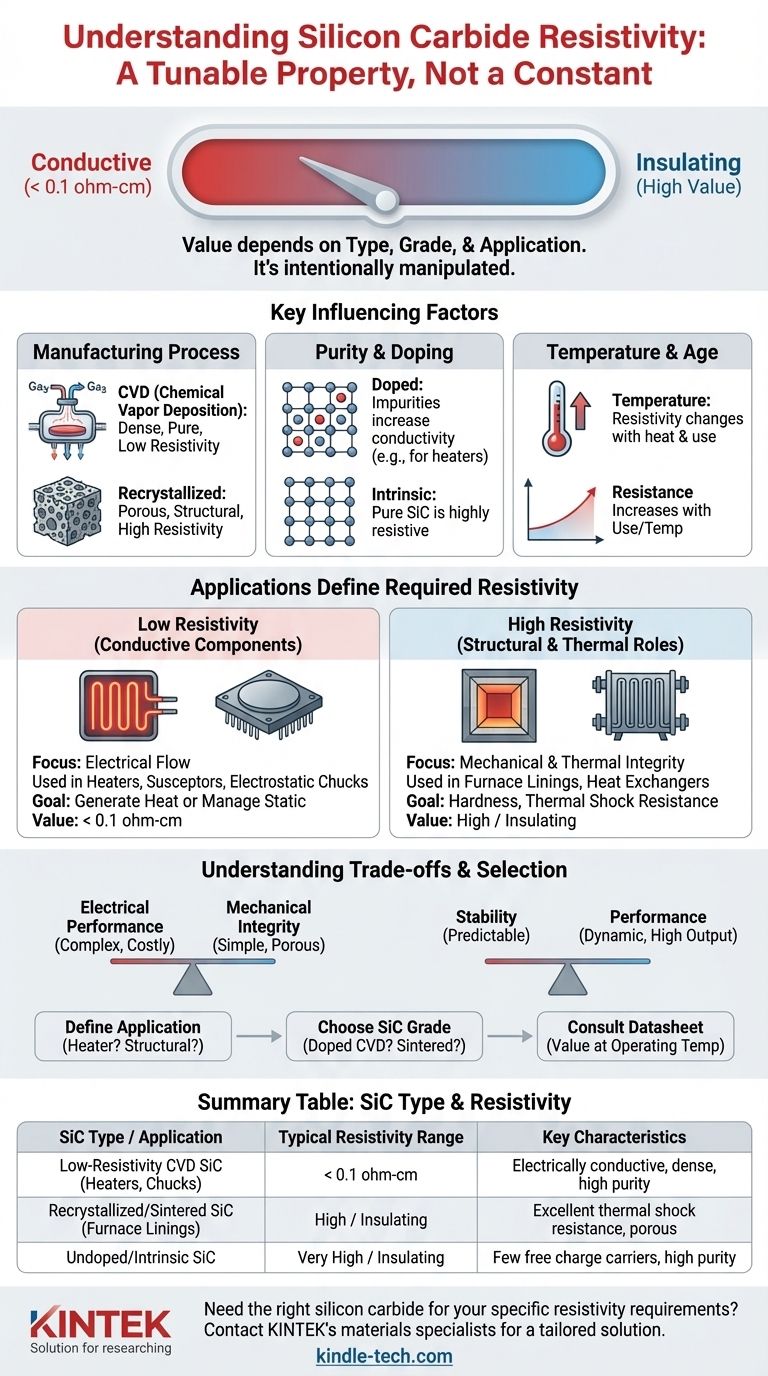
The resistivity of silicon carbide is not a single value but varies dramatically depending on its manufacturing process, purity, and intended application. While highly pure, structural forms can be quite resistive, specialized grades like low-resistivity Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) silicon carbide have a bulk resistivity of less than 0.1 ohm-cm. This wide range exists because SiC is engineered for specific tasks, from heating elements to advanced semiconductor components.
The core takeaway is that silicon carbide's resistivity is a tunable property, not a fixed natural constant. You must specify the type and grade of SiC to get a meaningful resistivity value, as it is intentionally manipulated to suit its final application.

Why "Resistivity" Isn't a Simple Number for SiC
Unlike a pure metal like copper, silicon carbide is a compound semiconductor. Its electrical properties are a direct result of its crystalline structure, purity, and the presence of intentional additives. Understanding these factors is key to understanding its resistivity.
### The Impact of Manufacturing Process
The method used to create a SiC component fundamentally alters its properties.
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) silicon carbide is theoretically dense and intrinsically pure. This process allows for the creation of low-resistivity parts, making it ideal for applications requiring electrical conductivity.
Recrystallized silicon carbide, in contrast, often has high porosity. It is valued for its thermal conductivity and shock resistance, not its electrical properties. Its resistivity is typically much higher and less controlled.
