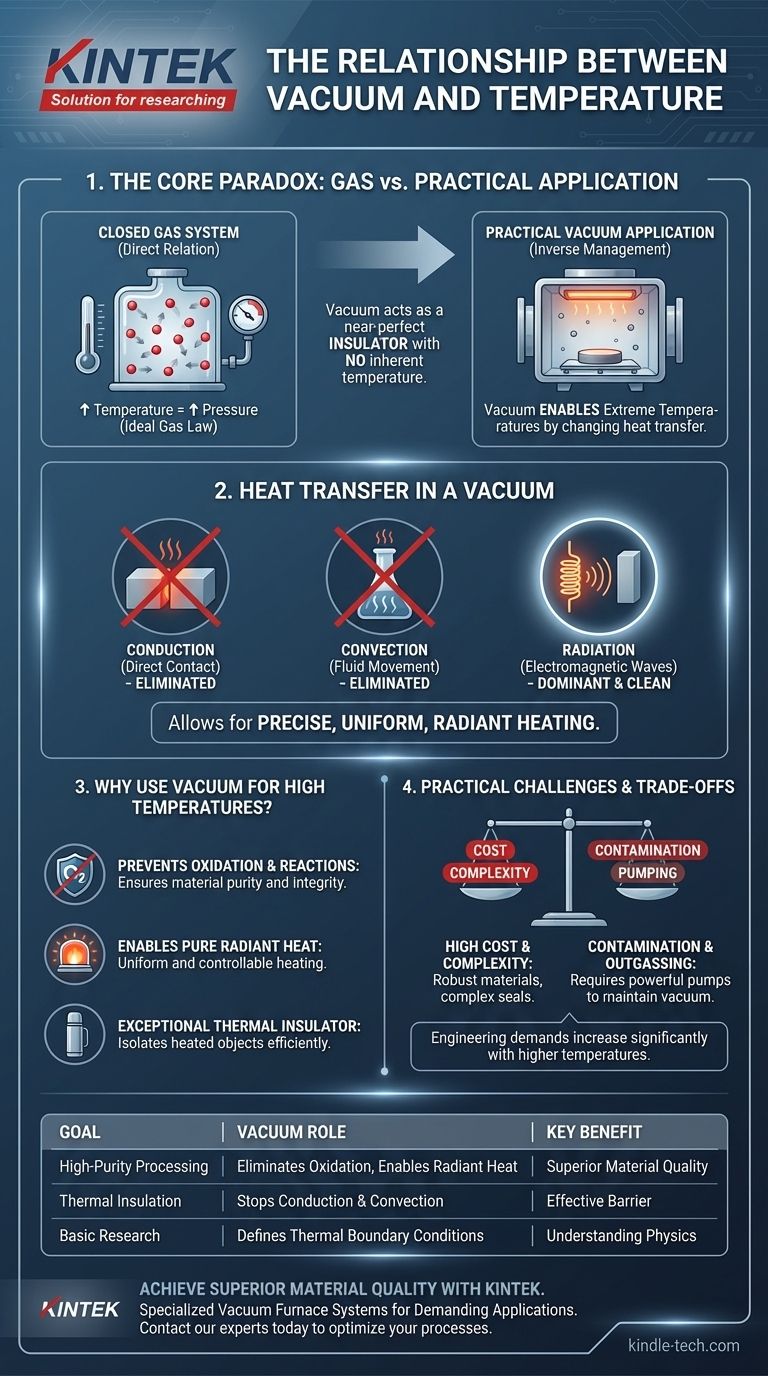
In a closed system containing a gas, the relationship between vacuum and temperature is direct: as you increase the temperature of the gas, its pressure increases, moving it away from a vacuum. However, in practical applications, the relationship is inverse. We use a vacuum precisely to manage and enable extremely high temperatures by fundamentally changing how heat is transferred.
The core principle to understand is that a vacuum does not have its own temperature. Instead, it acts as a near-perfect insulator, eliminating heat transfer through conduction and convection, which allows for precise and clean high-temperature control through thermal radiation alone.

The Fundamental Physics: Gas vs. Vacuum
The Ideal Gas Law
For any gas sealed in a container, its state is described by the Ideal Gas Law. This law shows a direct relationship between pressure and temperature.
If you heat a fixed amount of gas in a sealed chamber, the molecules move faster and collide more forcefully with the walls, increasing the pressure. Conversely, cooling the gas decreases the pressure, moving it closer to a vacuum.
What is "Temperature" in a Vacuum?
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles. A perfect vacuum, by definition, has no particles and therefore has no temperature in the traditional sense.
