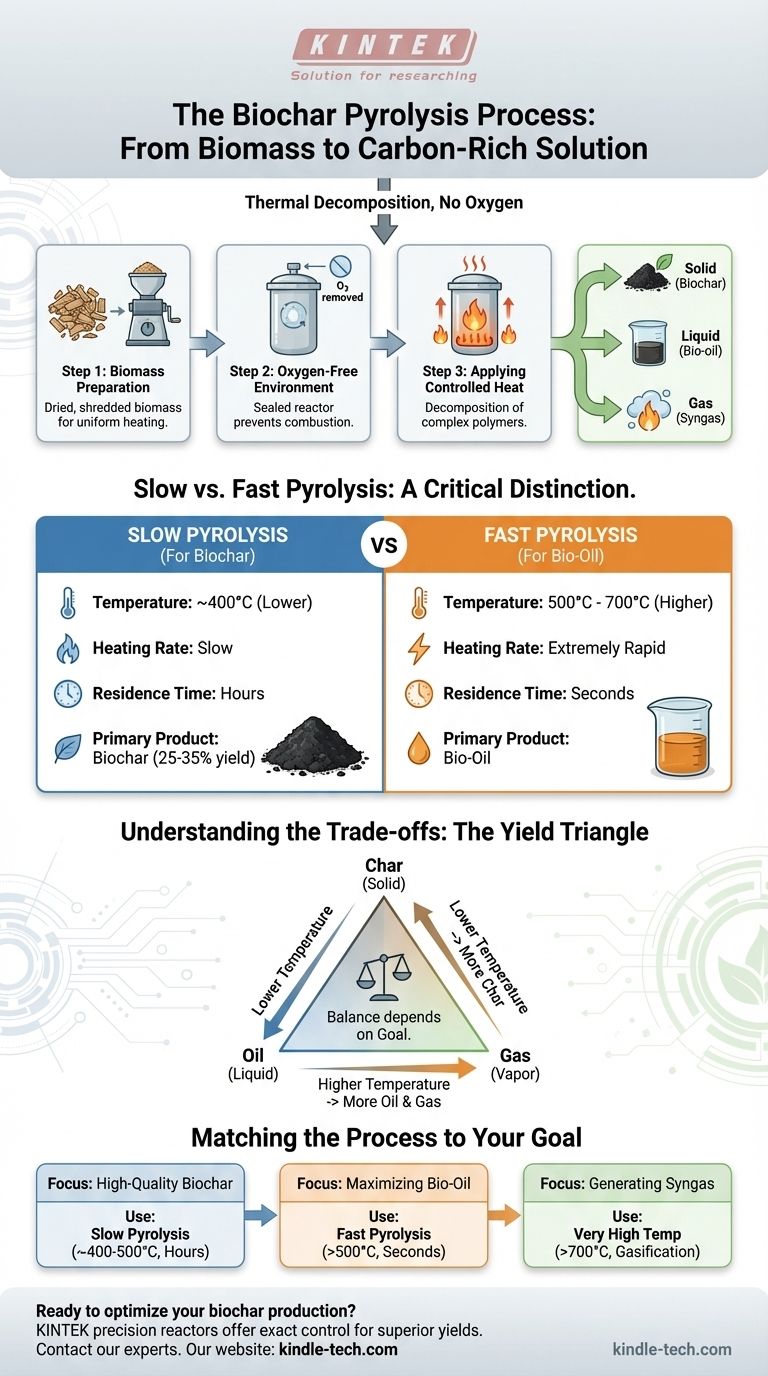
At its core, the production of biochar via pyrolysis involves heating organic material, known as biomass, in an environment completely free of oxygen. This thermal decomposition process is carefully controlled to favor the creation of a solid, carbon-rich material. Specifically, the method used is slow pyrolysis, which utilizes lower temperatures and longer heating periods to maximize the yield of biochar over other potential products like liquid bio-oil or gas.
The critical factor in producing biochar is not just heating biomass, but precisely controlling the process variables. Slow pyrolysis—using lower temperatures (around 400°C) and longer residence times (hours)—intentionally directs the chemical breakdown to favor the creation of solid char, rather than the liquids and gases prioritized by other methods.

The Core Mechanism: Deconstructing Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is thermal decomposition, meaning the chemical structure of the biomass is broken down by heat alone, not by burning. Understanding each stage is key to mastering the outcome.
