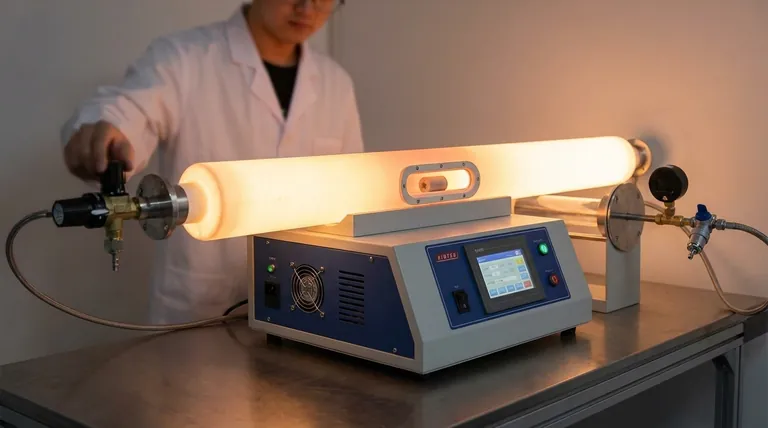
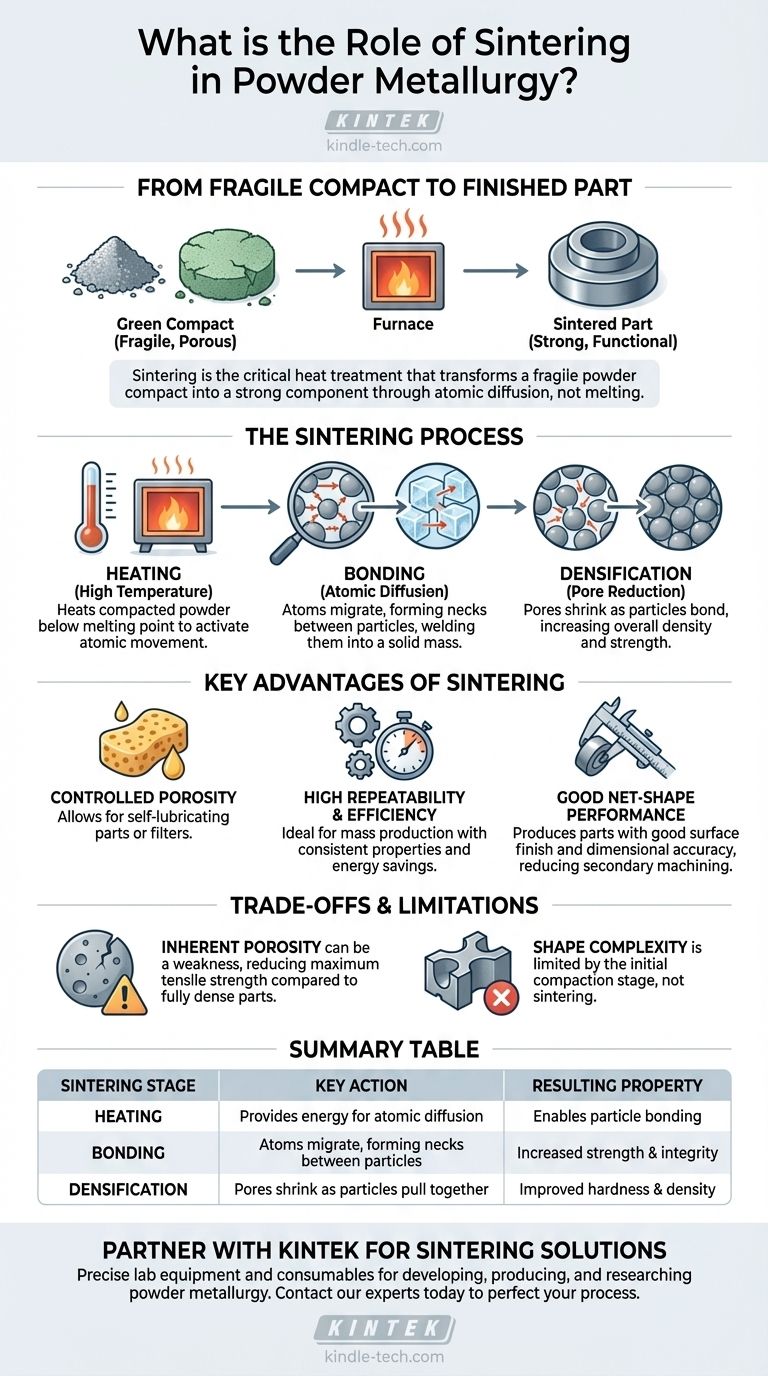
In powder metallurgy, sintering is the critical heat treatment step that transforms a fragile powder compact into a strong, functional component. This process involves heating the compacted metal powder in a controlled atmosphere to a temperature just below its melting point. This heat provides the energy for the individual particles to fuse, creating strong metallurgical bonds and giving the part its final strength, integrity, and hardness.
