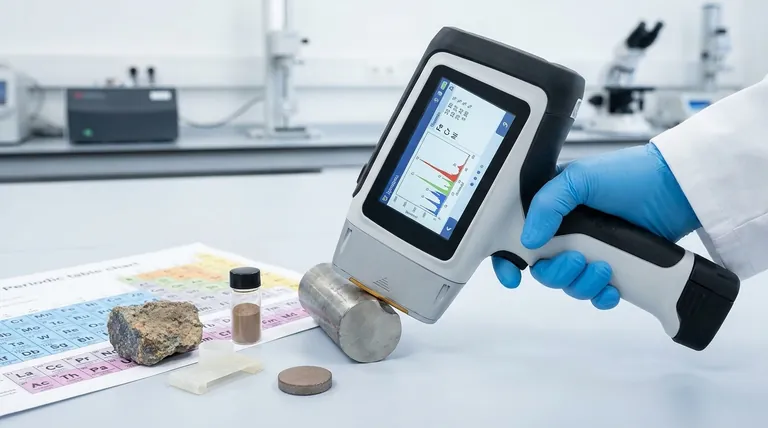
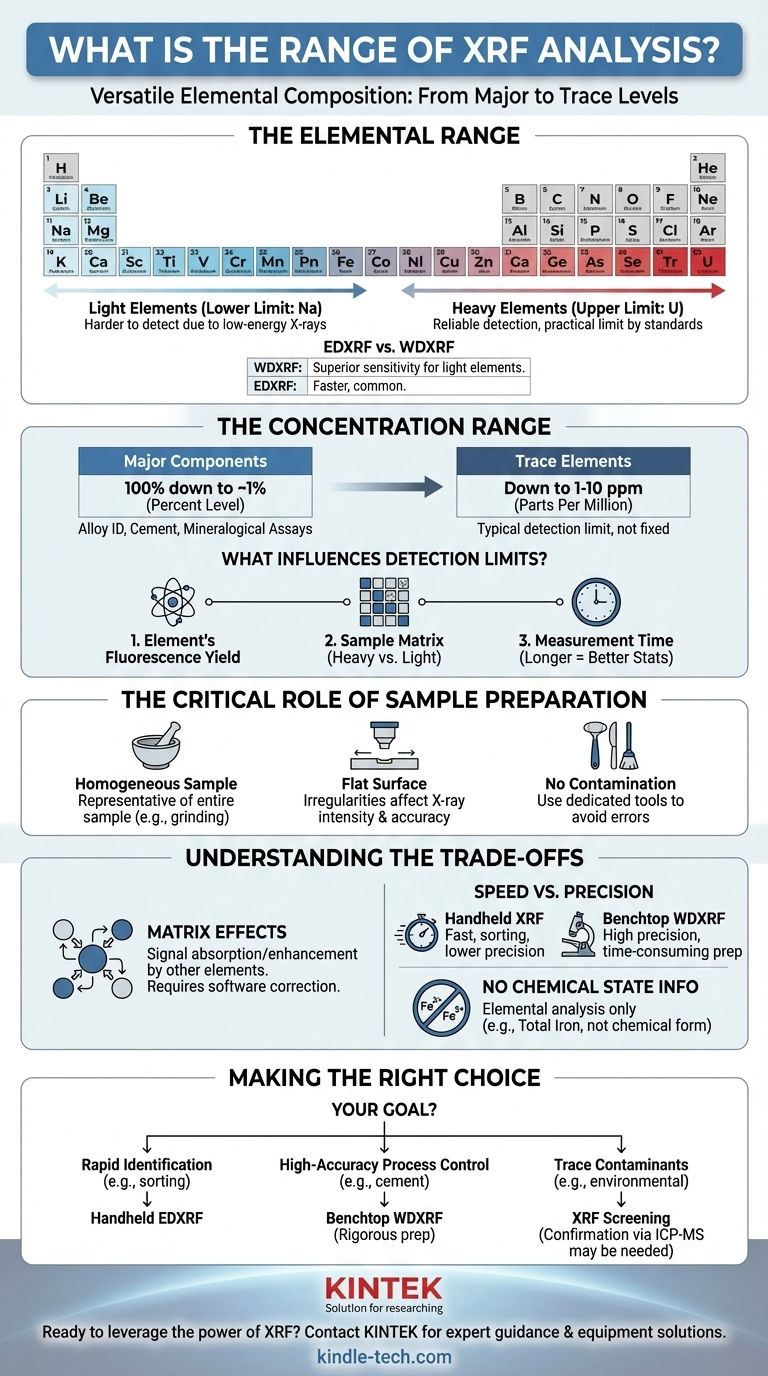
In short, X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) analysis is capable of detecting elements from Sodium (Na) up to Uranium (U) on the periodic table. Its concentration range is exceptionally wide, spanning from high-percentage major components down to trace levels in the parts per million (ppm) range, making it a highly versatile technique for elemental composition.
While XRF offers a broad analytical range, its true effectiveness is not universal. The specific elements you can detect and the precision of your measurements are fundamentally dictated by your instrument type, the surrounding sample matrix, and the quality of your sample preparation.

Understanding the Elemental Range
The range of elements an XRF instrument can measure is defined by the physics of X-ray generation and detection. This range has distinct and important boundaries, especially at the lighter end of the periodic table.
