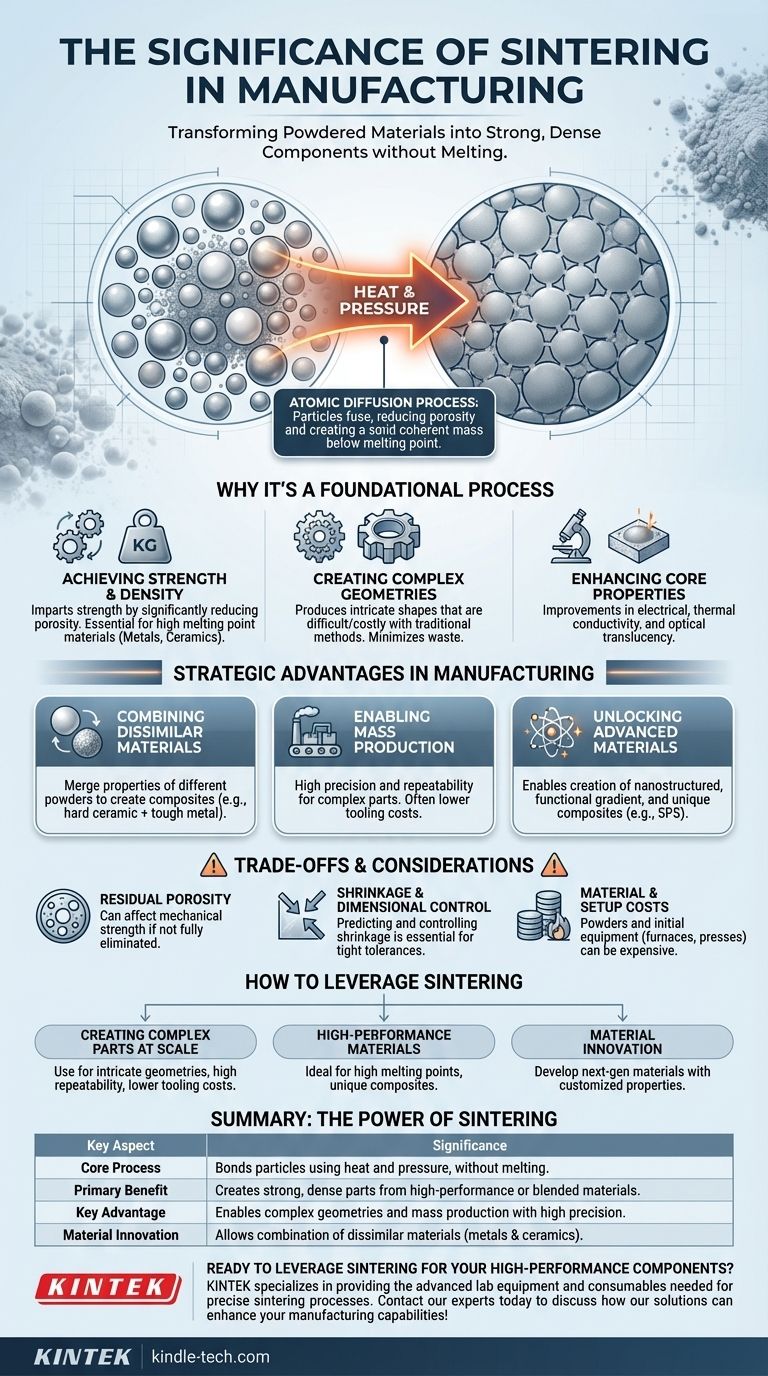
At its core, the significance of sintering lies in its ability to transform powdered materials into a solid, coherent mass using heat and pressure, all without melting the material. This process is fundamental to modern manufacturing because it creates strong, dense, and precisely shaped components from materials that are difficult or impossible to work with using traditional methods like casting or machining.
