At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is an advanced powder consolidation technique that uses simultaneous uniaxial pressure and a pulsed direct electrical current to transform loose powder into a dense, solid material. This process occurs at an exceptionally rapid rate, achieving full densification in minutes rather than the hours required by conventional methods.
Spark Plasma Sintering is not merely a faster way to heat material. It is a fundamentally different approach that uses an electric field to activate powder particles directly, enabling densification at lower temperatures and with greater speed, thereby preserving fine-grained microstructures that are critical for high-performance materials.

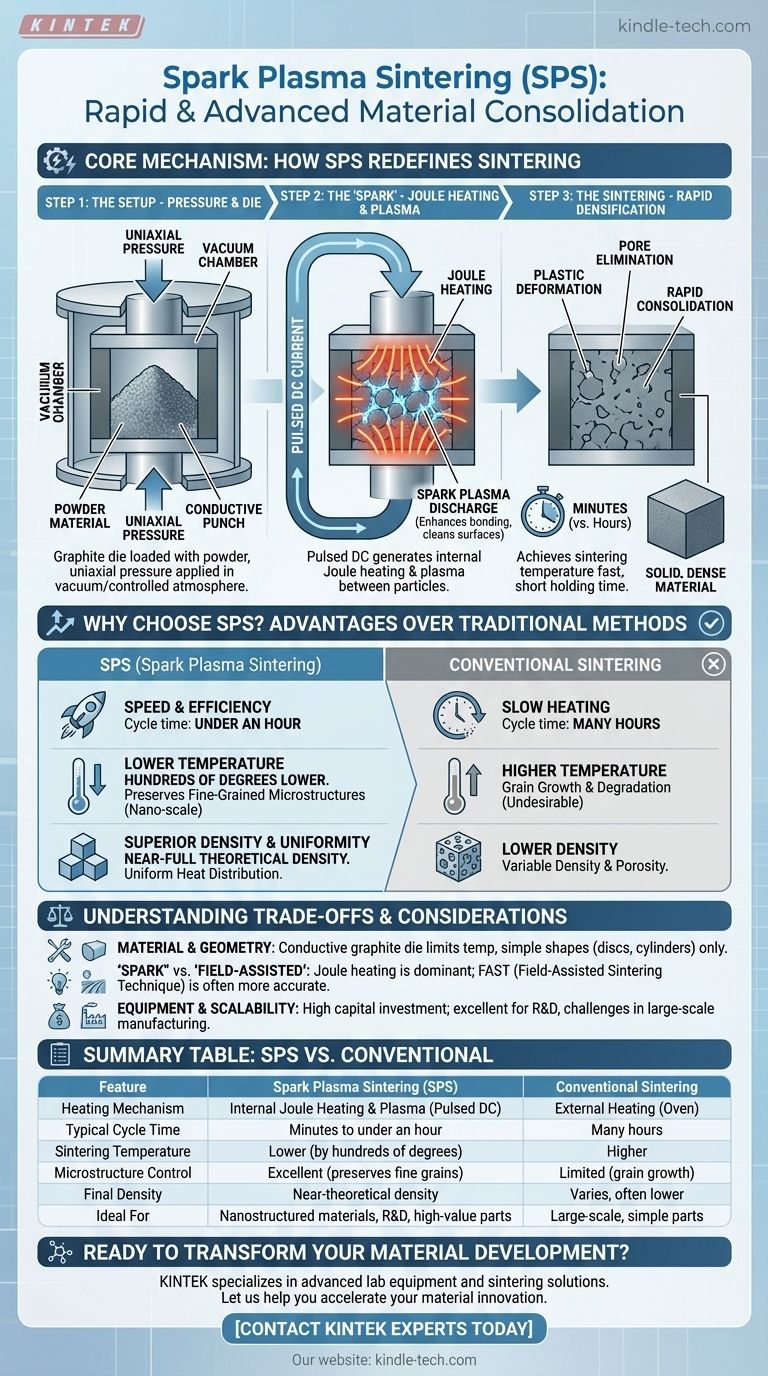
How SPS Redefines Sintering: The Core Mechanism
Traditional sintering is like a conventional oven; it slowly heats a material from the outside in. SPS, also known as Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST), is more like a combination of a hydraulic press and a targeted internal heating system.
Step 1: The Setup - Pressure and a Die
The process begins by loading the powder material into a conductive die, which is almost always made of graphite. This die is then placed between two punches inside a vacuum chamber.
A uniaxial mechanical pressure is applied through the punches, compacting the loose powder. The chamber is evacuated to create a vacuum or filled with a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation and contamination.
Step 2: The "Spark" - Joule Heating and Plasma
Once the pressure and atmosphere are set, a high-amperage, pulsed direct current (DC) is passed through the punches and the graphite die. This current is the key to the entire process and generates intense heat through two primary effects.
