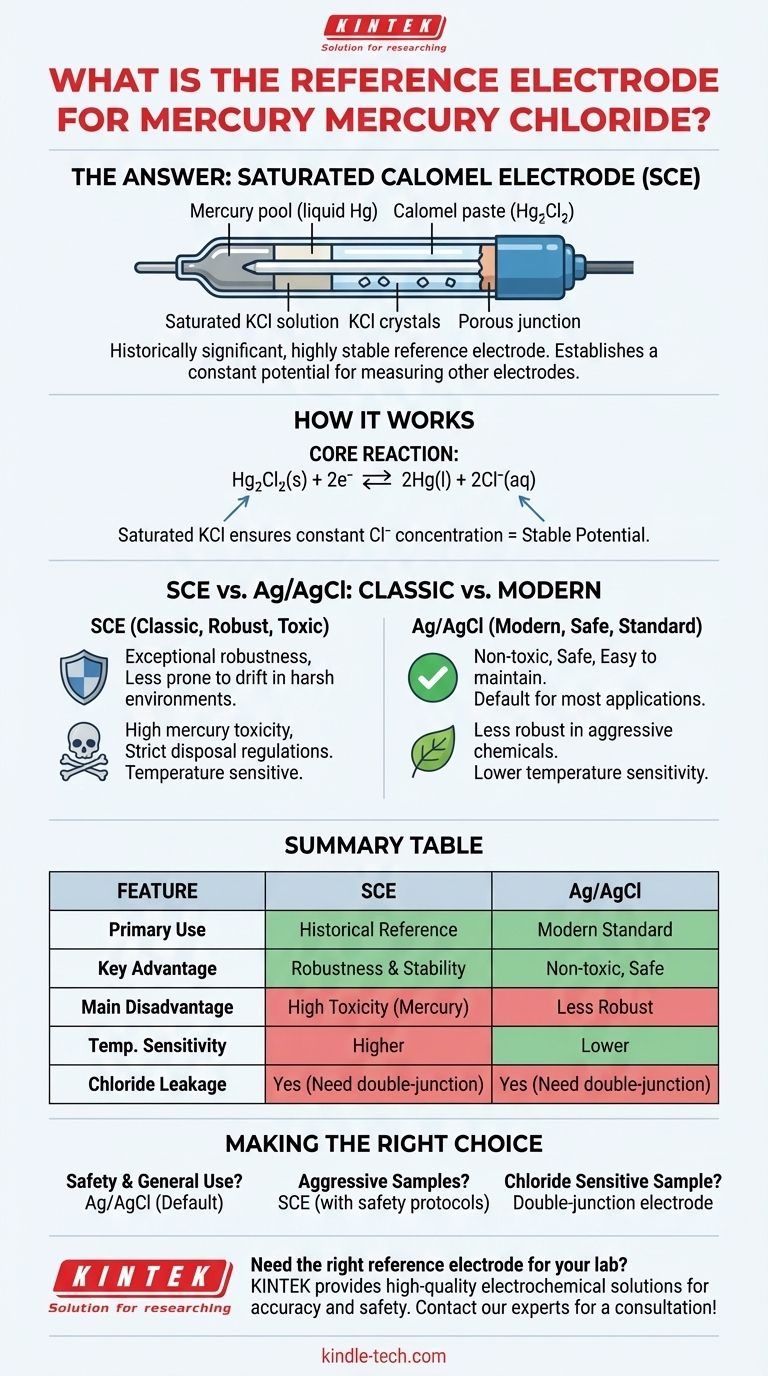
The reference electrode based on mercury and mercury(I) chloride is the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE). It is a historically significant and highly stable electrode that establishes a constant potential, against which the potential of other electrodes can be measured in an electrochemical cell. Its construction involves a paste of elemental mercury and mercury(I) chloride (calomel) in contact with a saturated aqueous solution of potassium chloride (KCl).
The Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) is a robust and highly stable reference electrode, but its use has largely been superseded by the Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode due to the significant toxicity and disposal challenges associated with its mercury components.

How the Calomel Electrode Establishes a Stable Potential
A reference electrode's sole purpose is to provide a stable, known potential that does not change during an experiment. The SCE achieves this through a carefully balanced chemical equilibrium.