Step 1: Biomass Preparation
The process begins with the feedstock. This can be any organic material, such as wood chips, crop residue, or manure. For an efficient process, the biomass is typically dried to reduce moisture content and shredded or ground (a process called comminution) to create a uniform particle size, ensuring it heats evenly.
Step 2: Creating the Oxygen-Free Environment
The prepared biomass is loaded into a reactor which is then sealed. All oxygen is removed or displaced, often with an inert gas. This step is non-negotiable; if oxygen were present, the biomass would simply combust and burn to ash, not transform into biochar.
Step 3: Applying Controlled Heat
Heat is introduced to the reactor, initiating the pyrolytic decomposition. The complex organic polymers in the biomass (like cellulose and lignin) become unstable and break down into smaller, volatile components and solid carbon.
Step 4: Separating the Products
This thermal breakdown creates three distinct outputs:
- Solid (Biochar): The stable, carbon-rich solid material left behind.
- Liquid (Bio-oil/Pyrolysis Oil): Condensed from the cooled vapors and gases.
- Gas (Syngas): Non-condensable gases that can be used for energy.
The goal of biochar production is to maximize the solid portion.
Slow vs. Fast Pyrolysis: A Critical Distinction
The specific conditions of the pyrolysis process determine which of the three products is maximized. The choice between slow and fast pyrolysis is the single most important decision influencing the final yield.
Slow Pyrolysis for Biochar Production
This is the preferred method for creating biochar.
- Temperature: Relatively low, around 400°C.
- Heating Rate: Slow and gradual.
- Residence Time: Long, often lasting for several hours.
These conditions allow for the complete carbonization of the biomass, maximizing the solid biochar yield to 25-35% of the initial feedstock mass.
Fast Pyrolysis for Bio-Oil Production
This method is optimized for producing liquid fuel, not biochar.
- Temperature: High, between 500°C and 700°C.
- Heating Rate: Extremely rapid.
- Residence Time: Very short, often just a few seconds.
These conditions rapidly vaporize the biomass before it can fully convert to char. The goal is to quickly cool and condense these vapors, maximizing the liquid bio-oil yield. Char is merely a byproduct.
Understanding the Trade-offs
You cannot maximize the output of char, oil, and gas simultaneously. Adjusting the process variables forces a choice, creating a trade-off between the three primary products.
The Yield Triangle: Char, Oil, and Gas
Think of the process as a balancing act. Pushing the conditions in one direction (e.g., higher temperature) increases the yield of one product at the direct expense of another. Your end goal dictates the process you must use.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary lever. Lower temperatures favor the formation of solid char. As temperatures increase, the biomass breaks down more aggressively, favoring the creation of volatile vapors that become liquid bio-oil and syngas.
The Impact of Residence Time
Residence time—how long the biomass is held at the target temperature—is the second key lever. Longer residence times (hours) give the chemical reactions enough time to form stable carbon structures, resulting in more biochar. Short residence times (seconds) get the volatile vapors out of the reactor before they can break down further into gas or form char.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
To select the correct approach, you must first define your primary objective. The process parameters are then engineered to meet that specific outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality biochar for soil amendment: You must use slow pyrolysis with lower temperatures (around 400-500°C) and a long residence time.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil as a potential fuel source: You must use fast pyrolysis with high temperatures (>500°C), a rapid heating rate, and a very short residence time.
- If your primary focus is generating syngas for immediate energy production: You should use very high temperatures (>700°C) or a related process like gasification, which intentionally limits oxygen to favor gas production.
By understanding these fundamental principles, you can effectively control the pyrolysis process to produce the exact output you require.
Summary Table:
| Process Variable | Slow Pyrolysis (For Biochar) | Fast Pyrolysis (For Bio-Oil) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | ~400°C | 500°C - 700°C |
| Heating Rate | Slow | Extremely Rapid |
| Residence Time | Hours | Seconds |
| Primary Product | Biochar (25-35% yield) | Bio-Oil |
Ready to produce high-quality biochar for your research or application?
KINTEK specializes in precision laboratory equipment for pyrolysis and thermal processing. Our reactors are engineered for the exact control over temperature and residence time required for optimal biochar yield from your specific biomass feedstock.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your biochar production process, improve your yields, and support your laboratory's sustainability goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time


















