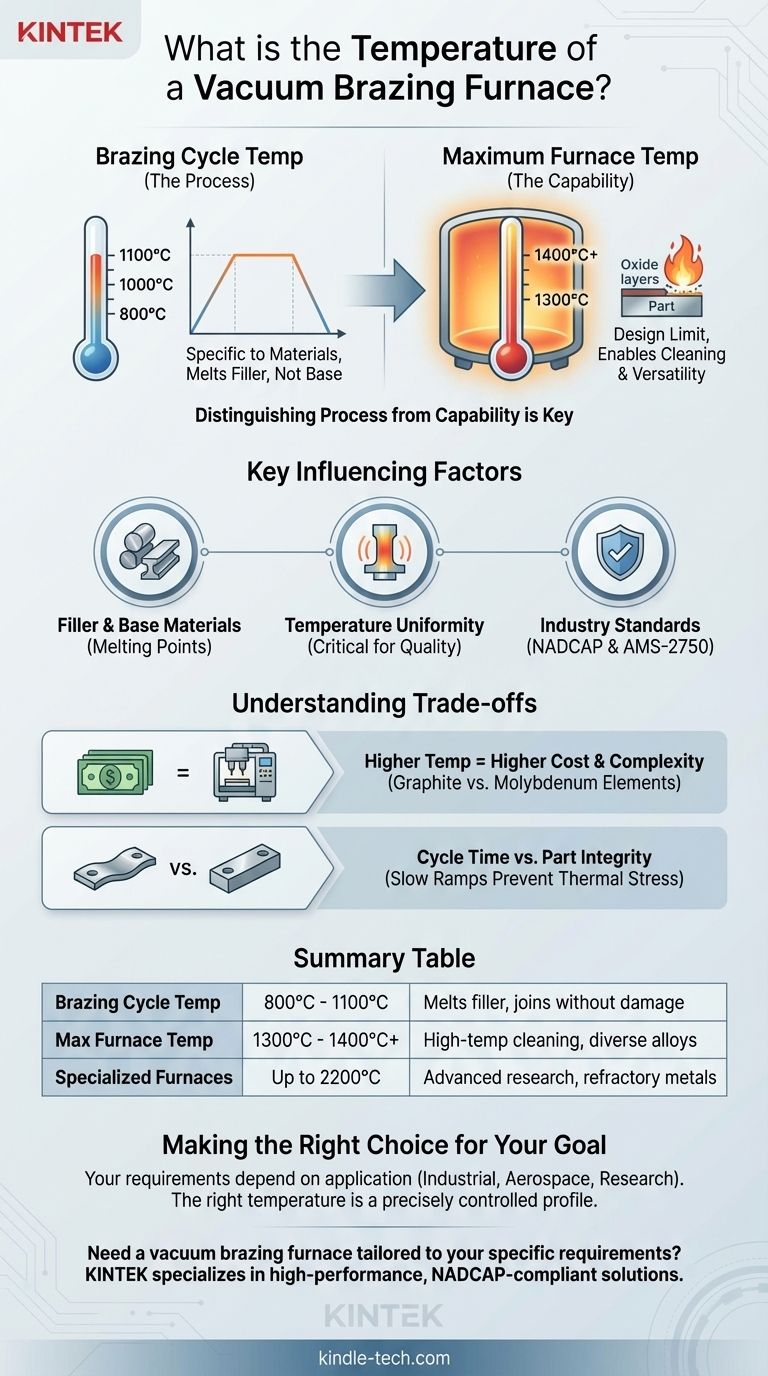
The temperature of a vacuum brazing furnace is not one single value but is defined by two key metrics: the specific brazing cycle temperature and the furnace's maximum operating temperature. A typical brazing cycle might run between 800°C and 1100°C, while the furnace itself must have a maximum capability that often exceeds 1300°C to 1400°C to handle a variety of alloys and perform essential high-temperature cleaning cycles.
Understanding the temperature of a vacuum brazing furnace requires separating the temperature needed for the specific process from the overall capability of the machine. The process temperature is dictated by the materials being joined, while the furnace's maximum temperature defines its versatility and ability to ensure part cleanliness.

Distinguishing Process Temperature from Furnace Capability
The most common point of confusion is failing to differentiate between the temperature at which a part is brazed and the maximum temperature the furnace can achieve. These serve different purposes.