The dominant effect is Joule heating. The electrical resistance of the graphite die and, if conductive, the sample powder itself, generates rapid and uniform heat. This heats the sample both externally (from the die) and internally (from within the powder).
A secondary effect, which gives the method its name, is the generation of spark plasma discharge in the voids between powder particles. This momentary plasma helps clean particle surfaces of oxides and impurities, which enhances bonding.
Step 3: The Sintering - Rapid Densification
The combination of intense, uniform heat and constant mechanical pressure causes the powder particles to undergo plastic deformation. The particles bond at their contact points, and the pores between them are eliminated.
Because the heating rates can be as high as 1000°C/min, the material reaches its sintering temperature almost instantly. This allows the entire densification process to be completed in a very short holding time, often just a few minutes.
Why Choose SPS? Key Advantages Over Traditional Methods
SPS offers distinct advantages that make it the preferred method for producing advanced ceramics, composites, and novel alloys.
Unprecedented Speed and Efficiency
The most significant advantage of SPS is its speed. By eliminating the long heating, soaking, and cooling times of conventional furnaces, SPS drastically shortens the production cycle from many hours to under an hour.
Lower Temperature, Better Microstructure
SPS typically achieves full densification at temperatures several hundred degrees lower than conventional sintering. This is critical because high temperatures and long exposure times cause undesirable grain growth, which can degrade a material's mechanical properties.
By minimizing both temperature and time, SPS is exceptional at producing nanostructured or fine-grained materials, preserving the unique properties that come from these small-scale features.
Superior Density and Uniformity
The combination of internal Joule heating and external heating from the die ensures a highly uniform temperature distribution throughout the sample. This, coupled with the applied pressure, effectively eliminates porosity and consistently produces materials with near-full theoretical density.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Material and Geometry Limitations
The standard SPS process relies on a conductive graphite die, which limits the maximum processing temperature and can cause carbon contamination in sensitive materials. Furthermore, the uniaxial pressure setup restricts sample geometries to relatively simple shapes like discs, cylinders, and squares.
The "Spark" vs. "Field-Assisted" Distinction
While "Spark Plasma Sintering" is the common name, many experts prefer the more accurate term Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST). This is because research indicates that Joule heating is the dominant mechanism, and a sustained plasma is not always present or necessary for densification.
Equipment and Scalability
SPS systems are specialized and represent a significant capital investment compared to conventional furnaces. While excellent for research, development, and high-value component production, scaling the process for very large parts or high-volume manufacturing remains a challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Deciding whether to use SPS depends entirely on your material and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping and developing novel materials: SPS is an unparalleled tool, as its speed allows for quick iteration and experimentation.
- If your primary focus is preserving nano-scale or fine-grained microstructures: SPS is the superior choice, as its low temperature and short duration prevent the grain growth common in other methods.
- If your primary focus is creating materials with the highest possible density: SPS excels at eliminating porosity and achieving near-theoretical density, especially for difficult-to-sinter materials.
- If your primary focus is producing large, geometrically complex parts at low cost: Traditional methods like casting or conventional press-and-sinter routes are likely more suitable.
SPS is a transformative technology that empowers the creation of next-generation materials by offering precise control over the densification process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Internal Joule Heating & Plasma (Pulsed DC) | External Heating (Oven) |
| Typical Cycle Time | Minutes to under an hour | Many hours |
| Sintering Temperature | Lower (by hundreds of degrees) | Higher |
| Microstructure Control | Excellent (preserves fine grains) | Limited (grain growth) |
| Final Density | Near-theoretical density | Varies, often lower |
| Ideal For | Nanostructured materials, R&D, high-value parts | Large-scale, simple parts |
Ready to Transform Your Material Development with SPS?
Spark Plasma Sintering is the key to unlocking the potential of advanced ceramics, composites, and novel alloys. If your research or production demands rapid prototyping, preservation of fine-grained microstructures, or achieving near-theoretical density, the right equipment is critical.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including sintering solutions, to meet the precise needs of laboratories and research facilities.
Let us help you accelerate your material innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss how SPS technology can benefit your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot press furnace? Optimize TZC Molybdenum Alloy Molding with Direct Processing
- What functions do high-purity graphite molds serve for IZO targets? Ensure Density and Prevent Sintering Cracks
- How does a vacuum hot press sintering furnace contribute to Al0.6CoCrFeNi/5052Al? Achieve 100% Dense Composites
- What technical conditions does a vacuum hot press sintering furnace provide? Master In-Situ TiC/Ti Synthesis
- What is hot press forging? Creating Complex, High-Strength Metal Components
- What are the process advantages of using a vacuum hot press vs. HIP? Simplify your steel preparation workflow.
- Why is precise pressure control from a vacuum hot press furnace necessary for IZO ceramic targets? Ensure High Density
- What specific functions does the high-vacuum environment of a Vacuum Hot Pressing Furnace serve? Master AMC Consolidation



















