Shredding & Drying Plastic | Clean, Uniform Feedstock |
| 2. Pyrolysis | Heating in Oxygen-Free Reactor (400-900°C) | Hydrocarbon Vapors |
| 3. Condensation | Cooling Hot Vapors | Pyrolysis Oil & Syngas |
| 4. Collection | Separating & Refining Products | Oil, Syngas (fuel), Carbon Black |
Ready to transform your plastic waste into valuable resources?
KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and process optimization. Whether you are developing a new pyrolysis method or scaling up your operations, our precise heating systems, reactors, and analysis tools can help you achieve higher yields and better product quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can support your plastic pyrolysis goals and enhance your laboratory's efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What roles do autoclaves play in MFI zeolite synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Crystalline Growth
- Why are sealed laboratory reaction vessels necessary in the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites? Ensure Purity and Yield
- What is the function of a constant temperature hydrothermal reactor? Master Coal Fly Ash Activation
- What is the purpose of using high-purity argon gas in a high-pressure reactor? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Data
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?













