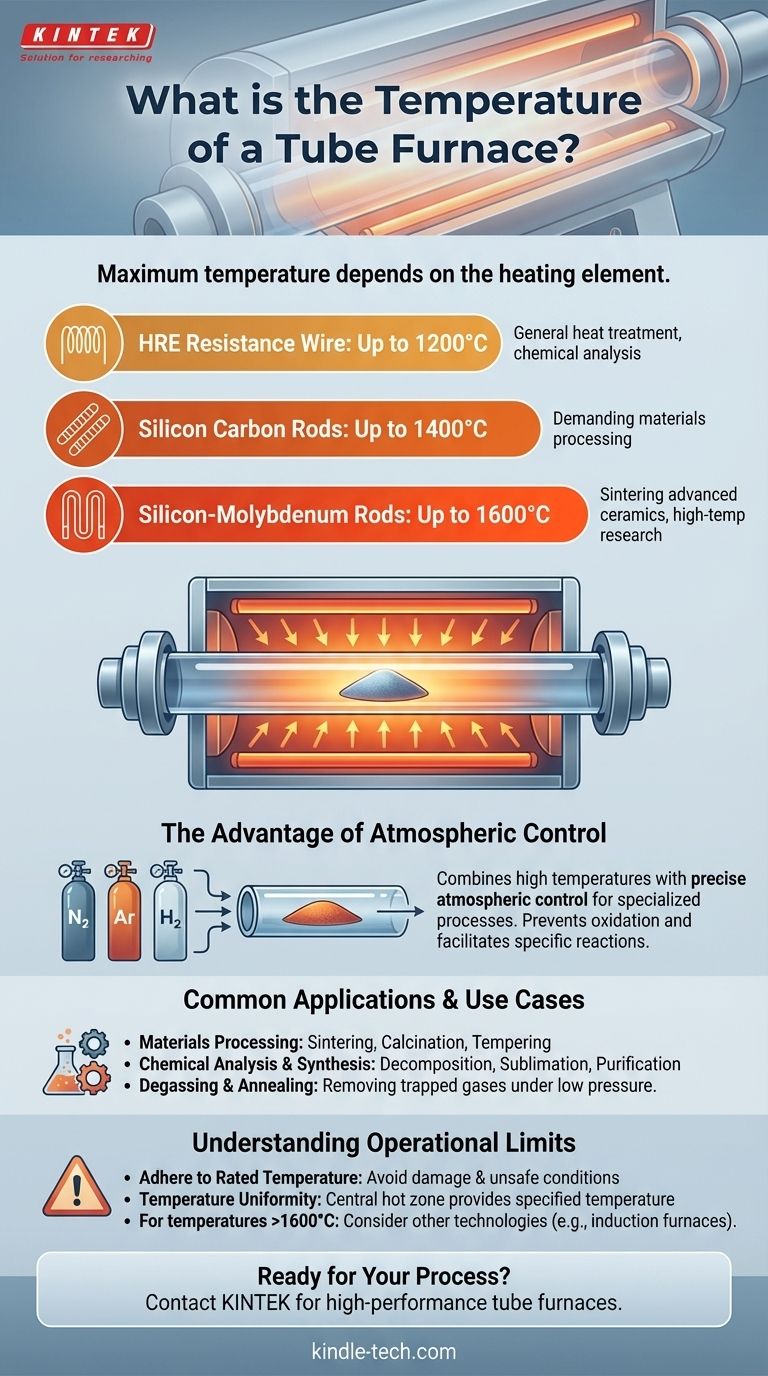
The temperature of a tube furnace is not a single value but is determined by the type of heating element it employs. A standard furnace can typically reach 1200°C using HRE resistance wire, while more advanced models can achieve 1400°C with silicon carbon rods or up to 1600°C with silicon-molybdenum rods.
The key takeaway is that a tube furnace's maximum temperature is dictated by its heating element technology, but its primary advantage lies in its ability to combine these high temperatures with precise atmospheric control for specialized processes.