The core function of sintering is not to melt the metal, but to use a solid-state process of atomic diffusion to bond powder particles at their contact points. This fundamental action is what gives a powder metallurgy part its final mechanical properties and structural integrity.

From Fragile Compact to Finished Part
Before sintering, a component is merely a "green compact." It has the desired shape but is extremely fragile, held together only by the mechanical interlocking of the pressed particles. Sintering is the transformative process that turns this delicate form into a durable product.
The Role of High Temperature
Heat is the catalyst for sintering. By raising the temperature to just below the material's melting point, the atoms within the metal particles gain enough energy to move.
This atomic mobility is essential for the bonding process to occur without liquefying the entire component, which would destroy its precise, compacted shape.
Atomic Diffusion and Bonding
Think of how two ice cubes left in a glass of water will fuse at their contact points. Sintering works on a similar principle at a microscopic level.
Atoms migrate, or diffuse, across the boundaries of adjacent particles. This movement creates and strengthens the "necks" between particles, effectively welding them together into a solid, cohesive mass.
Densification and Pore Reduction
As the particles bond and pull closer together, the empty spaces, or pores, between them shrink. This process increases the overall density of the part.
Closing these porous spaces is a primary reason for the dramatic increase in strength and hardness observed in a component after it has been sintered.
The Key Advantages of the Sintering Process
Sintering is not just a necessary step; it imparts several unique and valuable characteristics to the final product, making powder metallurgy a preferred method for many applications.
Controlled Porosity
Unlike in most metalworking, porosity can be a desirable feature. Sintering allows for precise control over the amount of residual porosity in a part.
This can be used to create self-lubricating components by impregnating the pores with oil or to produce filters. The porous structure is also excellent for vibration dampening.
High Repeatability and Efficiency
Sintering is an ideal process for the mass production of parts. It allows for the creation of large series of components with highly consistent dimensions and mechanical properties.
Furthermore, because the metal is never fully melted, the process consumes significantly less energy than casting, making it a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective technology.
Good Net-Shape Performance
The process generally produces parts with a good surface finish and dimensional accuracy. This "net-shape" capability often reduces or eliminates the need for costly secondary machining operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the sintering process has inherent characteristics that must be considered when designing a component. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for successful application.
Inherent Porosity Can Be a Weakness
The same porosity that can be an advantage can also be a structural limitation. Even after sintering, some residual porosity almost always remains.
This makes sintered parts inherently less strong than fully dense components created through forging or machining from solid stock. They may not be suitable for applications requiring extremely high tensile strength or impact resistance.
Limitations on Shape Complexity
The ultimate complexity of a sintered part is often dictated by the initial compaction stage, not the sintering itself.
Features that are difficult to press into the green compact—such as undercuts or holes perpendicular to the pressing direction—cannot be created through sintering alone.
How Sintering Defines Your Final Product
Leveraging the powder metallurgy process effectively means understanding how sintering will influence your component's final properties.
- If your primary focus is creating self-lubricating parts: The controlled porosity achieved during sintering is the key feature you will leverage for oil impregnation.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing of medium-complexity parts: The repeatability, energy efficiency, and excellent surface finish of the sintering process offer significant cost advantages over other methods.
- If your primary focus is maximum material strength: You must consider that the inherent porosity of a standard sintered part may be a limitation compared to a fully dense wrought or forged component.
Ultimately, sintering is the essential bridge in powder metallurgy that converts a shaped collection of individual particles into a cohesive, engineered material with predictable properties.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Stage | Key Action | Resulting Property |
|---|---|---|
| Heating | Provides energy for atomic diffusion | Enables particle bonding |
| Bonding | Atoms migrate, forming necks between particles | Increased strength and integrity |
| Densification | Pores shrink as particles pull together | Improved hardness and density |
Ready to leverage sintering for your component manufacturing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to perfect your powder metallurgy processes. Whether you are developing self-lubricating parts, producing high-volume components, or researching new materials, our solutions help you achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific sintering and powder metallurgy needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to the formation of non-sintered LLZTO? Expert Densification Guide
- What is the difference between mechanical presses and hydraulic presses? A Guide to Choosing the Right Force
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press assist in XAS sample quality? Precision Pellets for Superior Spectral Clarity
- What are the functions of a cylindrical pelleting mold and a hydraulic press in LATP ceramics? Create High-Density Pellets
- How do you prepare a sample for XRF analysis? Master the Key Methods for Accurate Results
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press in the manufacturing of composite boards? Essential Densification
- How many PSI is a hydraulic press? Unlocking the Real Power Behind Tonnage
- What is the purpose of applying 200 MPa of pressure? Optimize NZSP Solid Electrolyte Green Body Density



















