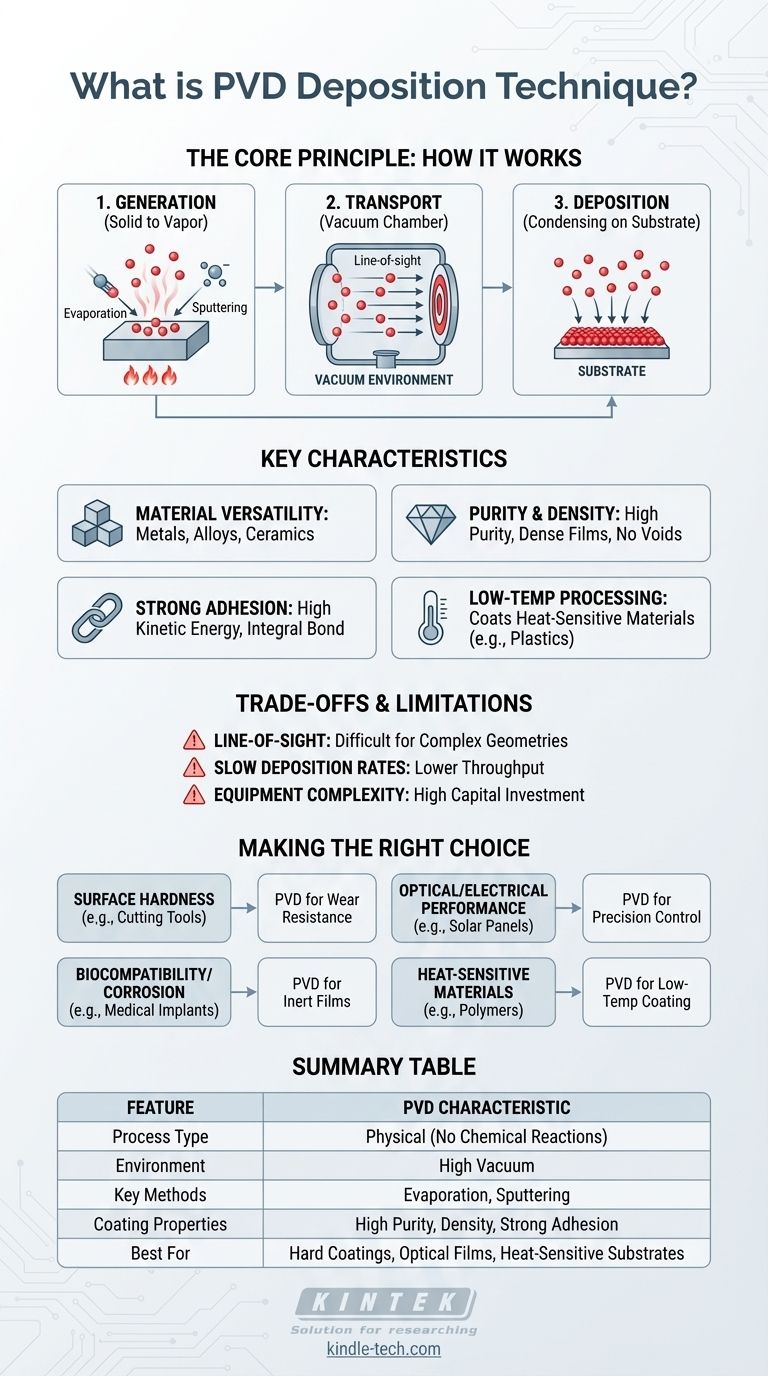
In short, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a vacuum-based process used to create high-performance thin films. It works by transforming a solid source material into a vapor, which then travels through a vacuum chamber and condenses onto the surface of a target object, or "substrate," to form a coating. This entire process is purely physical; no chemical reactions take place to form the final film.
The central concept to grasp is that PVD is not a single method, but a family of techniques for physically "transporting" atoms from a source to a surface. Its defining strength lies in its ability to deposit exceptionally pure, dense, and strongly bonded coatings from almost any inorganic material, often at low temperatures that won't damage the underlying part.
