At their core, dental ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic materials, primarily silicate-based, that are formed by heating minerals to extreme temperatures in a process known as sintering. Their defining characteristic is a duality: they possess exceptional compressive strength, making them ideal for resisting chewing forces, but exhibit very low tensile strength and are inherently brittle. This means they can fracture suddenly when subjected to bending or pulling stresses.
The fundamental challenge and genius of modern dentistry is in harnessing the unique properties of ceramics. Their atomic structure provides unparalleled aesthetics and hardness but also creates an inherent brittleness that must be managed through precise clinical application.

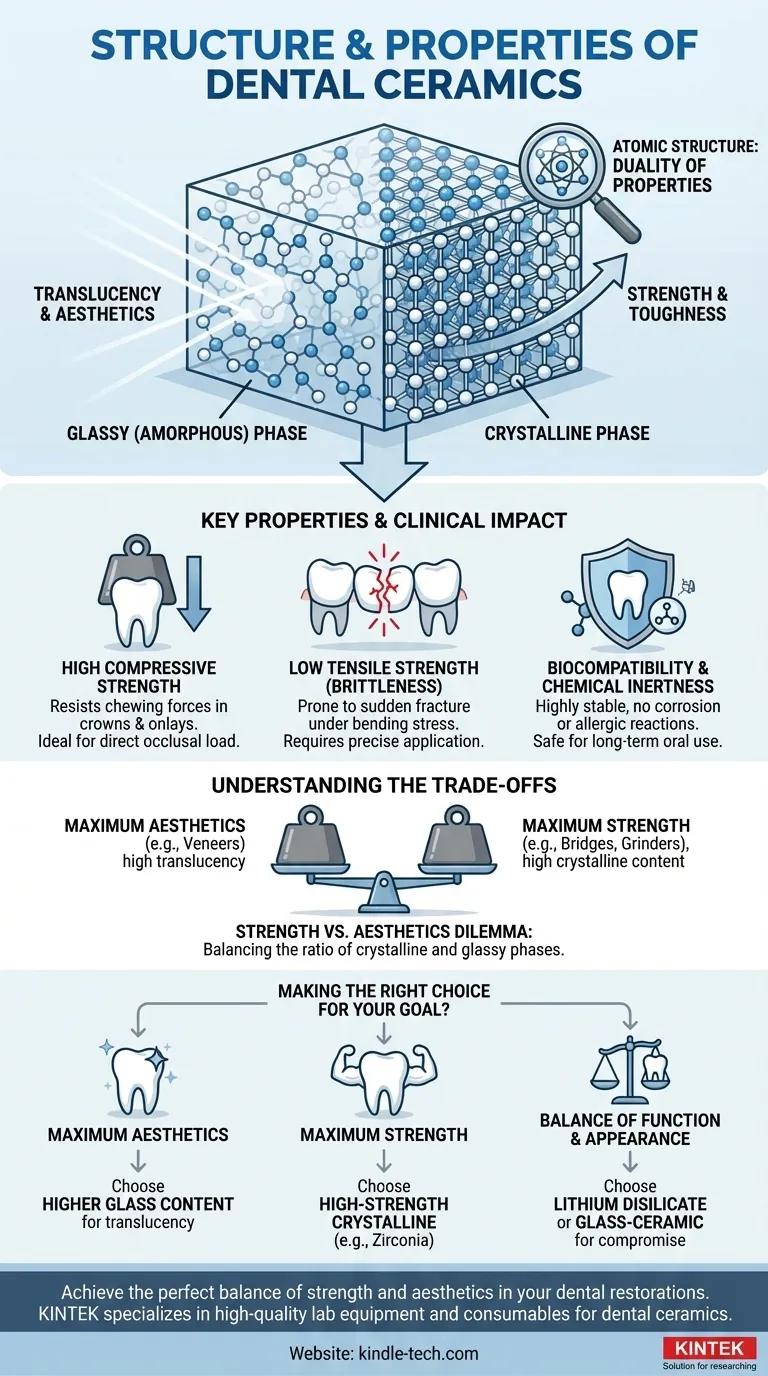
The Atomic Basis for Ceramic Properties
To understand how ceramics perform in the mouth, we must first look at their internal structure. Unlike metals, which have a simple, uniform crystalline lattice, ceramics are often a composite of two distinct phases.
