At its core, a hydraulic press is a force-multiplying system. It uses an incompressible fluid, typically oil, to translate a small applied force on a small piston into a significantly larger force on a larger piston. This entire system operates on a fundamental principle of fluid mechanics known as Pascal's Law.
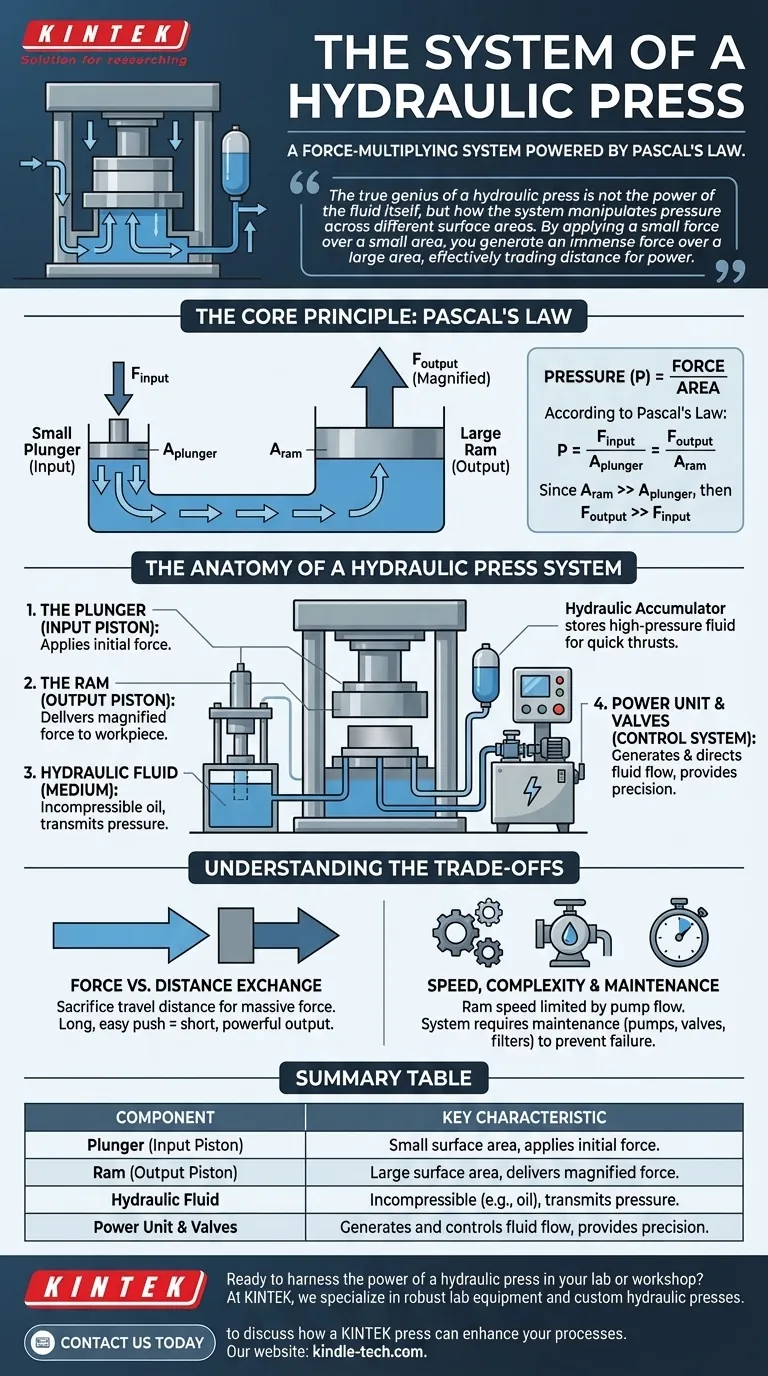
The true genius of a hydraulic press is not the power of the fluid itself, but how the system manipulates pressure across different surface areas. By applying a small force over a small area, you generate an immense force over a large area, effectively trading distance for power.

The Core Principle: Understanding Pascal's Law
The operation of a hydraulic press seems almost magical, but it is governed by a simple, elegant law of physics discovered by Blaise Pascal in the 17th century.