Brazing Cycle Temperature (The Process)
The actual temperature used during a brazing operation is determined by the filler metal alloy and the base materials being joined.
A typical cycle isn't a single setpoint. It involves a carefully controlled program of heating, holding (soaking), and cooling. For example, a program might involve heating to 800°C to stabilize the parts, then slowly ramping to a final brazing temperature of 1100°C and holding it there.
This final temperature is chosen to be above the liquidus (full melting point) of the brazing filler metal but safely below the melting point of the parent materials.
Maximum Furnace Temperature (The Capability)
This is a design specification for the furnace itself, indicating the highest temperature the hot zone can safely reach.
A typical industrial vacuum brazing furnace will have a maximum operating temperature around 1300°C to 1400°C (up to 2650°F). This headroom is critical.
The Role of High Temperatures in Cleaning
One of the key advantages of vacuum brazing is that it can be performed without flux. The furnace operates at temperatures high enough to cause metal oxides on the part's surface to dissociate, or "burn off," in the vacuum.
Having a maximum temperature well above the brazing point allows the furnace to run high-temperature "clean-up cycles" to ensure the parts and the furnace interior are exceptionally clean before the brazing filler metal is introduced or melted.
Key Factors Influencing Temperature Selection
The precise temperature profile for any given job is a function of the materials, the part's geometry, and the quality standards required.
The Filler Metal and Base Materials
This is the most critical factor. The goal is to melt the filler metal so it can flow into the joint via capillary action without melting or damaging the parts being joined. Different alloys have vastly different melting points.
The Importance of Temperature Uniformity
High-end furnaces are valued for their temperature uniformity across the entire hot zone. This ensures that a large, complex part or a full batch of smaller parts heats evenly.
Poor uniformity can cause one area of a joint to braze improperly while another area overheats, leading to component failure.
Industry Standards (NADCAP & AMS-2750)
For critical industries like aerospace and defense, standards such as NADCAP and AMS-2750 dictate extremely strict requirements for temperature control, measurement, and documentation.
Furnaces used for these applications must demonstrate and prove their temperature accuracy and uniformity to ensure process repeatability and part traceability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or operating a furnace involves balancing capability against cost and risk.
Higher Temperature vs. Cost and Complexity
A furnace's maximum temperature directly impacts its cost and complexity. A furnace capable of reaching 1400°C is significantly different from a specialized graphite furnace that can reach 2200°C.
Higher temperatures require more advanced heating elements (graphite vs. molybdenum), superior insulation, and more robust power and cooling systems, all of which dramatically increase price.
Cycle Time vs. Part Integrity
While a furnace may be able to heat up quickly, ramping the temperature too fast can introduce thermal stress, causing delicate parts to warp or crack.
Slow, controlled heating and cooling cycles, as seen in the example of warming from 800°C to 1100°C over an hour, are deliberate choices to protect the integrity of the final assembly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your temperature requirements depend entirely on your application.
- If your primary focus is standard industrial brazing: A furnace with a maximum operating temperature of 1300°C will provide more than enough capability for common copper, silver, and nickel-based filler alloys.
- If your primary focus is aerospace or high-purity components: Prioritize a furnace that meets NADCAP standards, has proven temperature uniformity, and offers a maximum temperature around 1400°C for process flexibility and cleaning cycles.
- If your primary focus is advanced research or joining refractory metals: You will need a specialized high-temperature furnace, likely with graphite elements, capable of reaching 2000°C or higher.
Ultimately, the right temperature is not a single number, but a precisely controlled profile engineered to match your materials and quality requirements.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Type | Typical Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Brazing Cycle Temperature | 800°C - 1100°C | Melts filler metal for joining without damaging base materials |
| Maximum Furnace Temperature | 1300°C - 1400°C+ | Enables high-temperature cleaning cycles and handles diverse alloys |
| High-Temperature Specialized Furnaces | Up to 2200°C | For advanced research and refractory metals |
Need a vacuum brazing furnace tailored to your specific temperature and quality requirements? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum brazing furnaces designed for precise temperature control, uniformity, and compliance with industry standards like NADCAP. Whether you're in aerospace, industrial manufacturing, or advanced research, our solutions ensure optimal brazing results and process reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can meet your laboratory's exact needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining
- What is oxidation in brazing? How to prevent it for strong, durable joints
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- What is the major advantage that brazing has over welding? Joining Dissimilar Metals with Ease
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints



















