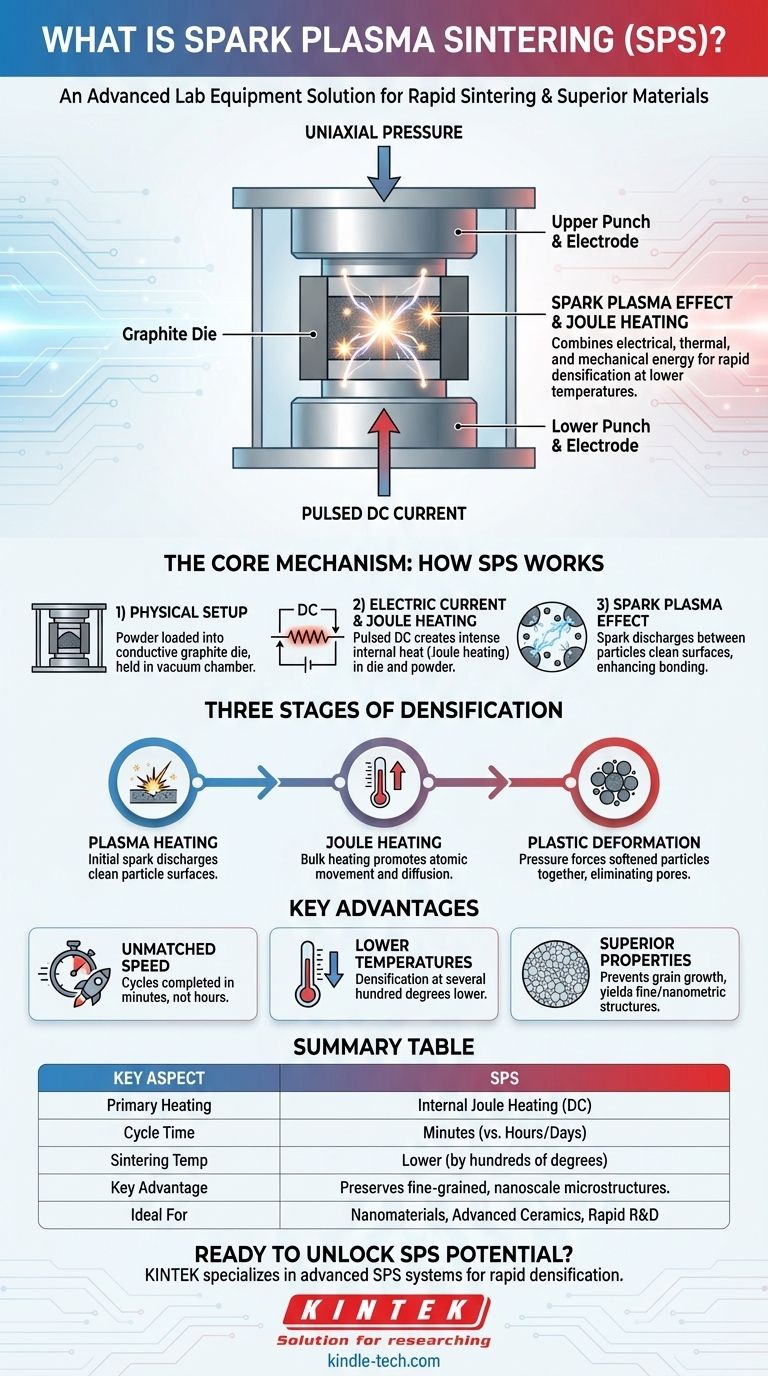
At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is an advanced sintering technique that uses pulsed direct electric current and uniaxial pressure to consolidate powders into a dense solid. Unlike conventional furnaces that heat externally, SPS passes current directly through a graphite mold and the powder itself, enabling incredibly rapid heating and significantly shorter processing times, often completing in minutes what traditional methods take hours to achieve.
The fundamental advantage of Spark Plasma Sintering is its ability to combine electrical, thermal, and mechanical energy simultaneously. This synergy allows for densification at lower temperatures and speeds, which is critical for producing advanced materials with fine-grained microstructures and superior properties.

The Core Mechanism: How SPS Works
To understand the power of SPS, we must first look at its unique setup and energy delivery method, which sets it apart from conventional hot pressing.
The Physical Setup
The process begins by loading a powder into a conductive die, which is almost always made of graphite. This die is then placed in the SPS machine between two opposing punches, which also function as electrodes. The entire assembly is held within a vacuum chamber to prevent oxidation.