### The Role of Purity and Doping
Like other semiconductors, the electrical conductivity of SiC can be precisely controlled by introducing impurities, a process known as doping.
Undoped, intrinsically pure SiC has very few free charge carriers and is thus highly resistive.
By adding specific elements, manufacturers can dramatically decrease resistivity. This is why some SiC grades are conductive enough to be used as heating elements or electrostatic chucks.
### Temperature's Critical Influence
Silicon carbide's resistivity is highly dependent on temperature. This is a crucial consideration for its most common applications.
As noted in materials for heating elements, the resistance of SiC rods gradually increases with use and temperature changes. This behavior requires systems, like auto-transformers, to compensate for the change over the component's lifespan.
This property is leveraged in heating applications but must be accounted for in any design where stable electrical performance is required across a range of temperatures.
How Applications Define the Required Resistivity
The intended use case is the single most important factor determining the resistivity of a given silicon carbide product. Manufacturers optimize the material for the properties that matter most for that application.
### Low Resistivity for Heaters and Conductive Components
For applications like heating elements, susceptors in semiconductor processing, gas distribution plates, and electrostatic chucks, low resistivity is a design requirement.
In these cases, a specific grade like low-resistivity CVD SiC is used, providing a value less than 0.1 ohm-cm. The goal is to allow current to flow and either generate heat or manage static electricity.
### High Resistivity for Structural and Thermal Roles
When SiC is used for its excellent mechanical and thermal properties—in furnace linings, heat exchangers, or kiln furniture—its electrical resistivity is a secondary concern.
These materials are optimized for hardness, chemical inertness, and resistance to thermal shock. They are typically undoped or sintered in a way that results in a much higher, and often unspecified, electrical resistivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a type of silicon carbide always involves balancing competing properties. It is impossible to optimize for all characteristics simultaneously.
### Electrical Performance vs. Mechanical Integrity
The processes that create dense, pure, low-resistivity SiC (like CVD) are often more complex and costly than those for creating porous, structural SiC.
A highly porous, recrystallized SiC part may have superior thermal shock resistance for a furnace nozzle but would be completely unsuitable for use as an electrical heater.
### Stability vs. Performance
The very characteristic that makes SiC a good heating element—its changing resistance with temperature and age—is a significant drawback in applications requiring stable, predictable electrical performance.
Engineers must design systems that can accommodate this drift in resistivity over the component's life, adding complexity and cost to the final product.
Selecting the Right Silicon Carbide
To get a meaningful answer for your project, you must shift from asking "What is the resistivity of SiC?" to "What grade of SiC meets my resistivity requirements?"
- If your primary focus is electrical heating or conductivity: Seek out doped or low-resistivity CVD silicon carbide and consult the manufacturer's datasheet for the specific resistivity value at your target operating temperature.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature structural integrity: Prioritize recrystallized or sintered SiC grades where datasheets will emphasize mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance over electrical properties.
- If your primary focus is semiconductor fabrication: You will need highly specialized, single-crystal SiC wafers with precisely controlled doping profiles, a category entirely separate from industrial ceramics.
Ultimately, the resistivity of silicon carbide is defined by its purpose.
Summary Table:
| SiC Type / Application | Typical Resistivity Range | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Resistivity CVD SiC (Heaters, Chucks) | < 0.1 ohm-cm | Electrically conductive, dense, high purity |
| Recrystallized/Sintered SiC (Furnace Linings, Kiln Furniture) | High / Insulating | Excellent thermal shock resistance, porous, structural |
| Undoped/Intrinsic SiC | Very High / Insulating | Few free charge carriers, high purity |
Need the right silicon carbide for your specific resistivity requirements?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and materials, including silicon carbide components for heating, semiconductor processing, and high-temperature applications. Our experts can help you select the optimal SiC grade—whether you need a conductive heater or an insulating structural part—ensuring your lab achieves peak performance and reliability.
Contact our materials specialists today to discuss your project's needs and get a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Silicon Nitride (SiN) Ceramic Sheet for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of ceramic sintering? Achieve Dense, High-Performance Ceramic Parts
- What is the strength of dental ceramics? Mastering the Compressive vs. Tensile Force Balance
- What is ceramic powder used for? Unlocking High-Performance Materials for Your Industry
- What are the different types of ceramic styles? A Guide to Earthenware, Stoneware, Porcelain & Bone China
- What are the applications of cubic zirconia? From Jewelry to High-Tech Components
- What are the disadvantages of ceramic fiber? Key Handling & Durability Risks Explained
- What is the advantage of using low fusing porcelain versus high or medium fusing porcelain? Achieve Perfect PFM Crowns & Bridges
- What is the type of silicon carbide? A Guide to Polymorphs, Grades, and Applications



















