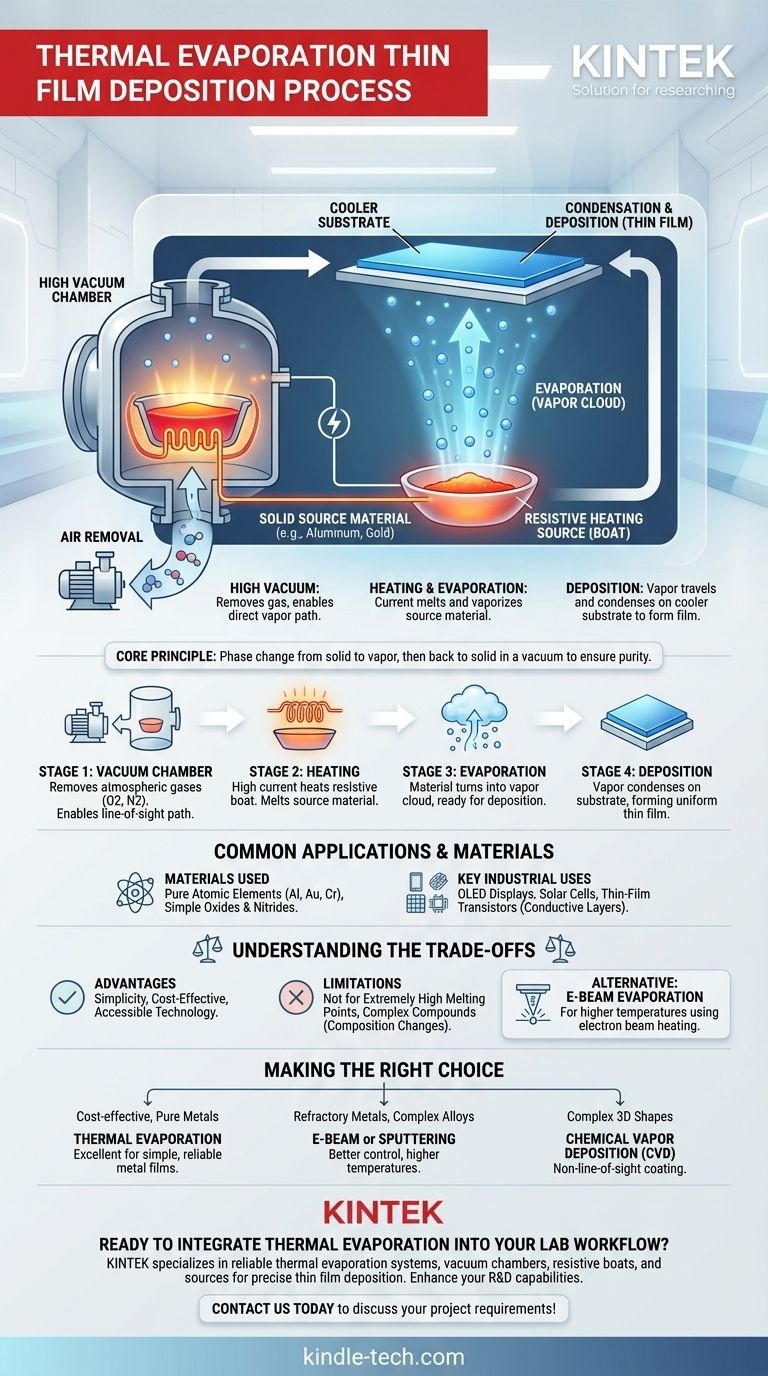
At its core, thermal evaporation is a straightforward process used to create ultra-thin films. It is a form of physical vapor deposition (PVD) where a source material is heated in a high vacuum chamber until it evaporates. This vapor then travels and condenses onto a cooler surface, known as a substrate, forming a solid, uniform thin film.
The fundamental principle of thermal evaporation is a phase change: a solid material is converted into a vapor using thermal energy and then back into a solid as it deposits onto a substrate. This entire process must occur in a vacuum to ensure the purity and quality of the resulting film.

The Core Principles of the Process
To truly understand thermal evaporation, it's essential to break down the key stages and the environment in which they occur. Each step is critical for the successful creation of a high-quality thin film.