The Role of Electric Current
Once under a controlled atmosphere and uniaxial pressure, a high-power, pulsed direct current (DC) is applied. This current travels through the punches and the graphite die. If the powder material is conductive, the current will also pass directly through the powder compact.
Rapid Joule Heating
The primary heating mechanism is Joule heating. As the electric current passes through the resistive graphite die and the powder, it generates intense and uniform heat. This method of direct, internal heating allows for extremely rapid temperature ramps, sometimes as high as 1,000°C per minute.
The "Spark Plasma" Effect
The name "Spark Plasma Sintering" comes from the theory that the pulsed current creates localized spark discharges in the gaps between individual powder particles. These sparks are thought to generate a temporary plasma, which cleans the particle surfaces by vaporizing impurities and surface oxides. This cleaning action dramatically enhances the bonding between particles once they are pressed together.
The Three Stages of Densification
The SPS process achieves full density through a rapid sequence of events, which can be broken down into three overlapping stages.
Stage 1: Plasma Heating
In the initial moments, the spark discharges between particles create localized hot spots. This initial burst of energy cleans the surfaces and prepares them for solid-state diffusion and bonding.
Stage 2: Joule Heating
As the current continues to flow, bulk Joule heating becomes the dominant effect. The entire powder compact rapidly rises in temperature, promoting atomic movement and diffusion across the newly cleaned particle boundaries.
Stage 3: Plastic Deformation
With the material at an elevated temperature and under constant mechanical pressure, plastic deformation occurs. The softened particles are forced together, eliminating the remaining pores and resulting in a highly dense final component.
Understanding the Key Advantages
The unique mechanism of SPS provides several significant advantages over traditional sintering techniques like hot pressing.
Unmatched Speed
The most dramatic advantage is speed. By delivering energy directly to the material, SPS cycles are completed in a matter of minutes, whereas conventional furnace sintering can take many hours or even days.
Lower Sintering Temperatures
Because the particle surfaces are so effectively activated by the spark discharges, densification can occur at temperatures several hundred degrees lower than required by conventional methods.
Superior Material Properties
The combination of lower temperatures and extremely short processing times effectively prevents unwanted grain growth. This allows for the production of materials with exceptionally fine, often nanometric, microstructures, which typically translates to enhanced mechanical strength and hardness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
SPS is not a universal replacement for all sintering methods, but it is an unparalleled tool for specific, high-performance applications.
- If your primary focus is rapid material discovery: SPS is the ideal choice, as its short cycle times allow for fast iteration and testing of new compositions and alloys.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanostructures: SPS is superior to almost any other method, as its low thermal budget (a combination of lower temperature and shorter time) prevents the coarsening of nanoscale features.
- If your primary focus is consolidating difficult-to-sinter materials: The intense, localized energy delivery of SPS makes it highly effective for densifying advanced ceramics, composites, and refractory metals that resist conventional techniques.
Ultimately, Spark Plasma Sintering is a powerful manufacturing process that enables the creation of advanced materials that were previously difficult or impossible to produce.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) |
|---|---|
| Primary Heating | Internal Joule Heating (Direct Current) |
| Cycle Time | Minutes (vs. Hours/Days for Conventional Methods) |
| Sintering Temperature | Lower (by hundreds of degrees) |
| Key Advantage | Preserves fine-grained, nanoscale microstructures |
| Ideal For | Nanomaterials, advanced ceramics, composites, rapid R&D |
Ready to unlock the potential of Spark Plasma Sintering in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including SPS systems, to help you achieve rapid densification and superior material properties. Whether you're developing new nanomaterials, high-performance ceramics, or complex composites, our expertise and solutions are tailored to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact us today to discuss how SPS can accelerate your research and development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What are the primary functions of high-strength graphite molds in VHP? Essential Roles in Composite Densification
- How does the programmed temperature control of a hot pressing sintering furnace impact nanocopper? Master the Microstructure
- Why must vacuum hot pressing equipment have high-tonnage pressure control for WC/Cu-Zr-Ti amorphous composites?
- How do vacuum hot press sintering and SPS differ for metal matrix composites? Optimize Your Composite Microstructure
- What roles do graphite molds perform during the vacuum hot pressing of metal matrix composites? Key Functions Explained
- Why does a vacuum hot pressing furnace achieve higher thermal conductivity than SPS for diamond-aluminum composites?
- What is the role of SPS equipment in Ti-Nb-Zr-O alloy fabrication? Achieve Rapid Densification & Precise Microstructure
- What is the role of a vacuum hot press furnace in TiC-steel composites? Achieve 99% Density with Precision



















