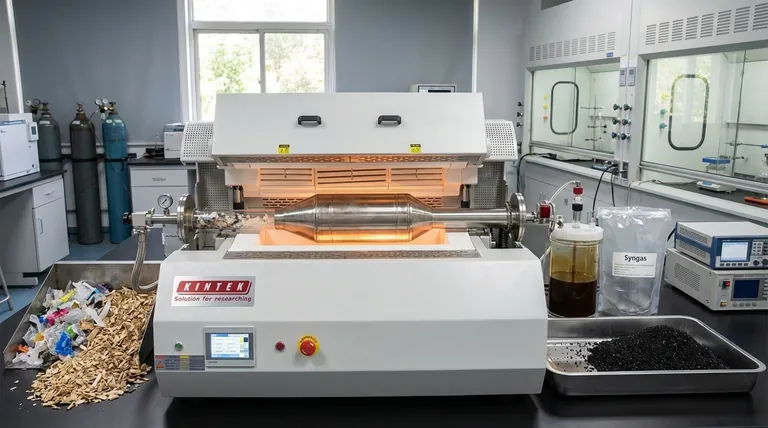
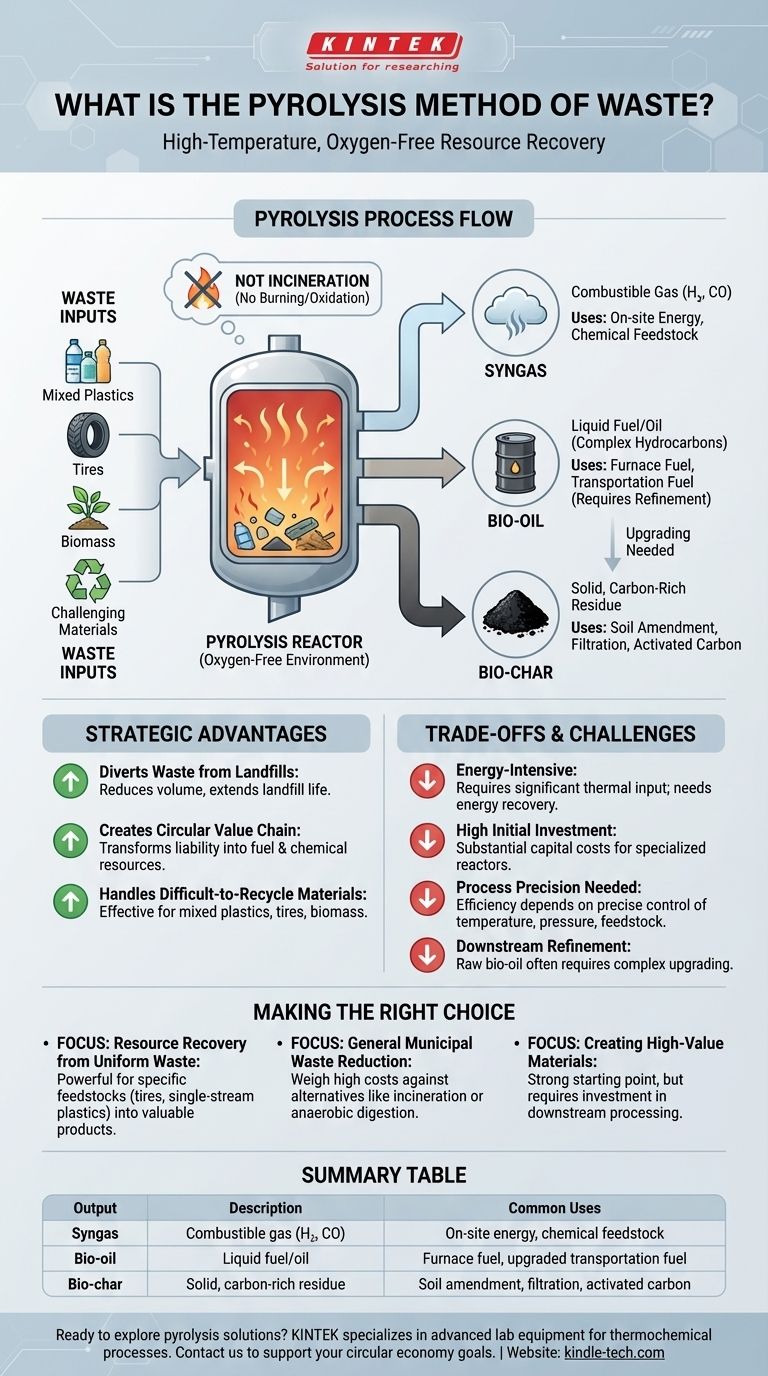
In essence, pyrolysis is a method of breaking down waste materials, like plastics or biomass, by heating them to high temperatures in an environment without oxygen. This thermochemical decomposition process transforms the waste not into ash, but into a mix of valuable outputs: a combustible gas (syngas), a liquid fuel (bio-oil), and a solid, carbon-rich residue (bio-char). It is a form of resource recovery, distinct from simple incineration.
