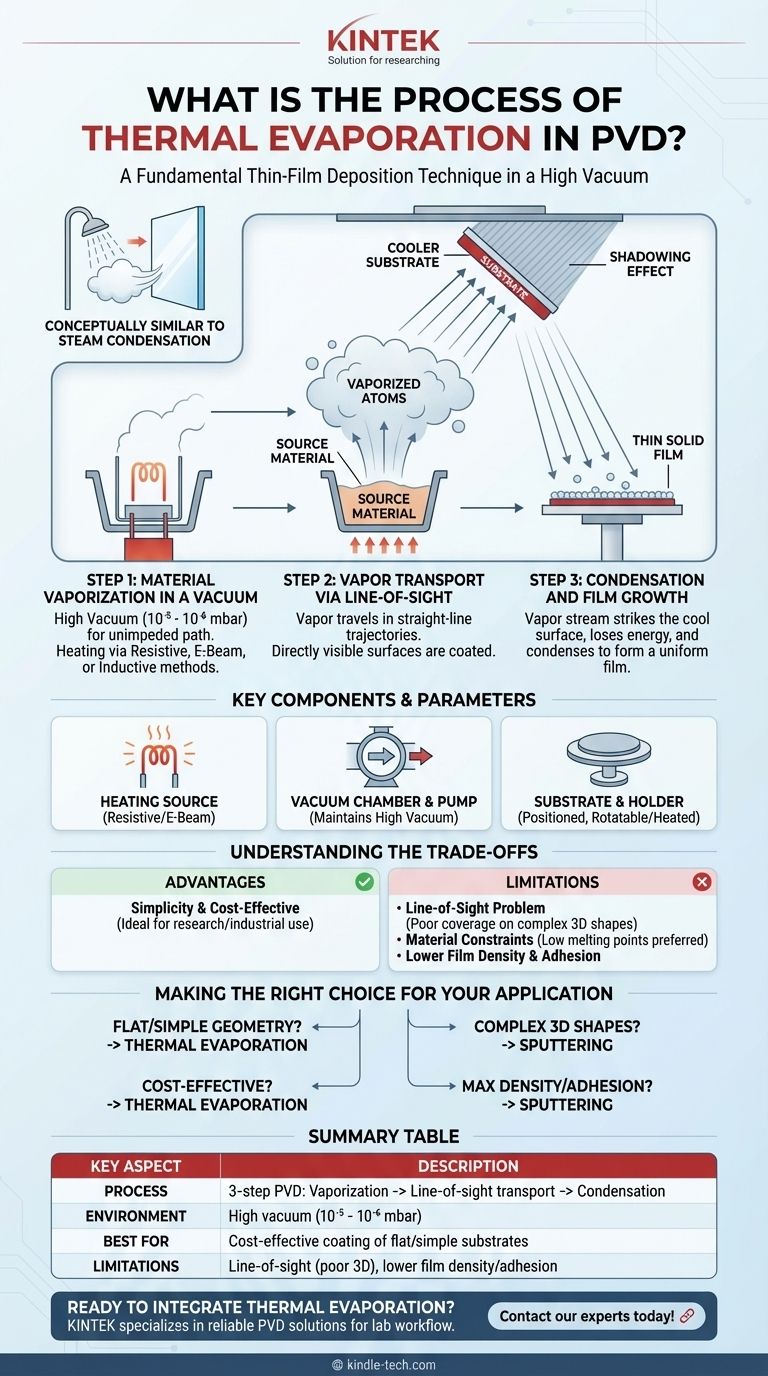
At its core, thermal evaporation is a Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) technique where a source material is heated in a high vacuum until it vaporizes. This vapor then travels through the vacuum chamber and condenses onto a cooler substrate, building up layer-by-layer to form a thin, solid film. The process is conceptually similar to how steam from a hot shower condenses on a cold mirror.
Thermal evaporation is a fundamentally simple, line-of-sight deposition process. Its effectiveness hinges on using a high-vacuum environment to allow vaporized atoms to travel unimpeded from the source to the substrate, ensuring film purity and adhesion.
The Core Mechanism: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To truly understand thermal evaporation, it's best to view it as a sequence of three distinct physical events occurring within a controlled environment.
Step 1: Material Vaporization in a Vacuum
The process begins by placing the source material, often in a ceramic or metallic crucible, inside a vacuum chamber. The chamber is evacuated to a high vacuum, typically between 10⁻⁵ and 10⁻⁶ mbar.