The Glassy and Crystalline Phases
Most dental ceramics contain a glassy (amorphous) phase and a crystalline phase. The glassy phase consists of a disordered network of atoms, which allows light to pass through, providing the material's crucial translucency and aesthetic appeal.
The crystalline phase consists of atoms arranged in a highly ordered, repeating lattice. These crystals act as a reinforcing filler within the glass matrix, disrupting crack propagation and significantly increasing the material's overall strength and toughness.
Strong Bonds, Limited Plasticity
The atoms within both phases are held together by extremely strong ionic and covalent bonds. These powerful bonds are what give ceramics their high hardness, chemical stability, and resistance to compression.
However, these bonds are also rigid. They do not allow for the atomic slip that occurs in metals when they are bent. Instead of deforming, the bonds break, a crack propagates, and the material fractures. This explains their fundamental brittleness.
Key Properties and Their Clinical Impact
The unique atomic structure of ceramics translates directly to a set of properties that define their use in restorative dentistry.
High Compressive Strength
This is the greatest advantage of dental ceramics. They are exceptionally resistant to being crushed, which is why they perform so well under the direct chewing forces experienced by crowns and onlays.
Low Tensile Strength (Brittleness)
This is their primary weakness. When a ceramic restoration is flexed or pulled, tensile forces concentrate at the tips of microscopic surface flaws. Because the material cannot deform to distribute this stress, a crack can propagate rapidly, leading to a complete, catastrophic fracture.
Biocompatibility and Chemical Inertness
Ceramics are highly stable and do not corrode or release ions in the oral environment. This makes them one of the most biocompatible materials available, with virtually no risk of allergic or toxic reactions.
Superior Aesthetics
The ability to control the ratio of glass to crystals allows manufacturers to create materials that mimic the color, translucency, and fluorescence of natural enamel with unmatched fidelity. This makes them the premier material for highly visible restorations.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
Selecting and using a dental ceramic successfully requires a clear understanding of its built-in compromises. Every clinical decision involves balancing competing properties.
The Strength vs. Aesthetics Dilemma
This is the classic trade-off. Increasing the amount and density of the crystalline phase (as in zirconia) dramatically improves strength but makes the material more opaque, reducing its aesthetic potential.
Conversely, ceramics with a higher proportion of the glassy phase (as in feldspathic porcelain) are more translucent and lifelike but are significantly weaker and more prone to fracture.
The Risk of Catastrophic Failure
Unlike a metal alloy that may bend or deform under excessive load, a ceramic restoration will fail suddenly and completely once its fracture toughness is exceeded. This places immense importance on proper tooth preparation, precise fit, and careful management of the patient's bite to minimize tensile stress on the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal ceramic is always the one that meets the specific demands of the clinical situation. Your decision should be guided by the primary goal of the restoration.
- If your primary focus is maximum aesthetics (e.g., anterior veneers): Choose a ceramic with a higher glass content that prioritizes translucency and light transmission.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength (e.g., posterior bridges or crowns on a heavy grinder): Choose a high-strength, predominantly crystalline ceramic like zirconia that can withstand immense occlusal forces.
- If your primary focus is a balance of function and appearance (e.g., a single molar crown): Modern lithium disilicate or glass-ceramic materials offer an excellent compromise, providing good strength without sacrificing aesthetics.
Ultimately, mastering dental ceramics means leveraging their immense compressive strength while meticulously protecting them from their inherent brittleness.
Summary Table:
| Property | Clinical Impact | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| High Compressive Strength | Resists chewing forces in crowns and onlays. | Ideal for direct occlusal load. |
| Low Tensile Strength (Brittle) | Prone to sudden fracture under bending stress. | Requires precise clinical application. |
| Biocompatibility & Chemical Inertness | Highly stable, no corrosion or allergic reactions. | Safe for long-term oral use. |
| Superior Aesthetics | Mimics natural enamel translucency and color. | Premier choice for visible restorations. |
Ready to achieve the perfect balance of strength and aesthetics in your dental restorations? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for dental ceramics, helping you master material selection and fabrication for superior clinical outcomes. Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's precision and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of zirconia ceramics? Unlock High-Performance Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- Why are zirconia grinding balls recommended for sulfide solid electrolytes? Essential Tips for High Purity Milling
- Why are high-purity zirconia grinding balls recommended for LATP ceramic powders? Ensure Purity and High Conductivity.
- What are the advantages of using zirconia milling jars for sulfide electrolytes? Enhance Purity and Conductivity














