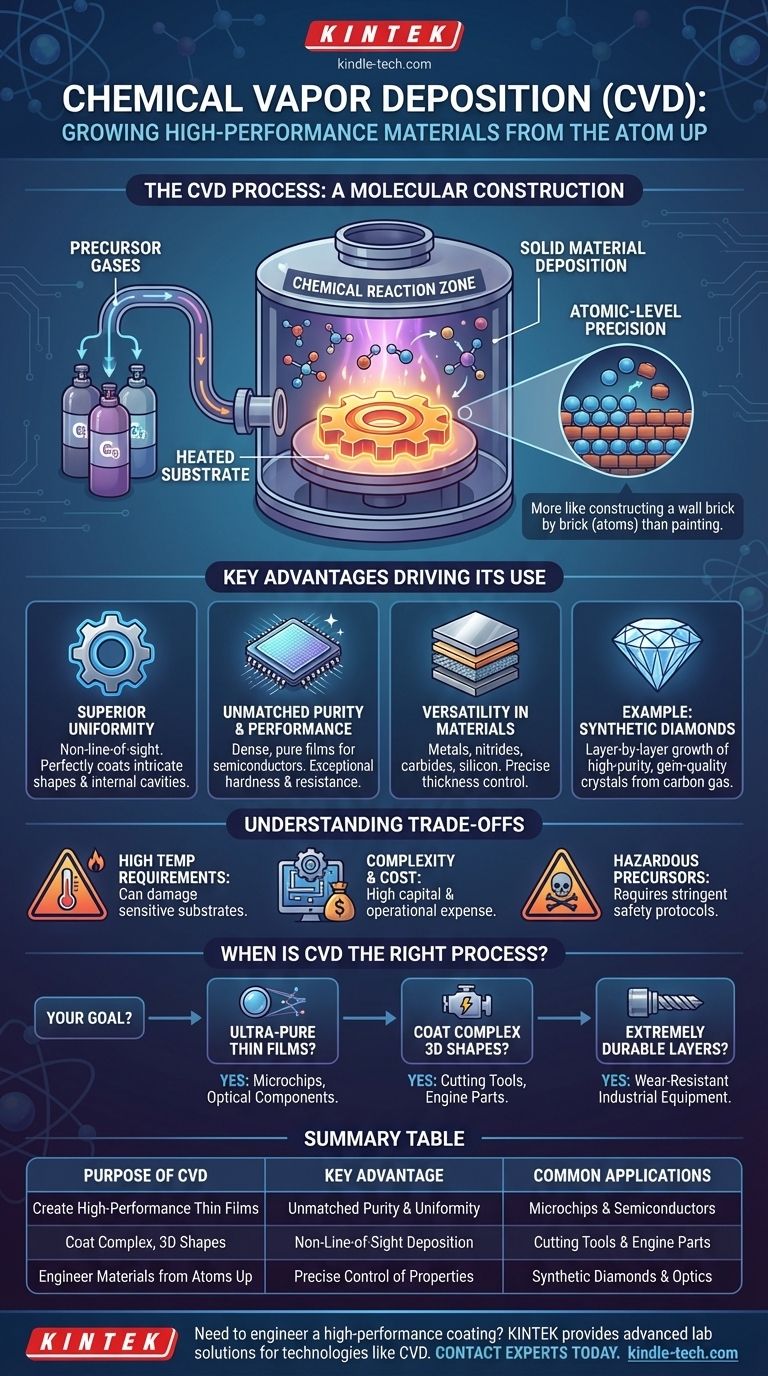
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a sophisticated manufacturing process used to create high-performance solid materials, typically in the form of thin films or coatings. It works by using a chemical reaction from a gas or vapor to deposit a layer of solid material onto a surface, known as a substrate. This technique is fundamental to producing everything from microchips to synthetic diamonds.
The true purpose of CVD is not just to apply a coating, but to grow a new solid material directly onto a surface with atomic-level precision. This unique capability allows it to create exceptionally pure, uniform, and durable films on even the most intricate shapes, something impossible with conventional coating methods.