The Core Electrochemical Reaction
The potential of the SCE is governed by a reversible half-reaction involving mercury and its chloride salt.
Hg₂Cl₂(s) + 2e⁻ ⇌ 2Hg(l) + 2Cl⁻(aq)
This reaction's potential depends on the concentration (more accurately, the activity) of the chloride ions (Cl⁻) in the solution.
The Role of Saturated KCl
To ensure the potential is constant, the chloride ion concentration must not change. The SCE accomplishes this by using a saturated solution of potassium chloride (KCl) as its internal electrolyte.
As long as there are undissolved KCl crystals present, the solution remains saturated, fixing the chloride ion concentration at a constant value. This makes the electrode's potential stable and reproducible.
SCE vs. Ag/AgCl: The Classic and The Modern
While the SCE was a workhorse for decades, the Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode is now the most common reference in modern laboratories.
The Rise of the Silver/Silver Chloride Electrode
The primary driver for the shift away from the SCE is safety. Mercury is a potent neurotoxin with strict regulations for handling and disposal.
The Ag/AgCl electrode is non-toxic, less expensive, and easier to manufacture and maintain, making it the preferred choice for most general-purpose applications.
Performance and Stability
Both electrodes provide excellent potential stability. The SCE has a reputation for being exceptionally robust and less prone to drift in certain industrial or complex chemical environments.
However, the potential of an SCE is more sensitive to temperature changes than an Ag/AgCl electrode. This is because the solubility of KCl, which dictates the chloride concentration, varies significantly with temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a reference electrode involves balancing performance requirements against practical and safety considerations.
Pro: Unmatched Robustness
The SCE is renowned for its durability. It can perform reliably in solutions that might "poison" or damage an Ag/AgCl electrode, such as those containing sulfides, bromides, or proteins that react with silver.
Con: The Mercury Problem
This is the single greatest disadvantage of the SCE. The toxicity of mercury makes its use a significant health and environmental liability. Accidental breakage and end-of-life disposal require specialized, costly procedures.
Con: Chloride Leakage
Like most reference electrodes, the SCE connects to the sample solution via a porous frit or junction. This junction can slowly leak KCl from the electrode's internal solution into your sample.
This can be a problem if your experiment is sensitive to chloride ions. In such cases, a "double-junction" electrode is necessary to isolate the sample from the KCl.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best reference electrode is the one that fits the specific demands of your measurement while adhering to modern safety standards.
- If your primary focus is safety and general laboratory use: The Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode is the default and correct choice for nearly all standard applications.
- If your primary focus is robustness in aggressive samples: The Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) might be considered, but only when its unique stability is essential and strict mercury safety protocols are in place.
- If your sample cannot be contaminated with chloride: You must use a double-junction reference electrode, which places a second, non-interfering electrolyte between the reference element and the sample.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs empowers you to select the correct tool for reliable and safe electrochemical analysis.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) | Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Historical reference electrode | Modern, standard reference electrode |
| Key Advantage | Exceptional robustness & stability | Non-toxic, safe, & easy to maintain |
| Main Disadvantage | High toxicity of mercury | Less robust in some aggressive chemicals |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Higher sensitivity | Lower sensitivity |
| Chloride Leakage | Yes (requires double-junction if problematic) | Yes (requires double-junction if problematic) |
Need the right reference electrode for your specific lab application?
Choosing between a traditional SCE and a modern Ag/AgCl electrode depends on your requirements for safety, robustness, and sample compatibility. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of electrochemical cells and reference electrodes, to ensure your experiments are both accurate and safe.
Let our experts help you select the perfect equipment for your needs. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Which type of electrode can be used as a reference point? Select the Right One for Accurate Measurements
- What is the reference electrode for mercury mercurous sulfate? A Guide to Chloride-Free Electrochemistry
- Why is the calomel electrode used as a secondary reference electrode? A Practical Guide to Stable Measurements
- What are the general precautions for using a reference electrode? Ensure Stable Potentials for Accurate Data
- Why and how should the electrodes of an electrolytic cell be calibrated? Ensure Reliable Results



















