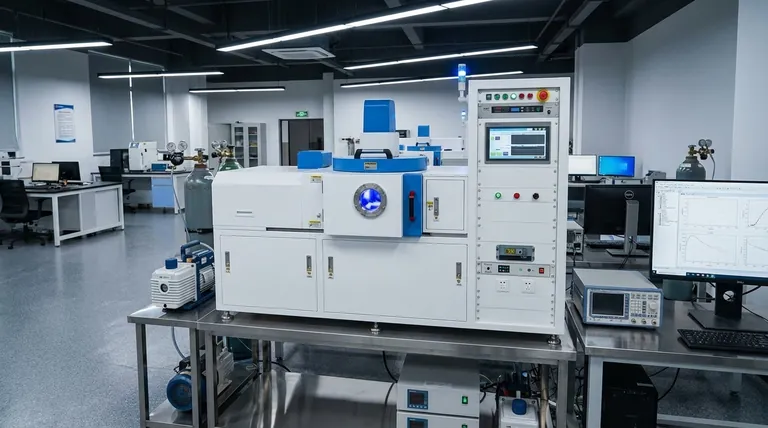
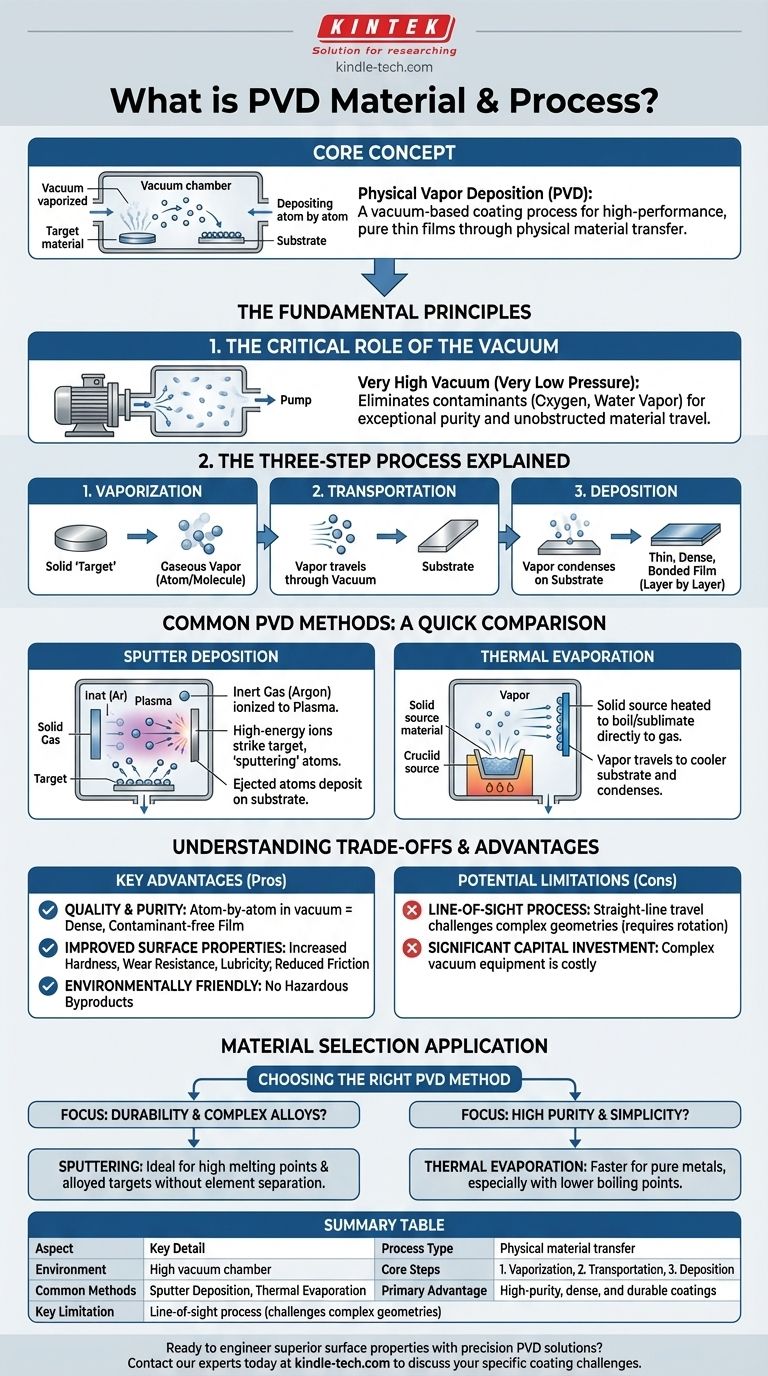
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a vacuum-based coating process where a solid source material is vaporized and then deposited atom by atom onto the surface of a part. This method is not a chemical reaction but a physical transfer of material, resulting in an exceptionally pure, thin, and high-performance film that enhances the properties of the underlying substrate.
