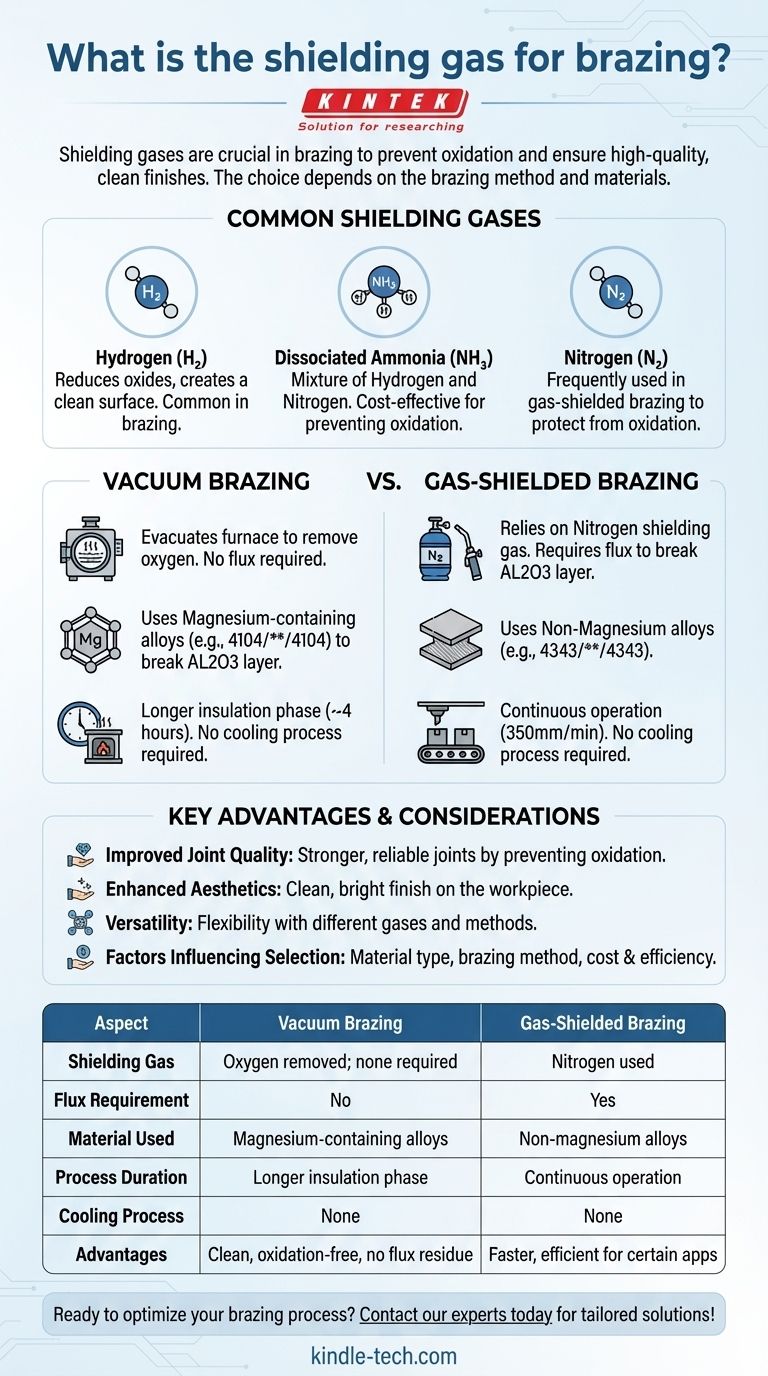
Shielding gases play a critical role in brazing processes by preventing oxidation and ensuring a clean, high-quality finish. The choice of shielding gas depends on the brazing method and the materials involved. Common shielding gases include hydrogen, dissociated ammonia, and nitrogen. In vacuum brazing, oxygen is removed entirely, while gas-shielded brazing relies on nitrogen and flux to achieve similar results. The selection of materials, such as magnesium-containing alloys for vacuum brazing or flux-dependent alloys for gas-shielded brazing, further influences the effectiveness of the shielding gas. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing brazing outcomes.

Key Points Explained:
-
Purpose of Shielding Gases in Brazing
- Shielding gases are used to create an inert atmosphere that prevents oxidation, scaling, and carbon buildup (soot) during brazing.
- They ensure a clean, bright finish on the workpiece, which is critical for achieving high-quality brazed joints.
-
Common Shielding Gases
- Hydrogen: Often used in brazing due to its ability to reduce oxides and create a clean surface.
- Dissociated Ammonia: A mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen, commonly used for its cost-effectiveness and ability to prevent oxidation.
- Nitrogen: Frequently used in gas-shielded brazing to protect the workpiece from oxidation.
-
Vacuum Brazing vs. Gas-Shielded Brazing
-
Vacuum Brazing:
- Involves evacuating the furnace to remove oxygen and other reactive gases.
- Does not require flux, as the vacuum environment eliminates the risk of oxidation.
- Uses materials like 4104/****/4104 double compound, which contains 1.5% magnesium to break through the AL203 layer on the workpiece surface.
-
Gas-Shielded Brazing:
- Relies on nitrogen as the shielding gas to protect the workpiece.
- Requires the application of flux to break the AL203 layer, as the materials used (e.g., 4343/****/4343 double compound) do not contain magnesium.
-
Vacuum Brazing:
-
Material Considerations
- Magnesium-Containing Alloys (e.g., 4104/****/4104): Used in vacuum brazing, magnesium helps break through the AL203 layer, ensuring proper bonding.
- Non-Magnesium Alloys (e.g., 4343/****/4343): Used in gas-shielded brazing, these materials rely on flux to achieve the same effect.
-
Process Differences
-
Vacuum Brazing:
- Involves a longer insulation phase (about 4 hours per furnace) to ensure uniform temperature distribution.
- No cooling process is required after brazing.
-
Gas-Shielded Brazing:
- Operates continuously at a speed of 350mm/min.
- Does not require a vacuum or cooling process, making it faster and more efficient for certain applications.
-
Vacuum Brazing:
-
Advantages of Shielding Gases
- Improved Joint Quality: Shielding gases prevent oxidation, leading to stronger and more reliable brazed joints.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: The use of inert gases results in a clean, bright finish on the workpiece.
- Versatility: Different gases and methods (vacuum vs. gas-shielded) allow for flexibility in addressing various brazing challenges.
-
Factors Influencing Gas Selection
- Material Type: The choice of shielding gas depends on the alloy being brazed and its specific requirements (e.g., magnesium content).
- Brazing Method: Vacuum brazing and gas-shielded brazing have distinct gas requirements.
- Cost and Efficiency: Dissociated ammonia is often chosen for its cost-effectiveness, while nitrogen is preferred for its availability and ease of use in gas-shielded brazing.
By understanding the role of shielding gases and their application in different brazing processes, manufacturers can optimize their operations to achieve superior results. The choice of gas, material, and method should align with the specific requirements of the workpiece and the desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Brazing | Gas-Shielded Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Shielding Gas | Oxygen removed entirely; no shielding gas required | Nitrogen used as shielding gas |
| Flux Requirement | No flux required | Flux required to break AL203 layer |
| Material Used | Magnesium-containing alloys (e.g., 4104/****/4104) | Non-magnesium alloys (e.g., 4343/****/4343) |
| Process Duration | Longer insulation phase (~4 hours per furnace) | Continuous operation at 350mm/min |
| Cooling Process | No cooling required | No cooling required |
| Advantages | Clean, oxidation-free joints; no flux residue | Faster and more efficient for certain applications |
Ready to optimize your brazing process? Contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification



