This vacuum is critical. It minimizes the number of background gas molecules, which ensures the vaporized atoms have a long mean free path—an unobstructed path to their destination.
The source material is then heated until it either boils or sublimates, transforming directly from a solid into a gas. This creates a cloud of vapor pressure above the source.
Step 2: Vapor Transport via Line-of-Sight
Once vaporized, the atoms or molecules travel away from the source in all directions. Because of the high vacuum, they move in essentially straight-line trajectories with very few collisions.
This behavior is known as "line-of-sight" deposition. Anything that has a direct, unobstructed view of the evaporation source will be coated, while surfaces that are hidden or "in shadow" will not.
Step 3: Condensation and Film Growth
When the vapor stream of atoms strikes the comparatively cool substrate, they rapidly lose their thermal energy. This causes them to condense back into a solid state.
Over time, these condensed atoms accumulate on the substrate surface, forming a thin, solid film. The quality, uniformity, and adhesion of this film can be influenced by factors like the substrate's temperature and the rate of deposition.
Key System Components and Parameters
The process is managed using a few essential pieces of hardware, each playing a critical role.
The Heating Source
The method of heating is what defines the "thermal" aspect. Common techniques include:
- Resistive Heating: Passing a high electrical current through a crucible or filament (often made of tungsten) that holds the source material.
- Electron Beam (E-Beam): Firing a focused beam of high-energy electrons at the source material to heat a localized spot to very high temperatures.
- Inductive Heating: Using electromagnetic fields to induce currents within the material itself, causing it to heat up.
The Vacuum Chamber and Pump
The entire process occurs within a sealed chamber. A powerful vacuum pumping system is essential to remove air and other gases, creating the necessary high-vacuum environment. This prevents oxidation of the hot source material and ensures a clean path for vapor transport.
The Substrate and Holder
The substrate is the object to be coated. It is mounted on a holder, often positioned directly above the evaporation source. This holder can sometimes be rotated to improve coating uniformity or heated to enhance the adhesion and structure of the depositing film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, thermal evaporation is not universally optimal. Its strengths and weaknesses must be understood.
Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
Compared to other PVD methods like sputtering, thermal evaporation systems are often simpler in design and more cost-effective to operate. This makes it an accessible technique for many research and industrial applications.
Limitation: The "Line-of-Sight" Problem
The straight-line trajectory of the vapor is a significant drawback for coating complex, three-dimensional objects. Surfaces not in the direct line of sight of the source will receive little to no coating, creating a "shadowing" effect and poor uniformity.
Limitation: Material Constraints
The process is best suited for materials with relatively low boiling or sublimation points. Materials with very high melting points (like tungsten or tantalum) are extremely difficult to vaporize with simple resistive heating and may require more complex E-beam sources. Alloying and depositing composite materials can also be challenging.
Limitation: Lower Film Density and Adhesion
The vaporized atoms in thermal evaporation arrive at the substrate with relatively low kinetic energy. This can result in films that are less dense and have lower adhesion compared to films deposited via sputtering, where atoms are ejected with much higher energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use thermal evaporation should be based on your specific goal and the constraints of your project.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective coating of flat or simple geometries: Thermal evaporation is an excellent and highly efficient choice.
- If you need to coat complex, 3D shapes with uniform coverage: You should consider a more conformal method like sputtering, which does not have the same line-of-sight limitation.
- If your film requires maximum density, hardness, or adhesion: Sputtering is often a superior choice due to the higher energy of the depositing particles.
- If you are working with high-melting-point metals or complex alloys: An E-beam evaporator or a sputtering system will likely be necessary.
Ultimately, choosing the right deposition technique requires matching the process capabilities to your desired film properties and application geometry.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | A 3-step PVD technique: 1. Vaporization, 2. Line-of-sight transport, 3. Condensation. |
| Environment | High vacuum (10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ mbar) to ensure purity and adhesion. |
| Best For | Cost-effective coating of flat or simple geometry substrates. |
| Limitations | Line-of-sight deposition (poor 3D coverage); lower film density/adhesion vs. sputtering. |
Ready to integrate thermal evaporation into your lab workflow? KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for all your PVD needs. Whether you're coating simple substrates or exploring advanced thin-film applications, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for maximum efficiency and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab



















