A classic example of pyrolysis is the process of making charcoal. When wood is heated to high temperatures in a container with little to no oxygen, it doesn't burn into ash; instead, it thermally decomposes, breaking down into a solid carbon residue (charcoal), flammable gases, and a liquid known as bio-oil.
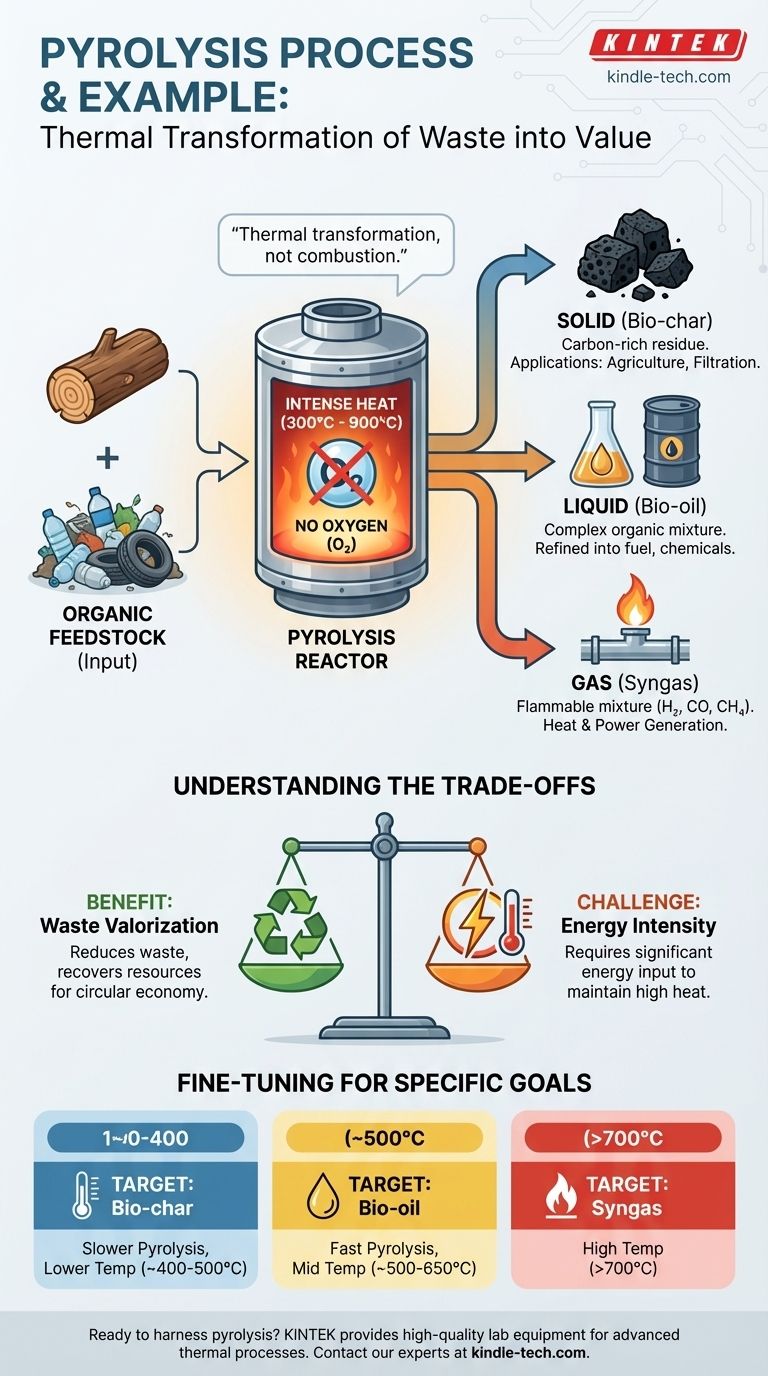
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a process of thermal transformation, not combustion. By applying intense heat in an oxygen-free environment, we break down complex organic materials into simpler, more valuable components: a solid, a liquid, and a gas.
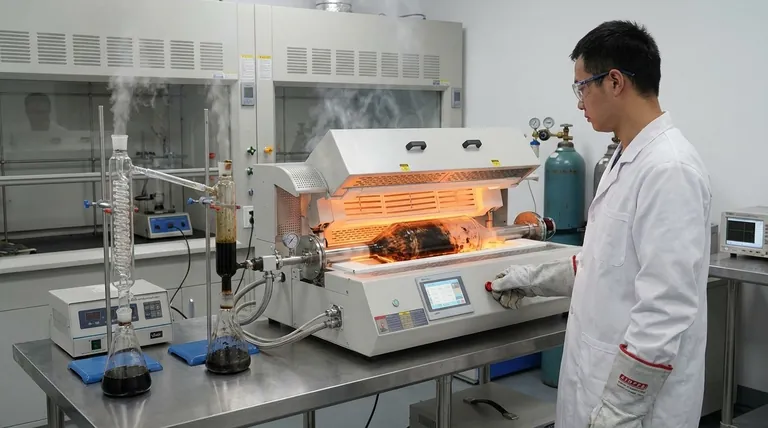

Deconstructing the Pyrolysis Process
To understand pyrolysis, you must grasp its core components: the environment it requires, the materials it acts upon, and the products it creates. It is a controlled decomposition driven by heat.
