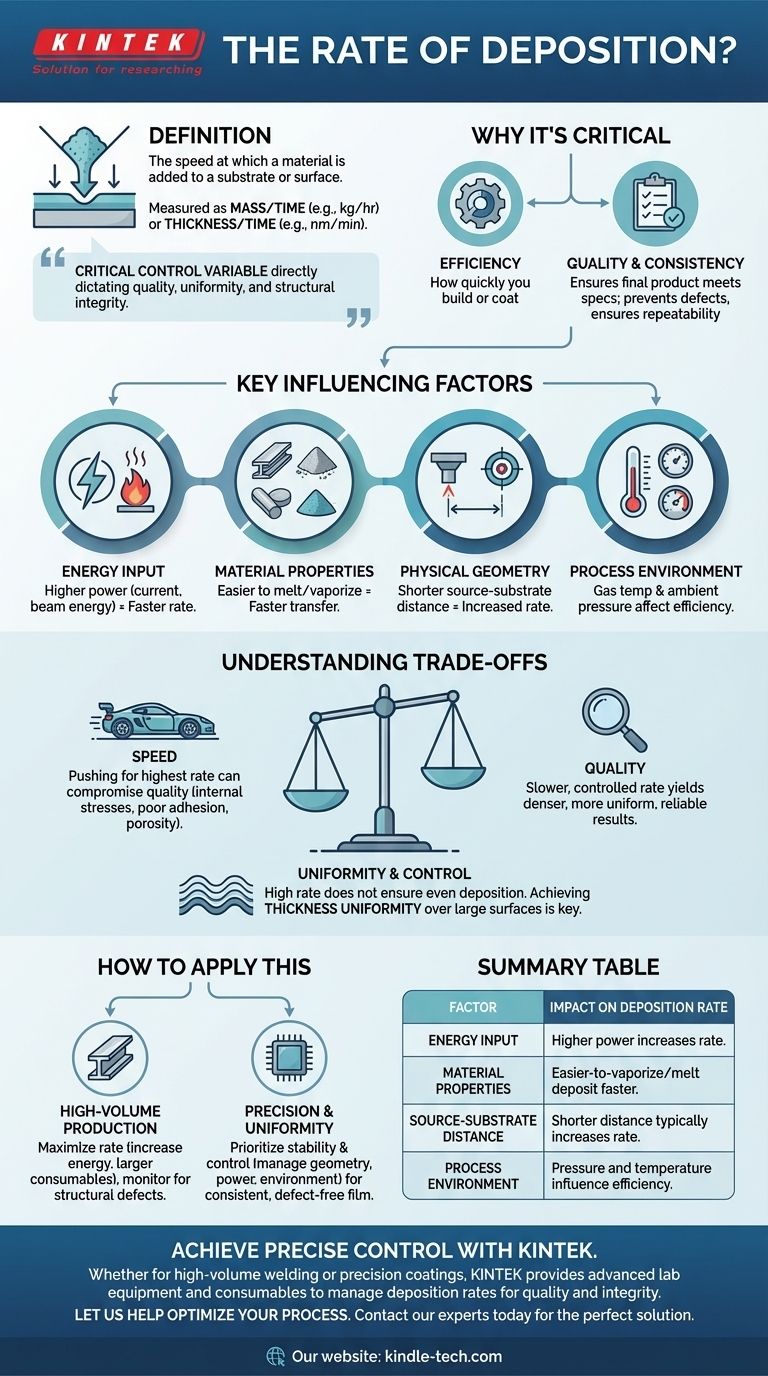
In material science and manufacturing, the rate of deposition is the speed at which a material is added to a substrate or surface. It is a fundamental process parameter measured either as mass added over time (e.g., kilograms per hour in welding) or as thickness gained over time (e.g., nanometers per minute in thin-film coating).
The deposition rate is not simply a measure of speed; it is the critical control variable that directly dictates the quality, uniformity, and structural integrity of the final product, whether that is a robust weld or a high-precision optical coating.

Why Controlling Deposition Rate is Critical
The Core Definition
At its heart, the deposition rate quantifies efficiency—how quickly you can build or coat something. This could be weld metal being deposited into a joint or a microscopic layer of material being sputtered onto a silicon wafer.
A Key to Quality and Consistency
Controlling the deposition rate is essential for ensuring the final product meets its specifications. Inconsistent rates lead to defects, such as non-uniform film thickness or weak points in a welded seam. A stable, controlled rate is the foundation of a repeatable, high-quality manufacturing process.
Key Factors That Influence Deposition Rate
The specific variables that control the deposition rate depend on the process, but they generally fall into a few key categories.
Energy Input
The amount of energy directed at the source material is often the most significant factor. More energy typically means a faster rate.
This includes variables like welding current, magnetron power in sputtering, and beam energy in other deposition techniques.
Material Properties
The physical characteristics of the material being deposited play a crucial role. Some materials simply melt, vaporize, or erode more easily than others under the same conditions, directly affecting how quickly they can be transferred to the substrate.
Physical Geometry
The physical setup of the equipment is a major controlling factor. This includes the distance between the material source and the substrate (target-substrate distance) and the specific position or angle of deposition, such as in multi-pass welding.
Decreasing the distance between the source and the target generally increases the deposition rate, as less material is lost in transit.
Process Environment
The conditions within the deposition chamber or around the weld have a direct impact. Variables such as gas temperature and ambient pressure can influence the efficiency of material transfer from the source to its destination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing the deposition rate is rarely about simply making it as fast as possible. The primary challenge is balancing speed with quality.
Speed vs. Quality
Pushing for the highest possible deposition rate can often compromise the quality of the final product. A very fast deposition can introduce internal stresses, poor adhesion, or a porous structure. A slower, more controlled rate often yields a denser, more uniform, and more reliable result.
Uniformity and Control
A high deposition rate does not guarantee that the material is being deposited evenly. Achieving thickness uniformity is a common challenge, especially over large surfaces. Factors like the size of the material source (or "erosion zone") and the geometry of the setup become critical for ensuring the deposited layer is consistent everywhere.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your approach to managing the deposition rate should be dictated by the primary objective of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production (e.g., structural steel welding): You will likely maximize the deposition rate by increasing energy input (current) and using larger consumables, while carefully monitoring to avoid critical structural defects.
- If your primary focus is precision and uniformity (e.g., semiconductor or optical coatings): You will prioritize stability and control over raw speed, carefully managing geometry, power, and the process environment to achieve a consistent and defect-free film.
Ultimately, mastering the deposition rate is about finding the optimal balance between manufacturing speed and the functional requirements of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Deposition Rate |
|---|---|
| Energy Input | Higher power (current, magnetron power) increases rate. |
| Material Properties | Easier-to-vaporize/melt materials deposit faster. |
| Source-Substrate Distance | Shorter distance typically increases rate. |
| Process Environment | Pressure and temperature can influence efficiency. |
Achieve precise control over your deposition processes with KINTEK.
Whether you are working on high-volume welding or precision thin-film coatings, the right equipment is essential for managing deposition rates to ensure quality, uniformity, and structural integrity. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for all your material science and manufacturing needs.
Let us help you optimize your process. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function during the fabrication of diamond films?
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- How do you calculate coating coverage? A Practical Guide to Accurate Material Estimation
- How does Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PACVD) equipment improve the performance of Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coatings?
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating

