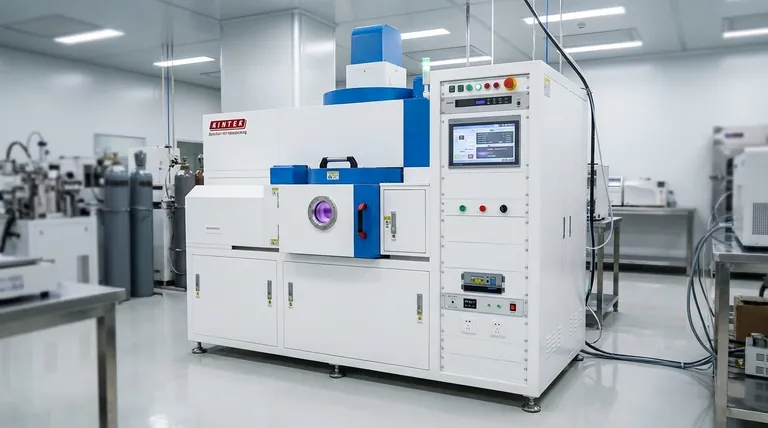

How PVD Works: The Core Principle
The PVD process can be broken down into three fundamental stages that occur within a high-vacuum environment. The vacuum is critical because it prevents vaporized atoms from colliding with air molecules, allowing them to travel directly to the substrate.
Step 1: Generation (Turning a Solid into Vapor)
To begin, atoms must be liberated from a solid source material, known as the target. This is accomplished primarily through two methods:
- Evaporation: The target material is heated until it evaporates or sublimes, releasing atoms into a vapor phase. This can be done with resistive heaters or, for higher melting point materials, a high-energy electron beam (e-beam evaporation).
- Sputtering: The target is bombarded with high-energy ions (usually an inert gas like argon). These collisions act like a microscopic sandblaster, physically knocking atoms off the target's surface.
Step 2: Transport (Moving Through a Vacuum)
Once freed, the vaporized atoms travel through the vacuum chamber. Because there are very few other gas molecules to interfere, they move in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This is known as line-of-sight deposition.
Step 3: Deposition (Condensing on the Substrate)
When the vapor atoms strike the substrate, they condense back into a solid state. They build up, atom by atom, to form a thin, dense, and highly uniform film across the surface of the part.
Key Characteristics of PVD Coatings
The "why" behind PVD's widespread use comes from the unique properties of the films it creates. These are not simply layers of paint; they are engineered surfaces.
Material Versatility
PVD can deposit a vast range of materials, including pure metals, alloys, and ceramics. This allows for the creation of films with specific properties, such as electrical conductivity, hardness, or corrosion resistance.
Purity and Density
Because the process occurs in a vacuum and involves no chemical reactions, the resulting films are extremely pure. The energetic deposition also creates coatings that are highly dense and free of voids, enhancing their protective capabilities.
Strong Adhesion
The atoms striking the substrate often have high kinetic energy, which promotes excellent adhesion between the film and the underlying material. The coating becomes an integral part of the surface rather than just sitting on top of it.
Low-Temperature Processing
Many PVD processes can be performed at relatively low temperatures. This is a critical advantage, as it allows for the coating of heat-sensitive materials like plastics, polymers, and even biological samples without causing damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No technology is a universal solution. Understanding PVD's limitations is crucial for making an informed decision.
The Line-of-Sight Problem
The most significant limitation of PVD is its line-of-sight nature. If a surface cannot be "seen" directly from the source material, it will not be coated effectively. This makes it difficult to coat complex internal geometries or deep, narrow holes.
Deposition Rates
Compared to older processes like electroplating, some PVD techniques (particularly sputtering) can have relatively slow deposition rates. This can impact throughput and cost for high-volume manufacturing.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
PVD systems require high-vacuum chambers, power supplies, and control systems. This equipment is complex and represents a significant capital investment, making it better suited for industrial or research applications than for small-scale projects.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
PVD is a powerful tool when applied to the right problem. Your specific goal will determine if it is the correct choice over other methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), plating, or painting.
- If your primary focus is surface hardness and wear resistance: PVD is the industry standard for applying hard ceramic coatings (like Titanium Nitride) to cutting tools, dies, and engine components.
- If your primary focus is optical or electrical performance: PVD provides the precise control over thickness, purity, and composition needed for anti-reflection coatings, solar panels, and semiconductor devices.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility or corrosion resistance: PVD creates dense, chemically inert films ideal for medical implants, decorative finishes, and protecting components in harsh environments.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive material: PVD's low-temperature capability is a key advantage for adding functional or metallic coatings to plastics and polymers without melting or warping them.
By understanding these core principles, you can leverage PVD as a powerful tool for engineering surfaces with precisely tailored properties.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (no chemical reactions) |
| Environment | High vacuum |
| Key Methods | Evaporation, Sputtering |
| Coating Properties | High purity, density, strong adhesion |
| Best For | Hard coatings, optical films, heat-sensitive substrates |
Ready to engineer superior surfaces with PVD technology? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thin film deposition. Whether you're developing wear-resistant tools, optical coatings, or semiconductor devices, our solutions deliver the purity, density, and adhesion your projects demand. Contact our experts today to explore how our PVD systems can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















