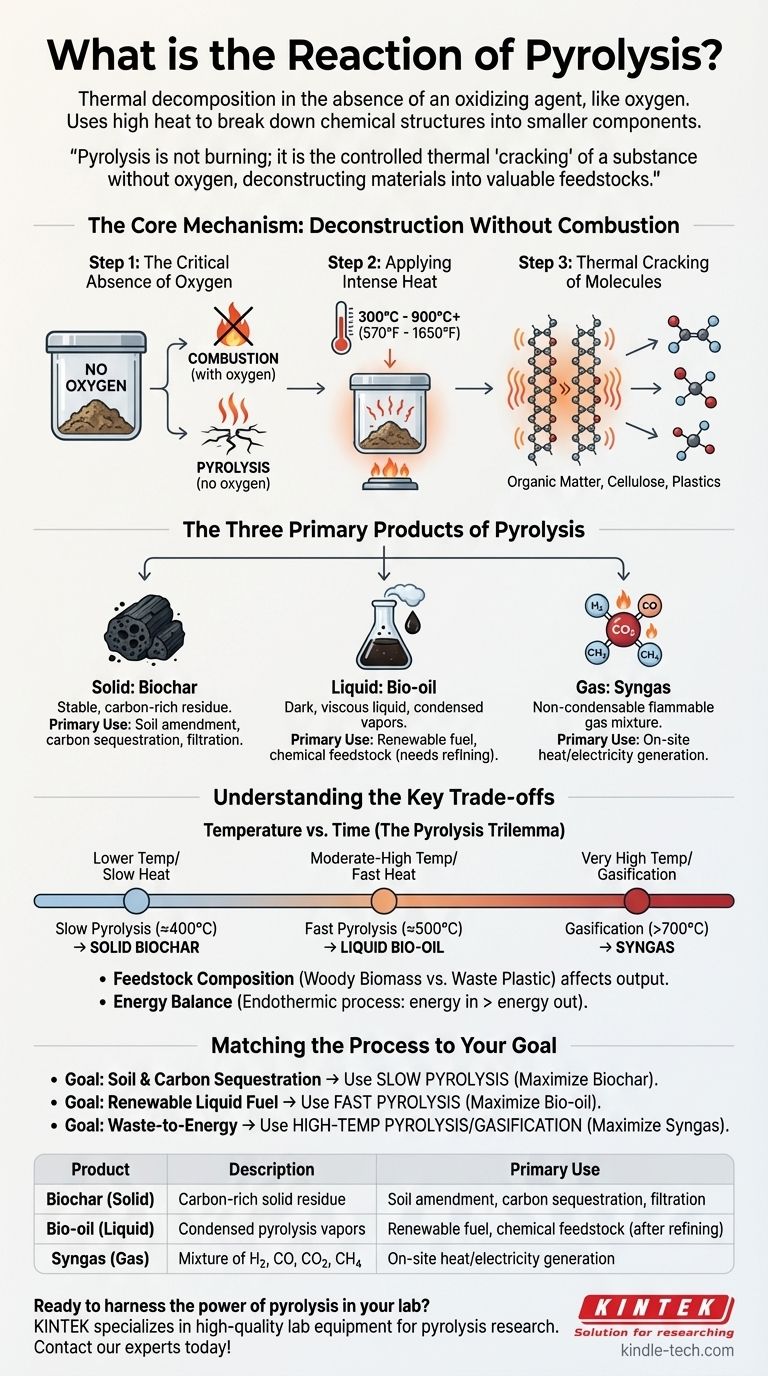
In essence, pyrolysis is thermal decomposition in the absence of an oxidizing agent like oxygen. Instead of burning a material, high heat is used to break down its chemical structure into smaller, more fundamental components. This process irreversibly transforms organic materials into a solid, a liquid, and a gas.
Pyrolysis is not burning; it is the controlled thermal "cracking" of a substance without oxygen. This critical distinction is what allows pyrolysis to deconstruct materials into valuable chemical feedstocks rather than reducing them to ash and exhaust gas.

The Core Mechanism: Deconstruction Without Combustion
At its heart, pyrolysis is a straightforward thermochemical process. Understanding the key steps reveals why it is such a powerful tool for material conversion.
