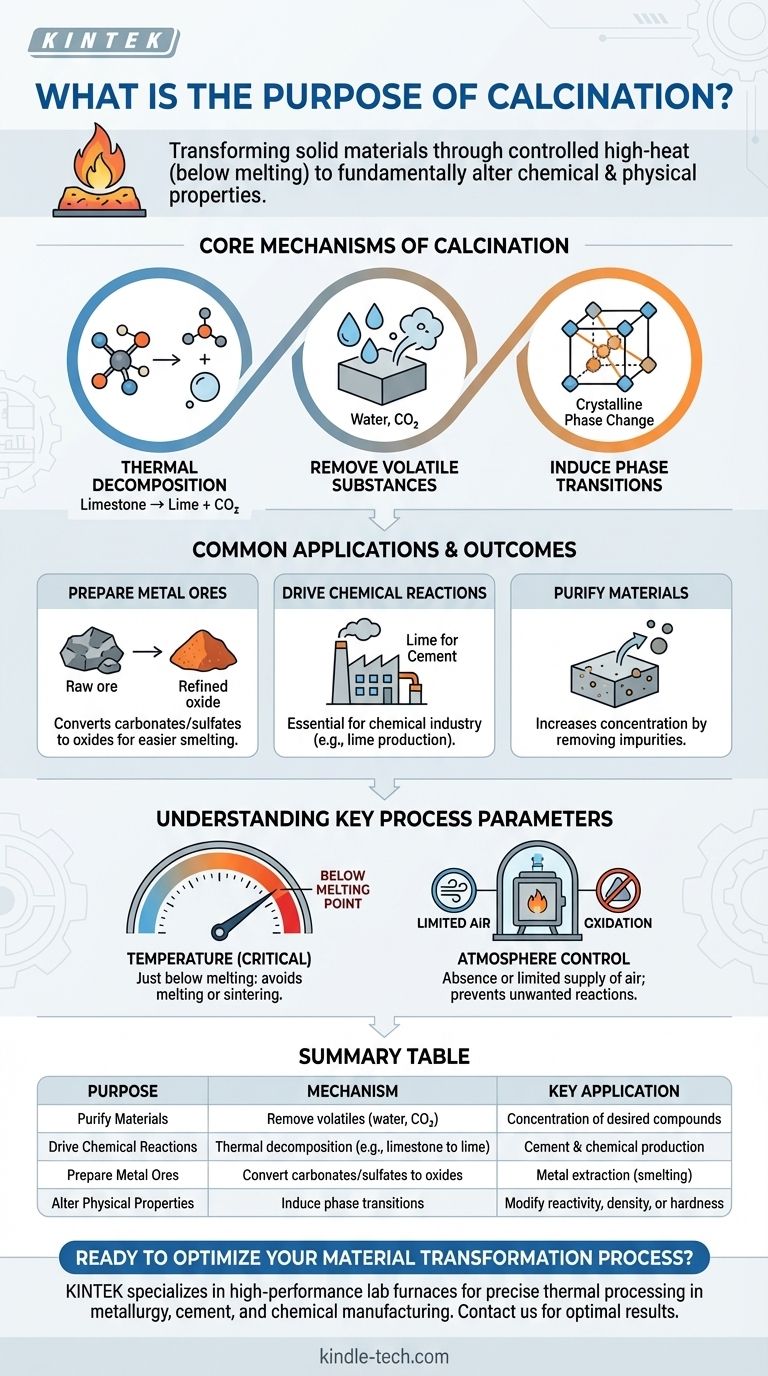
In essence, the purpose of calcination is to fundamentally alter a solid material's chemical and physical properties by heating it to a high temperature without melting it. This controlled heating is designed to drive out volatile substances like water and carbon dioxide, or to induce thermal decomposition, effectively purifying the material or preparing it for a subsequent process.
Calcination is not simply about heating; it is a transformative process used to purify and prepare materials. It changes a substance from a raw, complex form into a simpler, more reactive, or more concentrated state required for applications like metal extraction and cement production.