The Lower Limit: Light Elements
The primary limitation of XRF is its difficulty in detecting very light elements, typically those with an atomic number below 11 (Sodium).
When the primary X-ray beam hits a light element, the resulting fluorescent X-ray it emits has very low energy. These low-energy X-rays are easily absorbed by the air path between the sample and the detector, or even by the detector window itself, preventing them from being counted.
The Upper Limit: Heavy Elements
On the other end of the spectrum, XRF is excellent for analyzing mid-to-heavy elements. It can reliably detect and quantify all elements from the middle of the periodic table up through the heaviest naturally occurring ones, like Uranium (U). The practical upper limit is typically determined by the available calibration standards and software libraries.
EDXRF vs. WDXRF Sensitivity
It's important to distinguish between the two main types of XRF. Wavelength Dispersive XRF (WDXRF) generally offers superior resolution and sensitivity for lighter elements compared to the more common and faster Energy Disersive XRF (EDXRF) systems.
Deconstructing the Concentration Range
XRF's power lies in its ability to measure elements across a vast range of concentrations, from the main ingredients of a material down to minute impurities.
From Major Components (Percent Level)
XRF is ideally suited for quantifying elements that constitute a significant portion of a sample, typically anything from 1% to 100% by weight. This makes it a standard tool for applications like alloy identification, cement analysis, and mineralogical assays where major element composition is critical.
To Trace Elements (PPM Level)
Modern XRF systems can also detect trace elements down to the low parts per million (ppm) level. A typical detection limit might be between 1 to 10 ppm, but this is not a fixed guarantee.
What Influences Detection Limits?
The minimum concentration you can reliably measure depends heavily on three factors:
- The Element Itself: Each element has a different fluorescence yield.
- The Sample Matrix: A heavy matrix (like lead) will absorb the signal from a light trace element more than a light matrix (like plastic), making detection harder.
- Measurement Time: Longer analysis times allow the detector to collect more signal, improving statistics and lowering the detection limit.
The Critical Role of Sample Preparation
The theoretical range of an XRF instrument can only be achieved if the sample is prepared correctly. As noted in analytical best practices, improper preparation is a primary source of error.
Why a Homogeneous Sample Matters
For bulk analysis, the sample must be homogeneous. Methods like crushing, grinding, and pressing a powder into a pellet ensure that the small area being analyzed is truly representative of the entire sample. Without this, results can be misleading.
The Impact of Surface Irregularity
XRF systems are calibrated for a precise distance between the X-ray source, the sample surface, and the detector. An irregular, non-flat surface alters this distance, which directly affects the intensity of the detected X-rays and introduces significant error into the final concentration calculation.
The Risk of Contamination
Cross-contamination during sample preparation can artificially inflate the concentration of an element or introduce one that isn't actually in the sample. Using clean, dedicated tools like files or grinders for different sample types is essential for accurate trace analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, XRF is not without its limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is key to interpreting your results correctly.
Matrix Effects
The signal from your element of interest can be either absorbed or enhanced by other elements in the sample. This is known as the "matrix effect" and is the single biggest challenge in quantitative XRF. Modern software uses complex algorithms to correct for these effects, but they are always a factor to consider.
Speed vs. Precision
Handheld XRF analyzers offer incredible speed for sorting and screening but have lower precision and higher detection limits than benchtop systems. High-precision laboratory WDXRF systems provide the best performance but require more time-consuming sample preparation, such as fusing the sample into a glass disk.
No Chemical State Information
Standard XRF is an elemental analysis technique. It tells you how much iron is in a sample, but it cannot tell you if that iron exists as metallic iron (Fe), iron(II), or iron(III). This distinction requires other analytical methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To get the most out of XRF, align your methodology with your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is rapid material identification (e.g., alloy sorting): A handheld EDXRF analyzer is the ideal tool, providing near-instant results with minimal sample preparation.
- If your primary focus is high-accuracy process control (e.g., cement or polymer production): A benchtop WDXRF system with a rigorous sample preparation protocol (pressed pellets or fused beads) is necessary for reliable quantitative results.
- If your primary focus is measuring trace contaminants (e.g., environmental screening): XRF is a viable screening tool, but be mindful of its detection limits and potential matrix effects; confirmation with a more sensitive technique like ICP-MS may be required.
Understanding the capabilities and limitations of XRF empowers you to use it effectively as a powerful tool for elemental analysis.
Summary Table:
| Analytical Range | Capability | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Elemental Range | Sodium (Na) to Uranium (U) | Light elements (below Na) are difficult to detect due to low-energy X-rays. |
| Concentration Range | ~100% down to 1-10 ppm | Detection limits depend on the element, sample matrix, and measurement time. |
| Instrument Types | EDXRF (faster) & WDXRF (more precise) | WDXRF offers superior sensitivity for lighter elements. |
Ready to leverage the power of XRF analysis in your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to meet your precise analytical needs. Whether you require a rapid handheld EDXRF analyzer for material sorting or a high-precision benchtop WDXRF system for rigorous quality control, our experts can help you select the right instrument and support you with the necessary consumables for optimal sample preparation.
Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities and ensure accurate, reliable results for your specific applications.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis



