What is Pascal's Law?
Pascal's Law states that a change in pressure at any point in an enclosed, incompressible fluid is transmitted equally to all points throughout the fluid.
Imagine squeezing a sealed water bottle. The pressure you apply with your hand isn't just felt where your fingers are; it increases everywhere inside the bottle. A hydraulic press uses this principle with two pistons of different sizes.
How Pressure Creates Force Multiplication
The formula for pressure is Pressure = Force / Area. According to Pascal's Law, the pressure (P) exerted on the small piston (the Plunger) is the same as the pressure exerted on the large piston (the Ram).
Therefore, P = Force_input / Area_plunger = Force_output / Area_ram.
Because the Ram's area is much larger than the Plunger's, the output force must also be proportionally larger to keep the pressure equal. This is the source of the system's immense power.
The Anatomy of a Hydraulic Press System
A functional hydraulic press is more than just two pistons and some fluid. It is a complete system where each component plays a critical role.
The Plunger (Input Piston)
This is the smaller piston where the initial force is applied. An operator or a small motor can apply a modest force to the plunger, which is all that is needed to begin the process.
The Ram (Output Piston)
The Ram is the large-diameter piston that delivers the final, magnified compressive force. The workpiece—the object to be crushed, pressed, or formed—is placed under the Ram.
The Hydraulic Fluid (The Medium)
Oil is the most common hydraulic fluid because it is practically incompressible and also lubricates the system's components. Its job is to transmit the pressure from the Plunger to the Ram without loss.
The Power Unit and Valves (The Control System)
In industrial presses, a hydraulic power unit (containing a pump) generates the high-pressure flow of oil.
A hydraulic accumulator acts like a rechargeable battery, storing high-pressure fluid. This allows the press to deliver a powerful thrust quickly when needed, without requiring an enormous pump.
Directional control valves are the brains of the operation, directing the flow of oil to extend or retract the Ram, giving the operator precise control over the press.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The force multiplication of a hydraulic press is not free. It comes with inherent trade-offs that are critical to understand for any practical application.
The Force vs. Distance Exchange
This is the most fundamental trade-off. To achieve massive force multiplication, you must sacrifice travel distance.
The small Plunger must move a significant distance to displace enough fluid to move the large Ram just a short distance. You are exchanging a long, easy push for a short, powerful one.
Speed and System Limitations
The speed at which the Ram moves is determined by the flow rate of the hydraulic pump (measured in gallons or liters per minute). A higher force press with a very large Ram will move more slowly unless it is paired with a very high-flow pump, which increases cost and complexity.
System Complexity and Maintenance
While the principle is simple, a real-world hydraulic system is complex. It includes pumps, motors, accumulators, coolers, filters, and intricate valve systems. These components require regular maintenance to prevent leaks, contamination, and failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the components and their trade-offs allows you to evaluate a hydraulic system based on your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is maximizing force: The ratio of the Ram's area to the Plunger's area is the most critical design factor; a larger ratio yields greater force multiplication.
- If your primary focus is operational speed: The power unit's flow rate and the accumulator's capacity are the key specifications to scrutinize.
- If your primary focus is precision and control: The sophistication of the directional control valves and the overall system design, potentially using multiple smaller rams, become the most important features.
By understanding this interplay of pressure and area, you can effectively leverage hydraulic systems to achieve immense power with precision and control.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Plunger (Input Piston) | Applies the initial force. | Small surface area. |
| Ram (Output Piston) | Delivers the magnified force. | Large surface area. |
| Hydraulic Fluid | Transmits pressure throughout the system. | Incompressible (e.g., oil). |
| Power Unit & Valves | Generates and controls fluid flow. | Provides precision and control. |
Ready to harness the power of a hydraulic press in your lab or workshop?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust and reliable lab equipment, including hydraulic presses tailored to your specific needs. Whether you require maximum force, precise control, or high-speed operation, our systems are engineered for performance and durability.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK hydraulic press can enhance your material testing, sample preparation, or production processes. Let our experts help you find the perfect solution to multiply your capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples



















