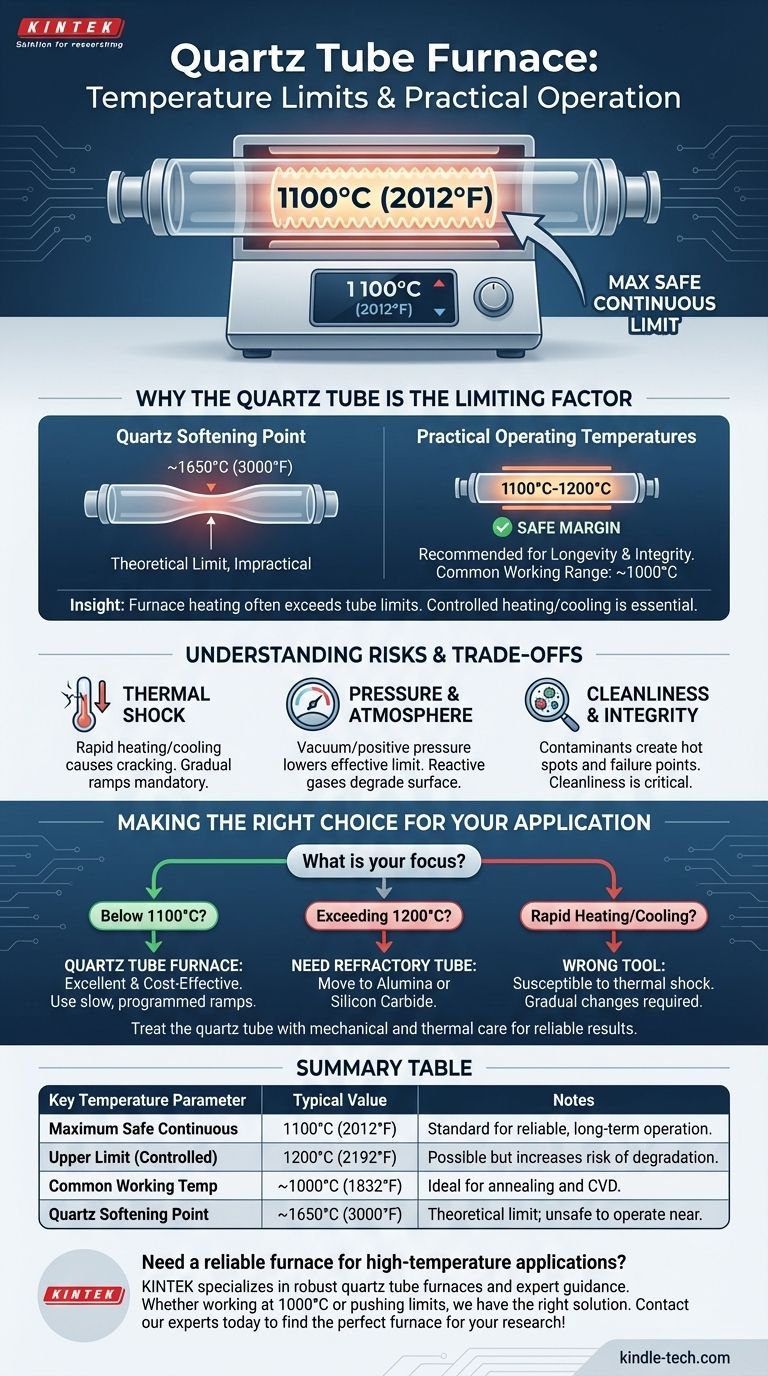
The maximum operating temperature of a quartz tube furnace is fundamentally limited by the physical properties of the quartz tube itself, not just the furnace's heating elements. While furnace models vary, a safe and common upper limit for continuous operation is typically around 1100°C (2012°F), with some applications pushing towards 1200°C under carefully controlled conditions.
The critical insight is that the furnace's heating capability often exceeds what the quartz tube can safely handle. The true operational ceiling is defined by the softening point of quartz and the risk of thermal shock, making controlled heating and cooling protocols essential for success.

Why the Quartz Tube is the Limiting Factor
A tube furnace is a system, and the quartz tube is often its most delicate component. Understanding its material properties is key to using the equipment effectively and safely.
The Softening Point of Quartz
Unlike metals that have a sharp melting point, quartz glass has a softening point, a temperature at which it begins to lose its structural rigidity. For high-purity fused quartz, this is around 1650°C (3000°F).
However, operating anywhere near this temperature is impractical. Long before it melts, the tube will deform under its own weight or any internal pressure, compromising your experiment.
Practical Operating Temperatures
To ensure longevity and experimental integrity, furnaces are operated well below the softening point. A maximum continuous temperature of 1100°C to 1200°C provides a safe margin.
The 1000°C figure mentioned for some furnaces is a very common and reliable working temperature suitable for a wide range of applications, from annealing to chemical vapor deposition.
The Role of the Furnace Body
The heating elements within the furnace body are often capable of reaching much higher temperatures. The furnace's controller is programmed to limit the temperature to protect the quartz tube and ensure stable, repeatable conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Pushing the limits of a quartz tube furnace without understanding the risks can lead to equipment failure and ruined experiments.
Thermal Shock and Cracking
Quartz has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion, which is why it's used. However, it is not immune to thermal shock.
Heating or cooling the tube too rapidly creates internal stress, which can easily cause it to crack or shatter. This is the most common mode of failure.
Pressure and Atmosphere
Operating the tube under a deep vacuum or positive pressure can lower its effective maximum temperature. The pressure difference creates stress on the tube wall, which is amplified as the quartz softens.
Certain reactive gases at high temperatures can also slowly degrade the surface of the quartz, reducing its strength over time.
Cleanliness and Tube Integrity
As noted in research applications, the cleanliness of the tube is critical. Contaminants can create hot spots or react with the quartz at high temperatures, becoming points of failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To operate a quartz tube furnace successfully, your procedure must respect the material's limitations.
- If your primary focus is working below 1100°C: A quartz tube furnace is an excellent and cost-effective choice, provided you use a slow, programmed temperature ramp rate.
- If your primary focus is exceeding 1200°C: You must move to a furnace system that uses a more refractory tube material, such as alumina or silicon carbide.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating or cooling: A quartz tube furnace is the wrong tool for the job; its susceptibility to thermal shock makes gradual temperature changes mandatory.
Ultimately, treating the quartz tube with mechanical and thermal care is the key to achieving reliable, high-temperature results.
Summary Table:
| Key Temperature Parameter | Typical Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Safe Continuous Temperature | 1100°C (2012°F) | Standard for reliable, long-term operation. |
| Upper Limit (Controlled Conditions) | 1200°C (2192°F) | Possible but increases risk of tube degradation. |
| Common Working Temperature | ~1000°C (1832°F) | Ideal for many processes like annealing and CVD. |
| Quartz Softening Point | ~1650°C (3000°F) | Theoretical limit; operation near this point is unsafe. |
Need a reliable furnace for your high-temperature applications?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust quartz tube furnaces and expert guidance to ensure your experiments run safely and efficiently. Whether you're working at 1000°C or pushing the limits, we have the right solution for your laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and find the perfect furnace for your research!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing



















