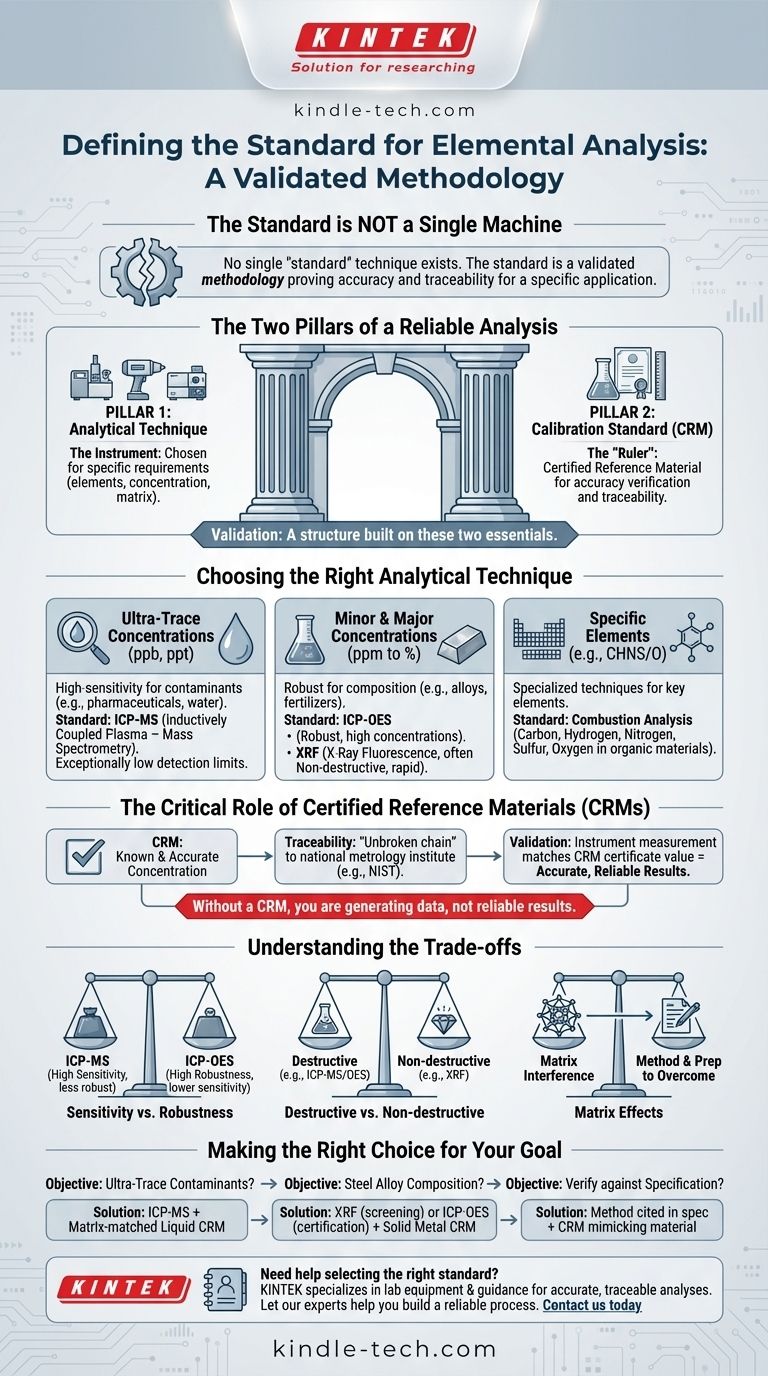
The short answer is that there is no single "standard" technique for elemental analysis. Instead, the standard is a validated methodology that combines the appropriate analytical instrument with a Certified Reference Material (CRM) to prove accuracy and traceability for a specific application. The "best" method depends entirely on the elements being measured, their expected concentration, and the material they are in (the matrix).
The fundamental standard in elemental analysis is not a particular machine, but the proven ability to produce accurate and repeatable results. This is achieved by selecting the right analytical technique for the job and verifying its performance against a Certified Reference Material traceable to a national metrology institute like NIST.

The Two Pillars of a Reliable Analysis
To understand the standard, you must think of it as a structure built on two essential pillars: the analytical technique and the calibration standard. One cannot provide a reliable result without the other.