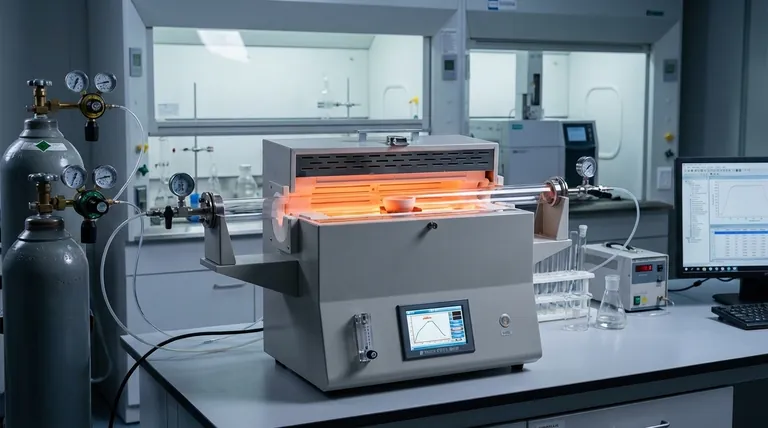

How a Tube Furnace Achieves High Temperatures
A tube furnace is a specialized piece of equipment designed for uniform heating of small samples within a tightly controlled environment. Its performance is a direct result of its core components.
The Central Heating Chamber
The design is fundamentally simple: a ceramic or quartz tube is passed through an insulated chamber. This chamber contains the heating elements that radiate heat inward, creating a central "hot zone" where the sample is placed.
The Critical Role of the Heating Element
The material used for the heating element is the primary factor limiting the furnace's maximum temperature. Different materials have different thermal and electrical properties, defining the furnace's operational range.
- Up to 1200°C: Furnaces using HRE (High-Resistance Element) wire are common for general-purpose heat treatment and chemical analysis.
- Up to 1400°C: To achieve higher temperatures, silicon carbon rods are used, enabling more demanding materials processing.
- Up to 1600°C: For the most advanced applications, silicon-molybdenum rods provide the highest temperature capabilities, suitable for sintering advanced ceramics and other high-temperature research.
The Advantage of Atmospheric Control
What truly sets a tube furnace apart is its ability to control the environment inside the tube. By flowing specific gases (such as nitrogen, argon, or hydrogen) through the tube, operators can prevent oxidation or facilitate specific chemical reactions that are impossible in open air.
Common Applications and Use Cases
The combination of high heat and atmospheric control makes tube furnaces indispensable for a variety of scientific and industrial tasks.
Materials Processing
Tube furnaces are workhorses for sintering, calcination, and tempering materials. These processes involve heating materials to change their physical properties, often in an inert atmosphere to maintain purity.
Chemical Analysis and Synthesis
They are frequently used for physical decomposition, sublimation, and purification of chemical compounds. The controlled environment is critical for achieving high-purity yields and analyzing reaction products without contamination.
Degassing and Annealing
The ability to create a vacuum or inert atmosphere inside the tube makes it ideal for degassing materials, a process that removes trapped or dissolved gases from a substance by heating it under low pressure.
Understanding the Operational Limits
While powerful, a tube furnace is a precision instrument that must be operated correctly to ensure safety and longevity.
Adhering to the Rated Temperature
The most critical rule is to never operate the furnace above its maximum rated temperature. Overheating can permanently damage the heating elements, the thermocouple, and the furnace insulation, leading to costly repairs and unsafe conditions.
Temperature Uniformity
The specified temperature typically applies to the very center of the heating chamber. The temperature may be slightly lower toward the ends of the tube. For processes that require high uniformity, it is essential to place the sample directly in this central hot zone.
Comparison to Other Furnaces
While 1600°C is a significant temperature, certain specialized applications in materials science and metallurgy require even higher heat. For temperatures approaching 1800°C and beyond, other technologies like induction furnaces are often necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct tube furnace requires matching its capabilities to your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment below 1200°C: A furnace with standard HRE resistance wire is a cost-effective and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is materials science requiring up to 1600°C: You must select a furnace equipped with advanced silicon-molybdenum heating elements.
- If your primary focus is precise atmospheric control for sensitive reactions: The tube furnace's core design is ideal, and your choice should be guided by the temperature your specific process requires.
Understanding these factors ensures you select not just a furnace, but the correct tool for your scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element | Maximum Temperature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| HRE Resistance Wire | Up to 1200°C | General-purpose heat treatment, chemical analysis |
| Silicon Carbon Rods | Up to 1400°C | Demanding materials processing |
| Silicon-Molybdenum Rods | Up to 1600°C | Sintering advanced ceramics, high-temperature research |
Ready to find the perfect tube furnace for your lab's specific temperature and atmospheric control needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including tube furnaces with precise temperature control and gas flow systems. Whether you require standard 1200°C heating or advanced 1600°C capabilities for materials science, our experts can help you select the ideal solution for sintering, annealing, or chemical synthesis.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What is the basic construction and temperature control mechanism of a laboratory tube furnace? Master Precision Heating for Your Lab
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing



