Sintering is a critical technology because it solves a fundamental manufacturing challenge: how to create strong, complex parts from high-performance or blended materials. It enables the production of components with unique properties by bonding particles together, offering a level of design freedom and material innovation that other methods cannot match.

Why Sintering is a Foundational Process
Sintering is more than just heating a powder; it's a controlled process of atomic diffusion that fundamentally changes a material's structure and enhances its properties.
Achieving Strength and Density Without Melting
The primary function of sintering is to impart strength and integrity to a loosely compacted powder.
By applying heat below the material's melting point, atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, causing them to fuse together. This process significantly reduces the porosity of the initial material, creating a dense, solid object.
This is especially significant for working with metals and ceramics with extremely high melting points, as it allows them to be formed into solid parts without the immense energy and complex equipment required for melting.
Creating Complex and Intricate Geometries
Sintering excels at producing components with intricate shapes and complex geometries that are exceptionally difficult or costly to achieve with conventional manufacturing.
Because the process starts with a powder that can be molded or pressed, it allows for near-net-shape manufacturing. This minimizes material waste and the need for extensive post-processing or machining.
Enhancing Core Material Properties
The densification that occurs during sintering directly enhances a material's physical characteristics.
Beyond simple strength, the process can significantly improve properties like electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and even optical translucency in certain ceramics.
The Strategic Advantages in Manufacturing
The principles of sintering translate into powerful, real-world advantages for engineers and product designers.
Combining Dissimilar Materials
Sintering makes it possible to merge the properties of multiple materials into a single component.
By mixing different powders before compaction—for example, a hard ceramic with a tough metal—you can create composite parts that possess combined characteristics, such as high abrasion resistance and excellent impact toughness.
Enabling Mass Production with High Precision
For complex parts, sintering can be a highly economical solution for rapid mass production.
The process provides excellent repeatability and dimensional accuracy while often requiring lower-cost tooling compared to other methods, making it a key technology for industries from automotive to electronics.
Unlocking Advanced and Novel Materials
Modern sintering techniques are pushing the boundaries of material science.
Processes like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) are key enabling technologies for creating nanostructured materials, functional gradient materials, and unique composites that were previously unobtainable.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, sintering is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for successful application.
Porosity is a Critical Factor
The primary goal of sintering is to reduce porosity, but achieving full theoretical density can be difficult. Any residual porosity can become a weak point in the final component, potentially compromising its mechanical strength.
Shrinkage and Dimensional Control
As the material densifies during sintering, the part inevitably shrinks. Accurately predicting and controlling this shrinkage is essential to meet tight dimensional tolerances, which often requires significant process expertise.
Material and Initial Setup Costs
While tooling can be economical for high-volume production, the specialized metal or ceramic powders themselves can be expensive. Furthermore, the initial investment in furnaces and presses can be substantial.
How to Leverage Sintering for Your Project
Choosing to use sintering depends entirely on your project's specific goals for material performance, geometric complexity, and production volume.
- If your primary focus is creating complex parts at scale: Sintering provides an outstanding method for manufacturing intricate geometries with high repeatability and potentially lower tooling costs.
- If your primary focus is high-performance materials: The process is ideal for forming components from metals and ceramics with high melting points or for creating unique composites by blending different powders.
- If your primary focus is material innovation: Advanced sintering techniques open the door to developing next-generation materials with customized, previously unattainable properties.
Ultimately, sintering is a foundational technology that gives engineers the power to build stronger, more complex, and more capable components.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Significance |
|---|---|
| Core Process | Bonds particles using heat and pressure, without melting the material. |
| Primary Benefit | Creates strong, dense parts from high-performance or blended materials. |
| Key Advantage | Enables complex geometries and mass production with high precision. |
| Material Innovation | Allows combination of dissimilar materials (e.g., metals and ceramics). |
Ready to leverage sintering for your high-performance components? KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for precise sintering processes. Our expertise helps you achieve superior material properties and complex part geometries. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your manufacturing capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution



