When we discuss temperature in a vacuum system, we are referring to the temperature of the objects and chamber walls within that vacuum. Heat energy exists and moves through the vacuum, primarily as electromagnetic waves (radiation).
Why We Use Vacuum in High-Temperature Systems
The most critical applications of vacuum technology involve creating controlled high-temperature environments, such as in vacuum furnaces for metallurgy or materials science.
Eliminating Conduction and Convection
Heat transfers in three ways: conduction (direct contact), convection (fluid or gas movement), and radiation. By removing the vast majority of air particles, a vacuum effectively stops conduction and convection.
This makes the vacuum an exceptional thermal insulator. The heat generated inside the chamber cannot easily escape to the outside walls, and the object being heated is isolated from unwanted thermal contact.
Enabling Pure Radiant Heat Transfer
With conduction and convection gone, thermal radiation becomes the dominant form of heat transfer. Powerful heating elements emit infrared radiation, which travels through the vacuum and is absorbed by the target material, heating it directly.
This allows for extremely uniform, clean, and controllable heating, which is impossible to achieve in the presence of air currents (convection).
Preventing Unwanted Chemical Reactions
Many materials react with air, especially at high temperatures. The most common reaction is oxidation. Creating a vacuum removes the oxygen and other reactive gases.
This prevents degradation, contamination, or burning of the material being processed, ensuring its purity and structural integrity. This is vital for producing high-performance alloys, semiconductors, and other advanced materials.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
Using a vacuum for thermal management is powerful but introduces significant engineering challenges and costs.
The Cost of High Temperatures
Achieving higher temperatures within a vacuum is expensive. It demands more complex and robust heating elements and thermal shielding, often made from exotic materials like molybdenum or graphite.
The furnace's construction must withstand extreme thermal stress without compromising the vacuum seal, which dramatically increases manufacturing complexity and cost.
The Challenge of Contamination
The integrity of the vacuum is paramount. Any contamination, such as microscopic leaks or the outgassing of molecules from the chamber walls, can degrade the vacuum.
As noted in furnace operations, this contamination can coat the heating elements and shielding. This reduces their radiation capacity, forcing the system to consume more power to reach the target temperature and eventually leading to component failure.
Pumping vs. Outgassing
As materials get hotter, they tend to release trapped gases from their surface—a process called outgassing. A high-temperature vacuum system must have pumps powerful enough to continuously remove these outgassed particles to maintain the required vacuum level.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this relationship allows you to select the right approach for your specific technical objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material processing: Use a high vacuum to eliminate oxidation and enable clean, uniform radiant heating for superior material quality.
- If your primary focus is thermal insulation: Use a vacuum to create a barrier that stops heat transfer via conduction and convection, as seen in cryogenic storage and vacuum flasks.
- If your primary focus is basic physics research: Remember that for a fixed gas, pressure and temperature are linked, but a vacuum's thermal properties are defined by radiation and the temperature of its boundaries.
Mastering the interplay between vacuum and temperature is fundamental to controlling heat in the most demanding scientific and industrial environments.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Physics in a Closed System | Temperature and pressure are directly related for a fixed gas (Ideal Gas Law). |
| Vacuum's Role | A vacuum is a near-perfect insulator, eliminating conduction and convection. |
| Primary Heat Transfer | In a vacuum, heat is transferred almost exclusively by thermal radiation. |
| Key Benefit | Enables clean, uniform, high-temperature processing by preventing oxidation and contamination. |
Ready to achieve superior material quality with precise high-temperature control?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance vacuum furnace systems designed for the most demanding metallurgical and materials science applications. Our solutions provide the clean, uniform heating environment you need to prevent oxidation, ensure material purity, and achieve consistent results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment can optimize your high-temperature processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the application of furnace brazing? Achieve Strong, Complex, and Clean Assemblies
- What are the advantages of using an independent internal charging tank in a vertical vacuum distillation furnace?
- What temperature is needed for metal casting? Achieve Perfect Casts with the Right Superheat
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum brazing furnace for TLP bonding? Achieve Superior Joint Integrity
- How does a pit furnace work? Prevent Distortion in Long Parts with Vertical Heat Treatment
- What role do high-precision melting furnaces play in stir casting? Master Precision in Zinc-Based Composites
- Why is a laboratory vacuum drying oven essential for N/TiO2-x mesocrystal nanocubes? Protect Your Nanoporous Structure
- Why is a high-vacuum high-temperature furnace necessary for Zr-4 alloy annealing? Ensure Superior Coating Adhesion



