Step 1: The Critical Absence of Oxygen
The defining feature of pyrolysis is that it occurs in an inert atmosphere, meaning there is little to no oxygen present.
If oxygen were present, the material would combust (burn), releasing its stored energy as heat and light, and producing primarily carbon dioxide and water. By removing oxygen, we prevent combustion and instead force the chemical bonds within the material to break apart from heat alone.
Step 2: Applying Intense Heat
Pyrolysis reactions require significant thermal energy, typically in the range of 300°C to over 900°C (570°F to 1650°F).
The specific temperature applied is a key control lever. Different temperatures and heating rates will favor the production of different end products, allowing operators to tune the process to a desired outcome.
Step 3: Thermal Cracking of Molecules
Once heated, the long, complex molecules that make up organic matter (like cellulose, lignin, or plastics) become unstable.
The intense heat and vibrations cause these long-chain polymers to "crack" or break apart into smaller, more volatile compounds. These new, smaller molecules are the primary outputs of the reaction.
The Three Primary Products of Pyrolysis
The decomposition of a single input material results in three distinct product streams, each with its own characteristics and uses.
Solid: Biochar
This is the stable, carbon-rich solid residue left behind. It is similar in appearance to charcoal.
Biochar is highly valued for its ability to improve soil health, sequester carbon for long periods, and act as a filtration medium.
Liquid: Bio-oil
This is a dark, viscous liquid produced when the hot pyrolysis vapors are rapidly cooled and condensed. It is also known as pyrolysis oil or tar.
Bio-oil is a complex mixture of hundreds of different organic compounds. While it is energy-dense, it is typically acidic and unstable, requiring further refining before it can be used as a transportation fuel or high-grade chemical.
Gas: Syngas
This is the non-condensable fraction of the pyrolysis vapors. It is a mixture of flammable gases.
Syngas primarily consists of hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and methane (CH₄). It can be combusted on-site to provide the heat needed to sustain the pyrolysis reaction or used to generate electricity.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The output of a pyrolysis reaction is not fixed; it is highly dependent on process conditions. Mastering these variables is key to achieving a specific goal.
The "Pyrolysis Trilemma": Temperature vs. Time
The ratio of char, oil, and gas produced is directly controlled by the heating rate and final temperature.
- Slow Pyrolysis: Lower temperatures (around 400°C) and slow heating rates maximize the production of solid biochar.
- Fast Pyrolysis: Moderate-to-high temperatures (around 500°C) and extremely rapid heating rates maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil.
- Gasification: Very high temperatures (above 700°C), often with a controlled amount of oxygen or steam, are used to maximize the production of syngas.
Feedstock Is Not Universal
The composition of the input material, or feedstock, dramatically influences the output.
Woody biomass will produce different oil and char than waste plastic or old tires. Contaminants in the feedstock can also end up in the final products, complicating their use and potentially requiring costly purification steps.
The Energy Balance
Pyrolysis is an endothermic process, meaning it requires a continuous input of energy to maintain the high temperatures. A successful pyrolysis plant must be energy-positive, meaning the energy value of its products (especially the syngas and bio-oil) is greater than the energy required to run the system.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
Choosing the right pyrolysis approach depends entirely on the desired end product.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment and carbon sequestration: Utilize slow pyrolysis at lower temperatures to maximize your yield of stable biochar.
- If your primary focus is creating a renewable liquid fuel source: Implement fast pyrolysis with rapid heating and quenching to maximize the production of bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy generation: Employ a high-temperature pyrolysis or gasification process to maximize the output of combustible syngas.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a versatile chemical tool for unlocking the value stored within complex organic materials.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar (Solid) | Carbon-rich solid residue | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration, filtration |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | Condensed pyrolysis vapors | Renewable fuel, chemical feedstock (after refining) |
| Syngas (Gas) | Mixture of H₂, CO, CO₂, CH₄ | On-site heat/electricity generation |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you are optimizing biochar production, analyzing bio-oil composition, or developing new waste-to-energy processes, our reliable ovens, reactors, and analytical tools are designed to deliver precise temperature control and consistent results.
Let us help you achieve your material conversion goals. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds



