How Chemical Vapor Deposition Works
Understanding the purpose of CVD requires a look at its fundamental mechanics. It is less like painting and more like constructing a wall brick by brick, where the "bricks" are individual atoms.
The Core Principle: From Gas to Solid
The process begins by introducing one or more volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber. These gases contain the chemical elements that will form the final solid material.
The Role of the Substrate and Heat
Inside the chamber is a substrate, which is the object to be coated. The substrate is heated to a precise, high temperature. This applied heat provides the necessary energy to trigger a chemical reaction in the gases, causing them to decompose and deposit a solid material onto the substrate's surface.
A Tightly Controlled Environment
This entire reaction takes place in a vacuum chamber with a sophisticated gas delivery system. Every variable—temperature, pressure, and gas flow—is meticulously controlled to dictate the final properties of the deposited film, such as its thickness, purity, and crystal structure.
The Key Advantages Driving Its Use
CVD is chosen over other methods when the performance and precision of the final coating are paramount. Its advantages solve challenges that other techniques cannot.
Superior Uniformity on Complex Shapes
CVD is a non-line-of-sight process. Because the precursor gas fills the entire chamber, it deposits material evenly on all exposed surfaces, including internal cavities, sharp edges, and highly intricate geometries. This ensures a homogenous coating that is impossible with line-of-sight methods like spraying or sputtering.
Unmatched Purity and Performance
By starting with highly purified gases, the CVD process can produce films of exceptional purity. This is critical in the semiconductor industry, where even minute impurities can ruin a microchip. The resulting films are dense and well-adhered, leading to superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and electronic properties.
Versatility in Materials and Thickness
The technique is incredibly versatile and can be used to deposit a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics (like nitrides and carbides), and semiconductors like silicon. The thickness of the coating is controlled by the deposition time and is, in theory, unrestricted.
Common Application: Synthetic Diamonds
One of the most well-known applications of CVD is the creation of lab-grown diamonds. By introducing a carbon-rich gas (like methane) into a chamber, the process can slowly deposit carbon atoms layer by layer to grow a high-purity, gem-quality diamond.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its power, CVD is not always the right solution. Its precision comes with significant technical requirements and limitations.
High Temperature Requirements
The high temperatures needed to drive the chemical reaction can damage or alter the properties of a temperature-sensitive substrate. This limits the types of materials that can be successfully coated.
Process Complexity and Cost
CVD systems are complex and expensive. They require vacuum chambers, precise gas handling systems, and high-temperature power supplies, all of which contribute to high initial capital investment and operational costs.
Use of Hazardous Precursors
Many of the precursor gases used in CVD are toxic, flammable, or corrosive. This necessitates stringent safety protocols and specialized handling systems, adding another layer of complexity and cost to the process.
When is CVD the Right Process?
Choosing this technique depends entirely on your end goal. It is a solution for high-value applications where performance justifies the investment.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-pure, high-performance thin films: CVD is the industry standard, offering unparalleled control over material purity and structure for demanding applications like microchips and optical components.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-flat surfaces: CVD is the ideal choice, as its non-line-of-sight nature ensures a perfectly uniform film on intricate geometries that other methods cannot reach.
- If your primary focus is producing extremely durable, wear-resistant layers: CVD excels at depositing hard ceramic materials to dramatically extend the life and performance of cutting tools, engine parts, and industrial equipment.
Ultimately, CVD provides a level of molecular control that allows us to engineer materials from the atom up, transforming a simple gas into a high-performance solid.
Summary Table:
| Purpose of CVD | Key Advantage | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Create High-Performance Thin Films | Unmatched Purity & Uniformity | Microchips & Semiconductors |
| Coat Complex, 3D Shapes | Non-Line-of-Sight Deposition | Cutting Tools & Engine Parts |
| Engineer Materials from Atoms Up | Precise Control of Properties | Synthetic Diamonds & Optics |
Need to engineer a high-performance coating for your lab equipment or components?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for precision coating applications. Our expertise can help you leverage technologies like CVD to achieve superior material performance, durability, and purity for your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your project with the right equipment and solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production



















