Crucially, there is no single sintering temperature for all polymers. The correct temperature is entirely dependent on the specific material's unique thermal properties. A value like 630°C is exceptionally high and only applies to specialized, high-performance composites or materials where a polymer binder is being burned out, not for common polymers like nylon or polyethylene, which would degrade long before reaching such a temperature.
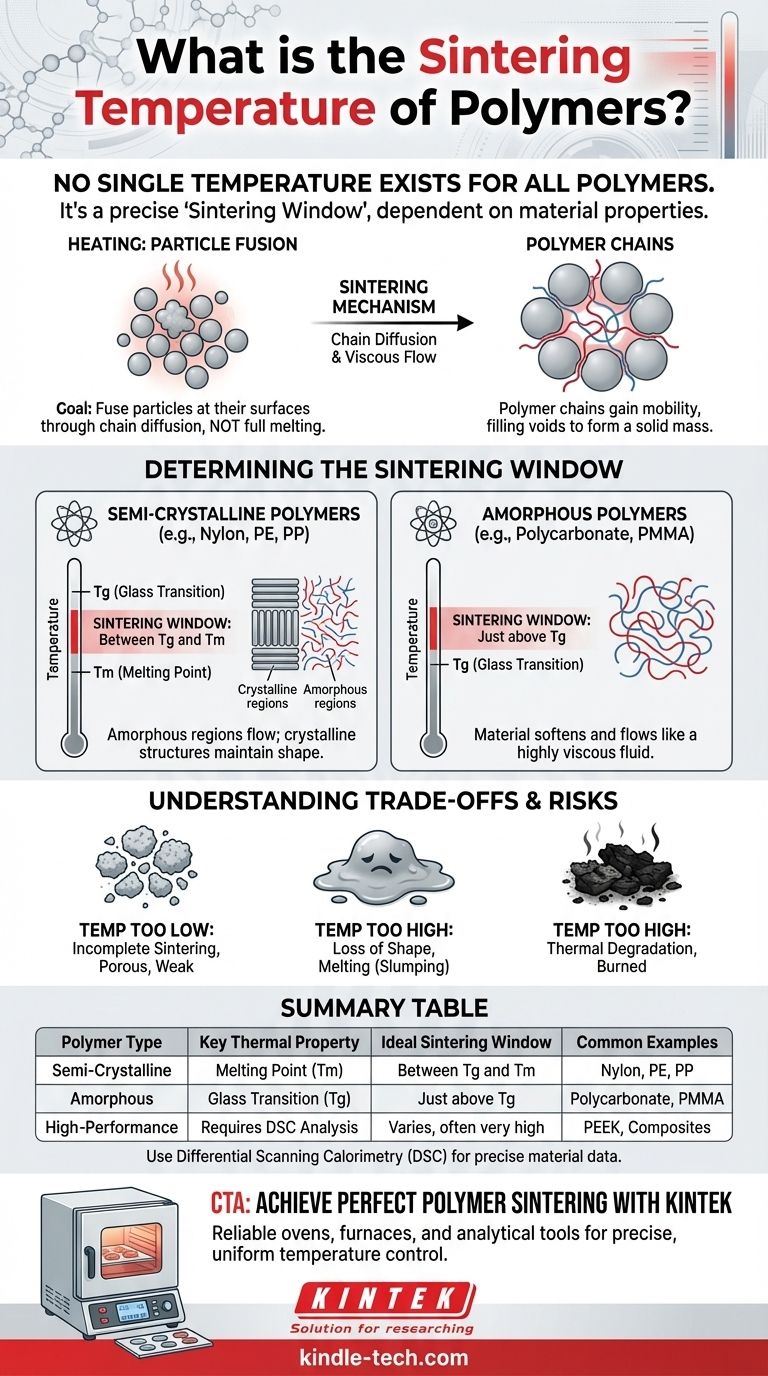
The core principle of polymer sintering is not to melt the material, but to heat it to a precise "sintering window." This is the temperature range where polymer chains have enough mobility to fuse particles together without causing the bulk material to lose its shape or thermally degrade.

What is Polymer Sintering?
Polymer sintering is a thermal process that converts a polymer powder into a solid, coherent mass. This is a fundamental technique used in processes like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing and the manufacturing of porous components like filters.
The Goal: Fusing Particles, Not Melting
Unlike injection molding, where the polymer is fully melted into a liquid, sintering aims to join powder particles at their surfaces.
Heat provides the energy for this fusion, reducing the surface area of the powder mass and creating a denser, stronger object.
The Mechanism: Chain Diffusion and Viscous Flow
When heated, the long-chain molecules of the polymer gain mobility. They begin to diffuse across the boundaries of individual powder grains.
This process, known as viscous flow, fills the voids between particles, effectively welding them together on a microscopic level to form a solid part.