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a deconstruction process, not a disposal one. It uses heat to break complex waste materials back into simpler, valuable chemical components in the absence of oxygen, but its practical application is defined by a significant trade-off between resource creation and high energy and capital costs.

How Pyrolysis Deconstructs Waste
Pyrolysis works by applying intense heat to a material, which causes its chemical bonds to vibrate and break apart. Because this occurs in an inert, oxygen-free atmosphere, the material does not combust or burn.
The Principle of Oxygen-Free Heating
The critical distinction between pyrolysis and incineration is the absence of oxygen. Incineration is burning—a rapid oxidation process that releases heat and converts most of the material into ash and flue gas.
Pyrolysis, by contrast, is more like high-temperature baking in a sealed container. It thermally cracks long-chain polymer molecules in plastics, tires, or biomass into smaller, more volatile compounds without burning them.
The Three Primary Outputs
The process consistently yields three core products, the proportion of which can be managed by adjusting process conditions like temperature and heating rate.
- Syngas: This is a mixture of combustible gases, primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide. It can be burned on-site to provide energy for the pyrolysis process itself or be refined into other chemicals.
- Bio-oil: Also known as pyrolysis oil, this is a complex liquid mixture of hydrocarbons. It can be upgraded into transportation fuels or used as a furnace oil, but often requires significant refinement.
- Bio-char: This stable, solid material is rich in carbon. It has applications as a soil amendment to improve fertility, as a filtration medium, or as a feedstock for producing activated carbon.
The Strategic Advantages of Pyrolysis
As a waste management strategy, pyrolysis is attractive because it reframes waste not as a problem to be disposed of, but as a resource to be harvested.
Diverting Waste from Landfills
By converting the bulk of waste material into gas, liquid, and a smaller solid fraction, pyrolysis dramatically reduces the volume of material that must be sent to a landfill. This extends the life of existing landfills and minimizes the environmental footprint of waste disposal.
Creating a Circular Value Chain
Unlike disposal, pyrolysis creates products with economic value. Waste that would otherwise be a liability is transformed into fuels and chemical feedstocks, creating a more circular economic model where resources are reused rather than discarded.
Handling Difficult-to-Recycle Materials
Pyrolysis is particularly effective for waste streams that are challenging for traditional mechanical recycling, such as mixed plastics, shredded tires, and certain types of biomass. It can handle contaminated materials that would otherwise be rejected.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While promising, pyrolysis is not a universally perfect solution. Its implementation requires a clear-eyed assessment of its technical and economic hurdles.
The Energy Equation
The process is energy-intensive, requiring significant thermal input to reach and maintain the high temperatures needed for decomposition. A successful plant must be designed so that the energy generated from the syngas can offset a large portion of this operational energy demand.
High Initial Investment
Pyrolysis facilities have high capital costs. The specialized reactors, gas handling systems, and product collection equipment represent a substantial upfront investment compared to simpler waste management options.
The Need for Process Precision
Efficiency is highly dependent on precise control over process conditions. Factors like temperature, pressure, and the type of feedstock must be carefully managed to maximize the yield of desired products and ensure operational stability.
Downstream Product Refinement
The raw outputs of pyrolysis are not always immediately usable. The bio-oil, in particular, can be acidic, unstable, and contain impurities, requiring costly and complex upgrading and refining steps before it can be used as a high-grade fuel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to implement pyrolysis depends entirely on your specific waste stream and strategic objectives.
- If your primary focus is resource recovery from specific feedstocks like tires or single-stream plastics: Pyrolysis is a powerful and direct technology for converting these uniform waste streams into valuable fuel and chemical products.
- If your primary focus is general municipal waste reduction: Carefully weigh the high capital and energy costs of pyrolysis against alternatives like waste-to-energy incineration or anaerobic digestion, which may be more economical for mixed, unsorted waste.
- If your primary focus is creating high-value materials: Pyrolysis is a strong starting point, but be prepared for the additional investment in downstream processing required to refine bio-oil and upgrade bio-char for specialized applications.
Ultimately, viewing pyrolysis as an industrial chemical process rather than a simple disposal method is the key to making an informed decision.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Output | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Syngas | Combustible gas (H₂, CO) | On-site energy, chemical feedstock |
| Bio-oil | Liquid fuel/oil | Furnace fuel, upgraded transportation fuel |
| Bio-char | Solid, carbon-rich residue | Soil amendment, filtration, activated carbon |
Ready to explore pyrolysis solutions for your laboratory or waste stream? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for analyzing and optimizing thermochemical processes like pyrolysis. Whether you are researching feedstocks, characterizing outputs like bio-oil and bio-char, or scaling up your process, our expertise can help. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your resource recovery and circular economy goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process



















