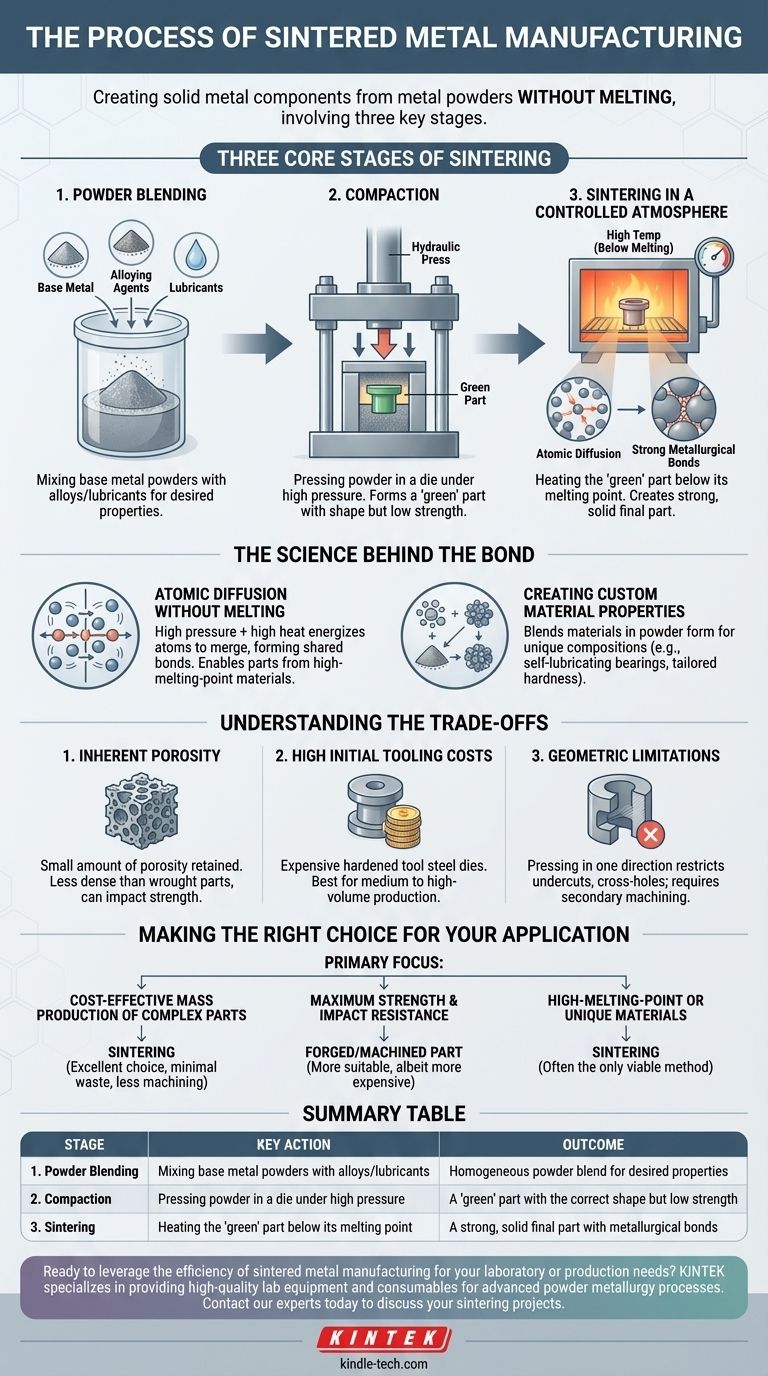
At its core, the sintered metal manufacturing process is a method of creating solid metal components from metal powders without melting the material. It primarily involves three distinct stages: blending the desired metal powders, compacting them under high pressure into a preliminary shape, and heating that shape in a furnace to bond the particles into a finished part.
Sintering is not just a manufacturing technique; it is a strategic approach to powder metallurgy. It excels at producing complex, net-shape parts in high volumes, offering a cost-effective alternative to traditional machining by minimizing material waste and post-processing.

The Three Core Stages of Sintering
The production of a sintered part is a precise, sequential operation. Each stage builds upon the last to transform loose powder into a durable, functional component.