The Role of the High Vacuum
The entire process takes place within a sealed vacuum chamber. The high vacuum (low pressure) is crucial for two reasons.
First, it removes atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen, which could otherwise react with the hot vapor and contaminate the final film.
Second, it allows the vaporized atoms to travel directly from the source to the substrate in a "line-of-sight" path without colliding with other gas molecules. This ensures an efficient and predictable deposition process.
The Heating Source and Source Material
The material to be deposited, often in the form of pellets or powder, is placed into a container. This container is also the heating element.
This element is commonly referred to as a "boat," "basket," or "coil" and is made from a material with a very high melting point, such as tungsten.
The Evaporation Phase
A high electrical current is passed through the boat. Due to its electrical resistance, the boat heats up rapidly, reaching temperatures high enough to melt and then evaporate the source material.
This is why the technique is often called resistive evaporation—it relies on electrical resistance to generate the required thermal energy.
The Deposition Phase
Once evaporated, the material exists as a vapor or cloud of atoms within the chamber. These atoms travel outward from the source.
When they reach the cooler substrate, which is strategically placed above the source, they lose their energy and condense, transitioning from a gas back to a solid. Layer by layer, these atoms build up to form the desired thin film.
Common Applications and Materials
Thermal evaporation is a versatile and widely used technique, particularly for its simplicity and effectiveness with certain materials.
Materials Used
This method is highly effective for depositing pure atomic elements, such as metals like aluminum, gold, and chromium, as well as some non-metals. It can also be used for certain molecules like simple oxides and nitrides.
Key Industrial Uses
The process is a workhorse in the electronics industry for creating electrically conductive layers. You will find films made by thermal evaporation in OLED displays, solar cells, and thin-film transistors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single deposition technique is perfect for every application. Understanding the advantages and limitations of thermal evaporation is key to using it effectively.
Advantages: Simplicity and Cost
The equipment for thermal evaporation is relatively simple and less expensive compared to more complex PVD methods like sputtering. This makes it a highly accessible technique for both research and industrial production.
Limitations: Material Constraints
The primary limitation is the heating method. It is not suitable for materials with extremely high evaporation temperatures that would exceed the melting point of the resistive boat itself.
Furthermore, complex compounds or alloys can be difficult to deposit, as their constituent elements may evaporate at different rates, changing the composition of the final film.
A Common Alternative: E-Beam Evaporation
For materials with higher melting points, a related technique called electron-beam (e-beam) evaporation is often used. Instead of a resistive boat, it uses a high-energy beam of electrons to heat and vaporize the source material, allowing for much higher temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method depends entirely on your material, budget, and the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective deposition of pure metals: Thermal evaporation is an excellent and highly reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing refractory metals or complex alloys: You should investigate e-beam evaporation or sputtering to achieve better control and higher temperatures.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex 3D shape uniformly: You may need to explore a non-line-of-sight technique like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Ultimately, thermal evaporation remains a foundational technique in materials science, valued for its simplicity in transforming a solid source into a precise, functional thin film.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Vacuum Chamber | Air is removed to create a high vacuum. | Prevents contamination; enables direct "line-of-sight" vapor travel. |
| 2. Heating | A resistive boat (e.g., tungsten) is heated with a high electrical current. | Melts and evaporates the source material (e.g., aluminum, gold). |
| 3. Evaporation | Source material turns into a vapor cloud. | Creates a stream of atoms ready for deposition. |
| 4. Deposition | Vapor travels and condenses on a cooler substrate. | Forms a solid, uniform thin film layer by layer. |
Ready to Integrate Thermal Evaporation into Your Lab Workflow?
Thermal evaporation is a cornerstone technique for depositing high-purity metal films for applications in electronics, optics, and research. Choosing the right equipment is critical for achieving consistent, high-quality results.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide reliable thermal evaporation systems and components—including vacuum chambers, resistive boats, and sources—to help you achieve precise thin film deposition.
Let us help you enhance your R&D or production capabilities. Our experts can guide you to the ideal solution for your specific materials and budget.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover the right thermal evaporation solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition



