How to Determine the Sintering Temperature
Finding the optimal temperature is a balancing act. It requires understanding two critical thermal transitions: the glass transition temperature (Tg) and the melting temperature (Tm).
The "Sintering Window"
The ideal processing zone is called the sintering window. This is the temperature range that enables particle fusion without causing catastrophic failure of the part.
For Semi-Crystalline Polymers (e.g., Nylon, PE, PP)
These polymers have both amorphous (disordered) and crystalline (ordered) regions. Their sintering window lies between the glass transition temperature (Tg) and the melting temperature (Tm).
Heating above Tg gives the amorphous regions rubbery, liquid-like properties, enabling the chains to flow and fuse. Staying below Tm preserves the crystalline structures, which act as a scaffold to maintain the object's overall shape.
For Amorphous Polymers (e.g., Polycarbonate, PMMA)
These polymers lack a crystalline structure and do not have a distinct melting point. For them, sintering occurs at temperatures just above their glass transition temperature (Tg).
Once past Tg, the entire material softens and behaves like a highly viscous fluid, allowing the particles to slowly fuse.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Factors
The choice of temperature has direct consequences on the final part's quality. This is not a forgiving process.
Temperature Too Low: Incomplete Sintering
If the temperature is not high enough to provide sufficient chain mobility, the particles will not fuse properly.
This results in a "green" part that is porous, brittle, and has poor mechanical properties. It will easily crumble or break.
Temperature Too High: Loss of Shape or Degradation
Exceeding the sintering window is disastrous. For semi-crystalline polymers, heating above Tm will cause the entire part to melt and "slump" into a puddle, losing all definition.
For all polymers, excessively high temperatures will cause thermal degradation, where the polymer chains themselves break down. The material may char, discolor, or burn, permanently ruining its chemical structure and integrity.
The Special Case of High-Performance Polymers
A temperature of 630°C, as mentioned in the reference, is far outside the processing range for nearly all common thermoplastics. Such a temperature suggests one of two scenarios:
- A Polymer-Ceramic or Polymer-Metal Composite: The process may involve sintering the non-polymer material while a polymer binder is burned away.
- A Typographical Error: Standard high-performance polymers like PEEK have a melting point around 343°C and would severely degrade at 630°C.
This highlights the absolute necessity of knowing the specific material you are working with.
Other Factors: Particle Size and Pressure
Smaller powder particles have a higher surface-area-to-volume ratio and will sinter faster and at slightly lower temperatures than larger particles.
Applying external pressure, as in hot pressing, can also lower the required sintering temperature by physically forcing the particles into closer contact.
Finding the Right Temperature for Your Polymer
To successfully sinter a polymer, you must move from generalized rules to material-specific data. Use the following guidelines to inform your approach.
- If your primary focus is a common semi-crystalline polymer (e.g., Nylon, PE): Your starting point for process development is the temperature range between its known glass transition (Tg) and melting (Tm) temperatures.
- If your primary focus is an amorphous polymer (e.g., Polycarbonate): Begin your experiments at temperatures slightly above its glass transition temperature (Tg), increasing incrementally.
- If your primary focus is a high-performance or unknown polymer: You must obtain a Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) analysis. This test will generate a thermal curve that definitively identifies your material's specific Tg and Tm, revealing its true sintering window.
Understanding these core thermal properties transforms sintering from guesswork into a precise and repeatable engineering process.
Summary Table:
| Polymer Type | Key Thermal Property | Ideal Sintering Window | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-Crystalline | Melting Point (Tm) | Between Tg and Tm | Nylon, Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP) |
| Amorphous | Glass Transition (Tg) | Just above Tg | Polycarbonate, PMMA |
| High-Performance/Composite | Requires DSC Analysis | Varies; can be very high | PEEK, Polymer-Ceramic Composites |
Achieve Perfect Polymer Sintering Results with KINTEK
Mastering the precise sintering window for your specific polymer is critical for producing strong, dimensionally accurate parts. Whether you are working with common thermoplastics for 3D printing or high-performance composites, having the right lab equipment is non-negotiable.
KINTEK specializes in supplying the reliable ovens, furnaces, and analytical tools you need to succeed. Our equipment provides the precise temperature control and uniform heating essential for hitting your material's sintering target without the risk of thermal degradation or slumping.
Let us help you optimize your process. Our experts can recommend the perfect thermal processing solution for your laboratory's specific polymer applications.
Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and ensure your next sintering project is a success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of ash determination? Choosing the Right Technique for Accurate Mineral Analysis
- How do you measure ash content? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results
- How do you determine the ash content of a plant sample? A Step-by-Step Guide to Mineral Analysis
- What does a high ash content mean? A Guide to Material Quality & Contamination
- What is the difference between a box furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Furnace for Your Application



