Pillar 1: The Analytical Technique
This is the instrument used to perform the measurement. The choice of technique is the most critical decision and is dictated by the specific requirements of the analysis.
Pillar 2: The Calibration Standard (CRM)
This is the "ruler" you use to measure your sample. A Certified Reference Material is a sample manufactured to have a highly accurate and known concentration of specific elements, allowing you to verify your instrument is working correctly.
Choosing the Right Analytical Technique
Different instruments are designed for different tasks. They vary widely in sensitivity, speed, cost, and the types of samples they can handle.
For Ultra-Trace Concentrations (ppb, ppt)
When you need to find minute quantities of an element, such as heavy metal contaminants in pharmaceuticals or drinking water, high-sensitivity techniques are the standard.
The most common choice here is Inductively Coupled Plasma - Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). It offers exceptionally low detection limits for a wide array of elements simultaneously.
For Minor and Major Concentrations (ppm to %)
When analyzing for major components, such as the composition of a metal alloy or the nutrients in a fertilizer, other techniques are more suitable.
Inductively Coupled Plasma - Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) is a workhorse in this domain. It is robust, handles higher concentrations than ICP-MS, and is less expensive to operate.
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) is another key technique, especially for solids like metals, minerals, and polymers. Its primary advantage is that it is often non-destructive, providing rapid analysis with minimal sample preparation.
For Specific Elements
Some elements are best measured with specialized techniques. For example, Combustion Analysis is the standard for determining the total percentage of Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Sulfur, or Oxygen (CHNS/O) in organic materials.
The Critical Role of Certified Reference Materials (CRMs)
An instrument's result is meaningless until it is proven to be accurate. This is the job of a CRM.
What Makes a Material "Certified"?
A CRM is not just a sample with a known value. It has a legally defensible "unbroken chain of comparisons" back to a primary standard, such as those maintained by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the United States. This property is called traceability.
How CRMs Ensure Accuracy
To validate a method, an analyst runs the CRM as if it were an unknown sample. If the instrument's measurement of the CRM matches the value on its certificate within an acceptable margin of error, the method is considered validated and accurate. Without this step, you are generating data, not reliable results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single technique is perfect for every situation. A true expert understands the compromises involved.
Sensitivity vs. Robustness
ICP-MS provides incredible sensitivity but is more susceptible to interferences and can be easily overwhelmed by high-concentration samples. ICP-OES is far more robust for high-concentration work but cannot detect the ultra-trace levels that ICP-MS can.
Destructive vs. Non-destructive
Most high-sensitivity techniques, like ICP-MS and ICP-OES, are destructive. They require the sample to be dissolved in acid, permanently altering it. In contrast, XRF is typically non-destructive, making it ideal for analyzing valuable or unique items.
The Challenge of "Matrix Effects"
The substance the element is in—the matrix—can significantly interfere with the measurement. For example, measuring lead in salt water is much harder than measuring it in pure water. A key part of developing a standard method is choosing a technique and a sample preparation procedure that overcomes these matrix effects.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct standard, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is detecting heavy metal contaminants at the lowest possible levels: The industry standard is to use ICP-MS, validated with a matrix-matched liquid CRM.
- If your primary focus is determining the composition of a steel alloy: The standard would be either XRF for rapid screening or ICP-OES for high-accuracy certification, validated with a solid metal CRM of a similar alloy.
- If your primary focus is verifying a raw material against a product specification sheet: The standard is to use the analytical method cited in the specification and confirm its accuracy using a CRM that closely mimics your material.
Ultimately, the standard for elemental analysis is a rigorous, validated process, not just a single piece of equipment.
Summary Table:
| Analytical Goal | Recommended Technique | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-Trace Analysis (ppb, ppt) | ICP-MS | Exceptional sensitivity for contaminants |
| Minor/Major Concentrations (ppm to %) | ICP-OES / XRF | Robust, versatile; XRF is non-destructive |
| CHNS/O in Organic Materials | Combustion Analysis | Specific, accurate for key elements |
Need help selecting the right standard for your elemental analysis?
Choosing the correct analytical technique and validating it with the proper Certified Reference Materials is critical for generating defensible data. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with expert guidance to ensure your analyses are accurate, traceable, and compliant.
Let our experts help you build a reliable analytical process. Contact us today to discuss your specific application and requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
People Also Ask
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials



