Stage 1: Powder Blending
The process begins with the raw material: metal in powdered form. The specific composition is chosen to achieve the final part's required mechanical and physical properties.
This base powder, often iron, copper, nickel, or an alloy, is precisely blended with other elements. These can include alloying agents like molybdenum for strength or lubricants that will aid in the next stage.
Stage 2: Compaction into a 'Green' Part
The blended powder is loaded into a die cavity that matches the component's desired geometry. A press then applies immense pressure (typically measured in tons per square inch) to the powder.
This force compacts the particles, eliminating most of the air between them and locking them together mechanically. The resulting component, known as a 'green' part, has the shape of the final product and enough integrity to be handled, but it has not yet achieved its final strength.
Stage 3: Sintering in a Controlled Atmosphere
The 'green' part is moved to a sintering furnace. The furnace heats the part to a high temperature, critically, below the melting point of the primary metal.
This heat triggers atomic diffusion. The atoms on the surfaces of the individual powder particles migrate across the boundaries, fusing the particles together and forming strong metallurgical bonds. This process also burns off the lubricants added during blending and reduces surface oxides, creating a clean, solid, and significantly stronger final piece.
The Science Behind the Bond
Understanding why sintering works is key to appreciating its value. The process is fundamentally different from casting, which relies on melting and solidification.
Atomic Diffusion Without Melting
Think of sintering as forcing solid particles to merge. The combination of high pressure during compaction and high heat during sintering energizes the atoms, causing them to move and create new, shared bonds between particles.
This allows for the creation of parts from materials with exceptionally high melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum, which are impractical or impossible to shape using traditional melting methods.
Creating Custom Material Properties
Because the process starts with a blend of powders, sintering allows for the creation of unique material compositions. Metals and other elements that do not easily alloy in a molten state can be combined in powder form.
This enables the design of materials with specific characteristics, such as self-lubricating bearings (by impregnating the part's inherent porosity with oil) or materials with tailored hardness and wear resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Sintering
No manufacturing process is perfect for every application. Objectivity requires acknowledging the limitations of sintering.
Inherent Porosity and Density
Sintered parts almost always retain a small amount of porosity. As a result, they are typically less dense than parts made from wrought bar stock or forging. This can impact ultimate tensile strength and fatigue resistance.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The dies required for the compaction stage are made from hardened tool steel and can be expensive to produce. This initial investment means sintering is most cost-effective for medium to high-volume production runs where the cost of the tooling can be amortized over thousands of parts.
Geometric Limitations
While sintering is excellent for complex shapes, there are constraints. The process relies on pressing powder in a single direction. Features like undercuts, cross-holes, or threads that are not parallel to the direction of pressing cannot be formed directly and must be added in secondary machining operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting sintering depends entirely on your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of complex parts: Sintering is an excellent choice, as it produces net-shape components with minimal material waste and reduces or eliminates the need for secondary machining.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and impact resistance: A forged or fully machined part from wrought metal may be a more suitable, albeit more expensive, alternative for critical, high-stress applications.
- If your primary focus is creating parts from high-melting-point or unique materials: Sintering is often the only commercially viable method for processing metals like tungsten or for creating custom composite materials.
Ultimately, understanding the sintering process empowers you to leverage its unique capabilities for efficient and innovative component manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Powder Blending | Mixing base metal powders with alloys/lubricants | Homogeneous powder blend for desired properties |
| 2. Compaction | Pressing powder in a die under high pressure | A 'green' part with the correct shape but low strength |
| 3. Sintering | Heating the 'green' part below its melting point | A strong, solid final part with metallurgical bonds |
Ready to leverage the efficiency of sintered metal manufacturing for your laboratory or production needs?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for advanced powder metallurgy processes. Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up production, our expertise and reliable products can help you achieve precise results and reduce waste.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your sintering projects and enhance your manufacturing capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- How does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace facilitate TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Achieve 100% Dense Titanium Composites
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance
- What critical processing conditions are provided by a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Achieve 98%+ Density.
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics



