The defining principle of PVD is a physical transition in a controlled vacuum environment: a solid material is converted into a vapor, transported, and then condensed onto a target surface to form an extremely pure and uniform thin film.

The Fundamental Principles of PVD
To truly understand PVD, you must grasp the environment it requires and the sequence of events that takes place within it. The process is defined by its precision and control at the atomic level.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The entire PVD process occurs under a very high vacuum (very low pressure).
This environment is non-negotiable because it eliminates unwanted atoms and molecules, such as oxygen or water vapor, which would otherwise contaminate the coating. The vacuum ensures the final film is exceptionally pure and allows the vaporized material to travel to the substrate without obstruction.
The Three-Step Process Explained
Regardless of the specific PVD technique used, the process universally follows three fundamental steps.
- Vaporization: A solid source material, known as the "target," is converted into a gaseous vapor.
- Transportation: These vaporized atoms or molecules travel through the vacuum chamber from the target to the part being coated (the "substrate").
- Deposition: The vapor condenses on the surface of the substrate, forming a thin, dense, and tightly bonded film. This film grows layer by layer, atom by atom.
Common PVD Methods: A Quick Comparison
While the principle is the same, the method of vaporization is what distinguishes different PVD processes. The two most common techniques offer different capabilities.
Sputter Deposition
In sputtering, the vacuum chamber is backfilled with a small amount of an inert gas, like Argon, which is then ionized to create a plasma.
These high-energy ions are accelerated towards the solid target material, striking it with enough force to physically knock off, or "sputter," individual atoms. These ejected atoms then travel to and deposit on the substrate.
Thermal Evaporation
Thermal evaporation is a more direct process. The solid source material is heated in the vacuum chamber until it begins to boil or sublimate directly into a gaseous state.
This vapor then travels in a straight line to the cooler substrate, where it condenses back into a solid, forming the coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
PVD is chosen for specific reasons, but like any industrial process, it comes with a distinct set of characteristics that make it suitable for some applications and less so for others.
Key Advantages
The primary benefit of PVD is the quality and purity of the resulting coating. Because it's formed atom by atom in a clean vacuum, the film is incredibly dense and free of contaminants.
This process can significantly improve surface properties, increasing hardness, wear resistance, and lubricity while reducing friction. It is also considered an environmentally friendly process with no hazardous byproducts.
Potential Limitations
PVD is a line-of-sight process. The vaporized material travels in a straight line, which can make it challenging to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes without sophisticated part rotation fixtures.
The equipment required to create and maintain a high vacuum is complex and represents a significant capital investment, making the process less suitable for low-cost, high-volume applications where coating precision is not the primary concern.
How This Applies to Material Selection
Choosing the right PVD method is directly tied to the material you want to deposit and the properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is durability and complex alloys: Sputtering is often the superior choice, as it can deposit materials with very high melting points and create coatings from alloyed targets without separating the constituent elements.
- If your primary focus is high purity and simplicity: Thermal evaporation is an excellent and often faster method for depositing pure metals, particularly those with lower boiling points.
Understanding these fundamental principles empowers you to see PVD not as a single solution, but as a sophisticated toolset for engineering surfaces at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (not chemical) material transfer |
| Environment | High vacuum chamber |
| Core Steps | 1. Vaporization 2. Transportation 3. Deposition |
| Common Methods | Sputter Deposition, Thermal Evaporation |
| Primary Advantage | High-purity, dense, and durable coatings |
| Key Limitation | Line-of-sight process (can challenge complex geometries) |
Ready to engineer superior surface properties with precision PVD solutions?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for thin-film deposition and materials science. Our expertise can help you select the right PVD process—whether sputtering or thermal evaporation—to achieve the high-purity, durable coatings your research or production demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific coating challenges and enhance your material performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