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
Calcination achieves its purpose through several key thermal processes. The specific goal dictates which of these mechanisms is most important for a given application.
Thermal Decomposition
This is the primary mechanism for many applications. Heat is applied to break down chemical compounds into simpler substances.
A classic example is the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃), which decomposes into lime (calcium oxide, CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas. This is a foundational step in making cement.
Removal of Volatile Substances
Calcination is highly effective at driving off unwanted volatile components that are physically absorbed or chemically bound within a solid.
This includes removing absorbed moisture, chemically bound water from hydrates (water of crystallization), and volatile gases like carbon dioxide or sulfur dioxide from mineral ores.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Beyond chemical changes, calcination can also alter a material's physical structure.
The process can be used to change the crystalline structure (phase) of a material, which can modify its properties like density, reactivity, or hardness, without changing its fundamental chemical composition.
Common Applications and Outcomes
The mechanisms of calcination are applied across various industries to achieve specific material transformations.
Preparing Metal Ores
In metallurgy, calcination is a critical preparatory step. It is used to convert metal ores, especially carbonates and sulfates, into their oxide forms.
These metal oxides are significantly easier to process in the next stage, which is typically smelting, where the oxide is reduced to produce pure metal.
Driving Chemical Reactions
The process is central to the chemical industry. The production of lime from limestone is a massive industrial application that creates a key ingredient for cement and other chemical processes.
Purifying Materials
By driving off water and other impurities, calcination effectively increases the concentration of the desired substance in the final product.
This purification step makes the material more suitable for its intended industrial use.
Understanding the Key Process Parameters
The effectiveness of calcination depends on precise control over two critical factors. Failing to manage these parameters can lead to an incomplete reaction or damage to the material.
The Critical Role of Temperature
The defining rule of calcination is to heat the material to a high temperature that is just below its melting point.
If the temperature is too low, the desired decomposition or phase change will not occur. If it is too high, the material will melt or sinter (fuse together), which is typically undesirable and changes the process entirely.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Calcination is formally defined as occurring in the absence or a limited supply of air (or oxygen).
This is a crucial distinction from a similar process called "roasting," which is done in the presence of excess air to promote oxidation. Controlling the atmosphere ensures that only the desired thermal decomposition occurs without unwanted side reactions.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Calcination is chosen when the goal is to prepare or purify a solid material through controlled thermal treatment.
- If your primary focus is metal extraction: Use calcination to convert carbonate or hydrate ores into their simpler oxide forms, which are easier to reduce to pure metal.
- If your primary focus is material purification: Apply calcination to drive off water, CO₂, and other volatile impurities, thereby increasing the purity and concentration of your desired compound.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing a specific chemical: Use calcination as a decomposition step, such as creating highly reactive calcium oxide (lime) from limestone for cement production.
Ultimately, calcination is a foundational thermal process for transforming raw materials into more valuable and usable forms.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Mechanism | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Purify Materials | Remove volatile substances (water, CO₂) | Concentration of desired compounds |
| Drive Chemical Reactions | Thermal decomposition (e.g., limestone to lime) | Cement and chemical production |
| Prepare Metal Ores | Convert carbonates/sulfates to oxides | Metal extraction (smelting) |
| Alter Physical Properties | Induce phase transitions | Modify reactivity, density, or hardness |
Ready to optimize your material transformation process? Calcination is a critical step for achieving purity and reactivity in your materials. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and equipment designed for precise thermal processing. Whether you're in metallurgy, cement production, or chemical manufacturing, our solutions ensure controlled heating and optimal results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific calcination needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the 3 types of heat transfer? Master Conduction, Convection & Radiation for Your Lab
- What is the function of an electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Uniform High-Temp Processing
- What is the function of muffle furnace in food industry? Ensure Accurate Ash Determination for Quality Control
- What is the effect of calcination temperature on the properties of nanoparticles? Master the Trade-Off for Optimal Performance
- Can a muffle furnace be used for calcination? Achieve Pure, Controlled Thermal Decomposition



