The Core Principle: Heat Without Combustion
The defining characteristic of pyrolysis is the absence of oxygen. When you burn wood in a fire, oxygen fuels a combustion reaction, releasing energy and leaving behind ash. In pyrolysis, the lack of oxygen prevents burning and instead forces the material's chemical bonds to break apart from the intense heat alone.
The Input: Organic Feedstock
Pyrolysis works on organic materials. This includes a wide range of inputs, from natural biomass like wood and agricultural waste to man-made materials.
Common feedstocks include biomass, plastics, and even used tires. The goal is often to convert low-value waste into higher-value products.
The Key Parameters: Temperature and Time
The process requires high temperatures, typically ranging from 300°C to 900°C (570°F to 1650°F). The specific temperature and the duration of the heating directly influence the final products. Lower temperatures and slower heating often yield more solid char, while higher temperatures and rapid heating can produce more gas and liquid.
The Outputs: Gas, Liquid, and Solid
Pyrolysis consistently separates a single input material into three distinct outputs.
- Solid (Bio-char): A carbon-rich solid residue. When the input is wood, this is charcoal. Bio-char has applications in agriculture and filtration.
- Liquid (Bio-oil): A complex mixture of liquid organic compounds. This can be refined into transportation fuels or used to produce chemicals.
- Gas (Syngas): A mixture of flammable gases, primarily hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This gas can be combusted to generate heat or electricity, often to power the pyrolysis process itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, pyrolysis is not a perfect solution. Understanding its benefits and drawbacks is key to evaluating its practical application.
The Benefit: Waste Valorization
The primary advantage of pyrolysis is its ability to turn problematic waste streams—such as non-recyclable plastics or agricultural residue—into valuable commodities. It is a powerful tool for waste reduction and resource recovery, contributing to a circular economy.
The Challenge: Energy Intensity
The process is highly energy-intensive. Reaching and maintaining temperatures of several hundred degrees Celsius requires a significant energy input. For the process to be economically and environmentally viable, this energy cost must be carefully managed, often by using the syngas produced as a fuel source.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The conditions of the pyrolysis process can be fine-tuned to favor one type of output over another. This allows operators to target the product that is most valuable for their specific goal.
- If your primary focus is producing solid bio-char for agriculture: Use a slower pyrolysis process at lower temperatures (around 400-500°C).
- If your primary focus is producing liquid bio-oil for fuel: Use a "fast pyrolysis" process with very rapid heating to higher temperatures (around 500-650°C).
- If your primary focus is maximizing syngas for energy generation: Use very high temperatures (above 700°C) to further break down the materials into gaseous components.
Ultimately, pyrolysis offers a controlled method for deconstructing organic matter to reclaim its chemical and energetic value.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen |
| Typical Temperature Range | 300°C to 900°C (570°F to 1650°F) |
| Common Feedstocks | Wood, agricultural waste, plastics, tires |
| Primary Outputs | Solid (Bio-char), Liquid (Bio-oil), Gas (Syngas) |
| Main Benefit | Converts low-value waste into valuable products |
| Main Challenge | High energy intensity |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your lab or facility? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced thermal processes. Whether you're researching bio-fuel production, waste valorization, or material science, our reliable pyrolysis systems provide the precise temperature control and performance you need to achieve your goals. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application and help you turn waste into valuable resources.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the factors that affect pyrolysis? Mastering Temperature, Feedstock, and Process Control
- What is the co-pyrolysis method? A Strategic Approach to Waste Valorization & Bio-Oil Upgrading
- What is a pyrolysis reactor? A Guide to Converting Waste into Valuable Resources
- How does pyrolysis work without oxygen? Transform Waste into Valuable Products
- What are the uses of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy, Fuel, and More
- How long does plastic pyrolysis take? From Minutes to Days, It Depends on Your System
- What acts as a continuous furnace? A Guide to High-Throughput Industrial Heating Systems
- How efficient is fast pyrolysis? Maximizing Biomass Conversion with High-Yield Bio-Oil Production



















